- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
The extraction process of quercetin.
2024-11-26

1. Introduction
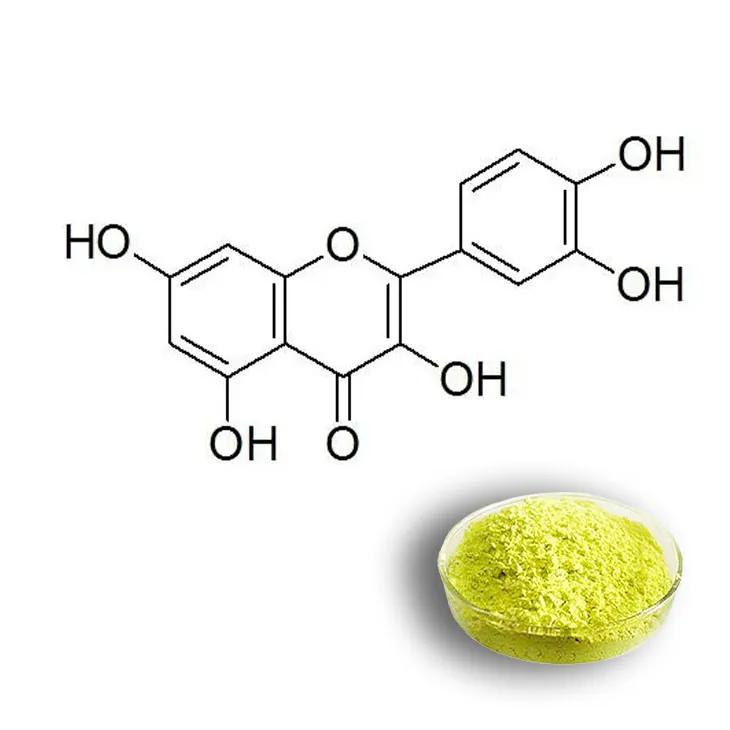
Quercetin is a flavonoid compound that has attracted extensive attention in the field of natural product research. It is widely distributed in plants and has various biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anticancer properties. Therefore, the extraction of Quercetin from plant sources is of great significance for further research on its pharmacological effects and applications in health - related products.
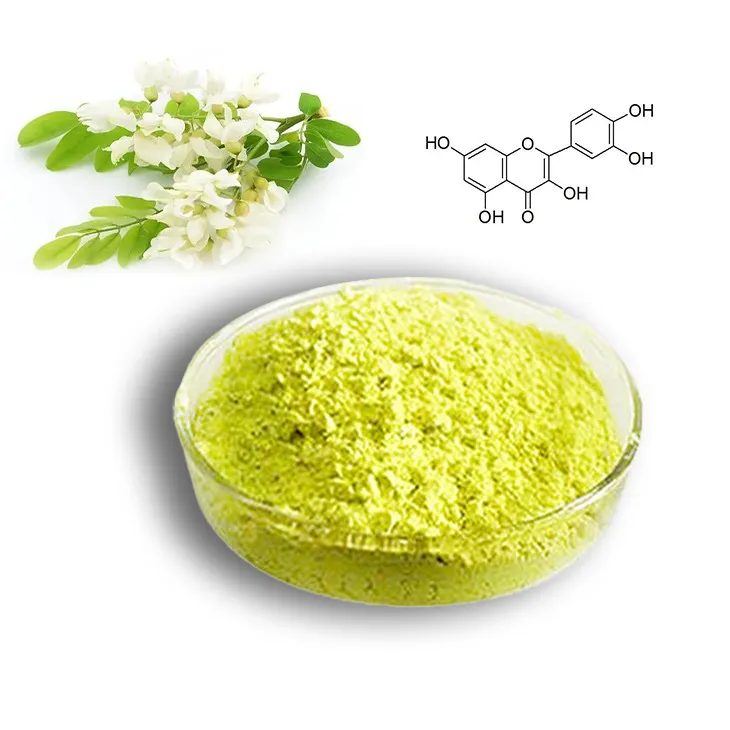

2. Selection of plant sources
2.1 Common plant sources
Quercetin can be found in many plants. Some of the common plant sources include onions, apples, and buckwheat.- Onions are rich in quercetin. The outer layers of onions usually contain a relatively high amount of this flavonoid. It is an easily accessible source for quercetin extraction in some cases.
