- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
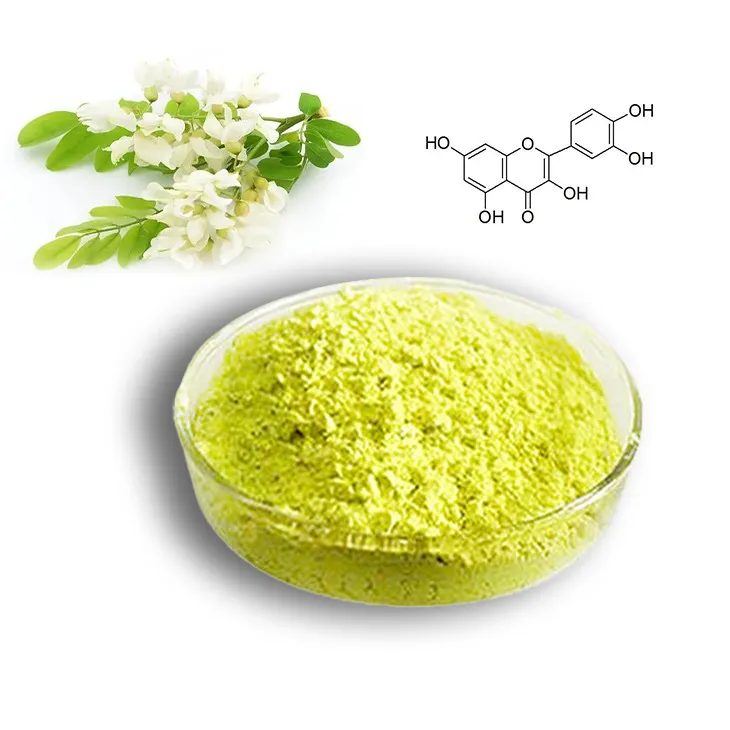
The application of quercetin in skin care.
2024-11-12

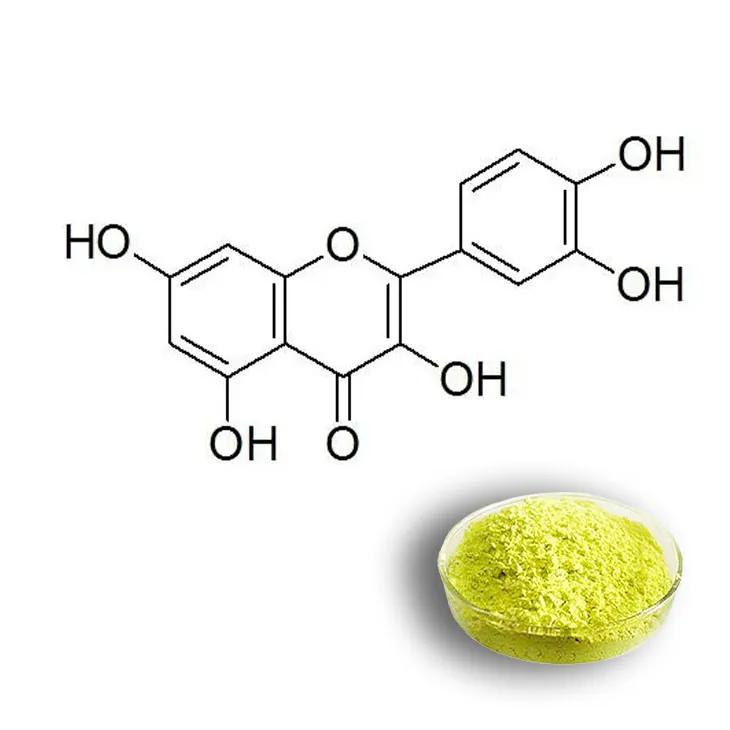
1. Introduction to Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid that is widely distributed in nature, found in various fruits, vegetables, and herbs. It has been the subject of extensive research due to its numerous health - promoting properties. In the context of skin care, Quercetin is emerging as a promising ingredient with a wide range of applications.

2. Antioxidant Properties of Quercetin in Skin Care
2.1 Free Radicals and Skin Damage
Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can cause significant damage to the skin. They are produced as a result of various factors such as exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pollution, and cigarette smoke. These free radicals can attack the skin cells, leading to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is associated with premature aging, wrinkles, and a decrease in skin elasticity. For example, UV radiation can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the skin, which can damage the DNA, proteins, and lipids in the skin cells.
2.2 How Quercetin Scavenges Free Radicals
Quercetin has a unique chemical structure that enables it to act as a potent antioxidant. It can donate electrons to free radicals, thereby neutralizing them and preventing them from causing further damage. This antioxidant activity is crucial for maintaining the health and integrity of the skin. In vitro studies have shown that quercetin can effectively scavenge different types of free radicals, such as superoxide anions, hydroxyl radicals, and peroxyl radicals. Moreover, quercetin can also enhance the antioxidant defense system in the skin by upregulating the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx).