- Apples also contain quercetin, especially in the peel. The consumption of apples has been associated with various health benefits, and part of these benefits may be attributed to the presence of quercetin.
- Buckwheat is another important plant source of quercetin. Buckwheat - based products, such as buckwheat flour and buckwheat tea, may potentially be used for quercetin extraction.
2.2 Considerations for selection
When choosing a plant source for quercetin extraction, several factors need to be considered.- The content of quercetin in the plant is a crucial factor. Higher - content plants are generally more favorable for extraction to obtain a sufficient amount of quercetin.
- The availability and cost of the plant material also play an important role. Some plants may be abundant and inexpensive, making them more suitable for large - scale extraction.
- Environmental factors and sustainability should not be ignored. Selecting plants that are grown in an environmentally friendly and sustainable manner is beneficial for long - term extraction operations.

3. Ultrasonic - assisted extraction
3.1 Principle
Ultrasonic - assisted extraction is a commonly used method in quercetin extraction. The principle behind this method is based on the cavitation effect of ultrasound. When ultrasound is applied to the extraction system, it generates high - intensity pressure waves that cause the formation and collapse of microscopic bubbles in the solvent. These bubbles can disrupt the cell walls of plant tissues, facilitating the release of quercetin into the solvent.3.2 Procedure
The general procedure for ultrasonic - assisted extraction of quercetin is as follows:- Prepare the plant material. The selected plant material needs to be dried, ground into a fine powder to increase the surface area for extraction.
- Select an appropriate solvent. Solvents such as ethanol, methanol, or a mixture of water and organic solvents can be used. Ethanol is often a popular choice due to its relatively low toxicity and good solubility for quercetin.
- Place the plant powder and solvent in an ultrasonic bath. The extraction time, ultrasonic power, and solvent - to - sample ratio need to be optimized. For example, an extraction time of 30 - 60 minutes, an ultrasonic power of 200 - 500 W, and a solvent - to - sample ratio of 10:1 - 20:1 may be suitable in some cases.
- After the extraction process, the mixture is filtered to separate the liquid extract from the solid residue.
3.3 Advantages
Ultrasonic - assisted extraction offers several advantages compared to traditional extraction methods.- It significantly improves the extraction efficiency. The cavitation effect can break down the cell walls more effectively, allowing for a faster and more complete extraction of quercetin.
- It reduces the extraction time. In traditional extraction methods, long extraction times may be required, but ultrasonic - assisted extraction can shorten the extraction process, which is beneficial for industrial - scale production.
- It can also reduce the amount of solvent used. Since the extraction is more efficient, less solvent is needed to achieve a similar extraction yield, which is both cost - effective and environmentally friendly.
4. Centrifugation
4.1 Purpose
After the extraction process, centrifugation is often used to clarify the extract. The purpose of centrifugation is to separate the suspended particles in the extract, such as cell debris and undissolved substances, from the liquid phase containing quercetin. This helps to obtain a cleaner and more homogeneous extract for further purification.4.2 Procedure
The following steps are typically involved in the centrifugation process:- Transfer the filtered extract obtained from the extraction step into centrifuge tubes. Make sure to balance the tubes properly to ensure the smooth operation of the centrifuge.
- Set the centrifuge parameters. The centrifugal speed and time need to be determined according to the characteristics of the extract. For example, a centrifugal speed of 3000 - 5000 rpm for 10 - 20 minutes may be appropriate.
- After centrifugation, carefully remove the supernatant, which is the clarified extract containing quercetin, and transfer it to a new container for further purification.

5. Purification processes
5.1 Column chromatography
Column chromatography is one of the most important purification methods for quercetin.- Column preparation. A suitable column, such as a silica gel column or a reversed - phase C18 column, needs to be selected. The column is then packed with the stationary phase material.