3. Anti - Inflammatory Effects of Quercetin on the Skin
3.1 Inflammation and Skin Disorders
Inflammation is a complex biological response that can play a role in various skin conditions. For instance, in acne, inflammation is a key factor in the development of redness, swelling, and pustules. In eczema, chronic inflammation leads to itchy, dry, and inflamed skin. The inflammatory process involves the activation of immune cells, the release of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes, and the disruption of the skin barrier function.
3.2 Quercetin's Anti - Inflammatory Mechanisms
Quercetin exerts its anti - inflammatory effects through multiple mechanisms. It can inhibit the activation of nuclear factor - kappa B (NF - κB), a key transcription factor that regulates the expression of many inflammatory genes. By suppressing NF - κB activation, quercetin can reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin - 1β (IL - 1β), interleukin - 6 (IL - 6), and tumor necrosis factor - α (TNF - α). Additionally, quercetin can also inhibit the activity of enzymes involved in the production of inflammatory mediators, such as cyclooxygenase - 2 (COX - 2) and lipoxygenase (LOX). These enzymes are responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes, respectively.
4. Quercetin and Collagen Synthesis in Skin Care
4.1 The Importance of Collagen in the Skin
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the skin, providing structural support and elasticity. As we age, the production of collagen in the skin decreases, leading to the formation of wrinkles and sagging skin. Additionally, factors such as UV radiation, smoking, and poor diet can also accelerate collagen degradation. Maintaining a healthy level of collagen is essential for youthful - looking skin.
4.2 How Quercetin Promotes Collagen Synthesis
Quercetin can stimulate the synthesis of collagen in the skin. It does this by activating fibroblasts, the cells responsible for producing collagen. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that quercetin can increase the expression of genes involved in collagen synthesis, such as type I and type III collagen genes. Moreover, quercetin can also protect collagen from degradation by inhibiting the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes that break down collagen.

5. Applications of Quercetin in Different Skin Care Products
5.1 Anti - Aging Creams and Serums
Given its antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and collagen - promoting properties, quercetin is an ideal ingredient for anti - aging skin care products. Anti - aging creams and serums containing quercetin can help reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. They can also improve skin elasticity and firmness. For example, some high - end anti - aging products combine quercetin with other active ingredients such as retinol, vitamin C, and hyaluronic acid to provide comprehensive anti - aging benefits.
5.2 Treatments for Acne and Eczema
Quercetin's anti - inflammatory effects make it useful in the treatment of acne and eczema. In acne products, quercetin can help reduce inflammation, redness, and the size of pimples. In eczema creams, it can soothe itchy and inflamed skin. Some natural skin care brands are starting to incorporate quercetin into their acne and eczema treatment products.
5.3 Sun Protection Products
Although quercetin cannot replace traditional sunscreens, it can provide additional protection against UV - induced skin damage. Quercetin can be added to sun protection products such as sunscreens and after - sun lotions. It can help scavenge free radicals generated by UV radiation and reduce inflammation caused by sun exposure. This can enhance the overall effectiveness of sun protection and help prevent premature aging and skin cancer.
6. Safety and Efficacy Considerations
6.1 Safety Profile of Quercetin
Quercetin is generally considered safe for topical use in skin care products. However, some people may experience mild skin irritation or allergic reactions. It is important to conduct patch tests before using products containing quercetin, especially for those with sensitive skin. Additionally, quercetin should be used in appropriate concentrations to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
6.2 Efficacy in Different Skin Types
The efficacy of quercetin in skin care may vary depending on skin type. For example, in oily skin, quercetin's anti - inflammatory properties may be more beneficial in treating acne and reducing sebum production. In dry skin, its ability to promote collagen synthesis and improve skin elasticity may be more pronounced. However, more research is needed to fully understand how quercetin interacts with different skin types.
7. Conclusion
Quercetin has significant potential in skin care due to its antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and collagen - promoting properties. It can be applied in various skin care products to address different skin concerns such as aging, acne, eczema, and sun - induced damage. While more research is still required to optimize its use and fully understand its mechanisms of action, quercetin is already emerging as a valuable ingredient in the field of skin care.
FAQ:
What are the main benefits of quercetin in skin care?
Quercetin has several main benefits in skin care. Firstly, it has strong antioxidant capabilities that can eliminate harmful free radicals in the skin. Secondly, it has anti - inflammatory effects, which are helpful for treating skin conditions such as acne and eczema. Additionally, it promotes collagen synthesis, making it a great ingredient for anti - aging skin care products.
How does quercetin scavenge free radicals in the skin?
Quercetin scavenges free radicals in the skin through its chemical structure. It has certain functional groups that can react with free radicals, neutralizing their unpaired electrons and thus reducing their reactivity and potential damage to skin cells.
Can quercetin really improve acne?
Yes, quercetin can potentially improve acne. Its anti - inflammatory properties can help reduce the inflammation associated with acne. By reducing inflammation, it can also prevent the formation of new acne lesions and help in the healing process of existing ones.
Is quercetin suitable for all skin types in skin care?
Generally, quercetin is considered suitable for most skin types. However, as with any skincare ingredient, some individuals may be sensitive to it. It is always advisable to do a patch test before using a product containing quercetin, especially for those with sensitive skin.
How does quercetin contribute to anti - aging in skin care?
Quercetin contributes to anti - aging in skin care mainly by promoting collagen synthesis. Collagen is an important protein that gives the skin its firmness and elasticity. As we age, collagen production decreases. By promoting collagen synthesis, quercetin helps to keep the skin looking youthful, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Related literature
- Quercetin and Skin Health: A Review of Its Antioxidant and Anti - Inflammatory Properties"
- "The Role of Quercetin in Collagen - Mediated Skin Aging Prevention"
- "Quercetin - Based Skincare: New Insights and Therapeutic Applications"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Bilberry Extract
2024-11-12
-
Cat Claw Extract
2024-11-12
-
Selenium yeast
2024-11-12
-
Elderberry Extract
2024-11-12
-
Dan Shen Root Extract/Salvia Root Extract
2024-11-12
-
Cocoa Extract
2024-11-12
-
Lily extract
2024-11-12
-
Hops Extract
2024-11-12
-
Nettle Root Extract
2024-11-12
-
Europen Bilberry Extract
2024-11-12





