- Sample loading. The centrifuged extract is carefully loaded onto the top of the column. It is important to ensure that the sample is evenly distributed on the column to achieve good separation results.
- Elution. An appropriate eluent is used to elute the quercetin from the column. The choice of eluent depends on the type of column and the properties of quercetin. For a silica gel column, a mixture of solvents such as hexane - ethyl acetate may be used as the eluent, while for a reversed - phase C18 column, a gradient of water - methanol or water - acetonitrile may be employed.
- Collection of fractions. As the eluent passes through the column, different components are separated and eluted at different times. Fractions are collected at regular intervals, and the fractions containing quercetin are identified by methods such as thin - layer chromatography or high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
5.2 Other purification means
Besides column chromatography, there are other advanced separation means for quercetin purification.- High - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) can be used not only for the identification of quercetin in fractions but also for further purification. By optimizing the HPLC conditions, pure quercetin can be obtained directly from the extract.
- Counter - current chromatography is another alternative method. It is a liquid - liquid partition chromatography technique that can achieve high - resolution separation of quercetin from other components in the extract.
6. Conclusion
The extraction of quercetin involves multiple steps, from the selection of plant sources to the final purification of the compound. Each step plays a crucial role in obtaining high - quality quercetin. With the development of extraction and purification techniques, more efficient and environmentally friendly methods are expected to be developed in the future, which will further promote the research and application of quercetin in the fields of pharmacology and health - related products development.
FAQ:
What are the common plant sources for quercetin extraction?
Some common plant sources for quercetin extraction include onions, apples, berries (such as cranberries and blueberries), and certain types of tea (like green tea). These plants contain quercetin in varying amounts and can be used as starting materials for extraction.
How does ultrasonic - assisted extraction enhance the extraction efficiency of quercetin?
Ultrasonic - assisted extraction enhances the extraction efficiency of quercetin by creating cavitation bubbles in the extraction solvent. When these bubbles collapse, they generate intense local forces and high - temperature and - pressure micro - environments. This helps to break the cell walls of the plant material more effectively, allowing the quercetin to be released more easily into the solvent, thus increasing the extraction yield compared to traditional extraction methods.
What is the role of centrifugation in the quercetin extraction process?
Centrifugation plays a crucial role in the quercetin extraction process. It is used to separate the solid particles from the liquid extract. After the extraction step, there are usually plant debris and other insoluble materials in the extract. Centrifugation forces these solid components to the bottom of the centrifuge tube, leaving a clarified supernatant that contains the quercetin and other soluble compounds, which is then ready for further purification.
Can you briefly explain column chromatography for quercetin purification?
Column chromatography for quercetin purification involves passing the crude extract through a column filled with a stationary phase (such as silica gel or an ion - exchange resin). Different compounds in the extract, including quercetin, interact differently with the stationary phase. By using an appropriate mobile phase (a solvent or a solvent mixture), the components are eluted from the column at different rates. Quercetin can be selectively collected based on its unique interaction with the column materials, allowing for its separation from other impurities in the crude extract.
What are the potential pharmacological properties of quercetin?
Quercetin has several potential pharmacological properties. It has antioxidant activity, which helps to neutralize free radicals in the body and protect cells from oxidative damage. It also has anti - inflammatory properties, which may be beneficial in treating various inflammatory conditions. Additionally, quercetin has been studied for its potential anti - cancer effects, as it may interfere with cancer cell growth and proliferation. It may also have cardioprotective effects, such as reducing blood pressure and improving lipid profiles.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Versatile Flavonoid with Potential Health Benefits"
- "Extraction and Characterization of Quercetin from Natural Sources: A Review"
- "The Pharmacological Significance of Quercetin in Modern Medicine"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Citrus Aurantii Extract
2024-11-26
-
Echinacea Extract
2024-11-26
-
Sugarcane Extract
2024-11-26
-
Troxerutin
2024-11-26
-
Green Tea Extract
2024-11-26
-
Stevia Extract
2024-11-26
-
Ivy Extract
2024-11-26
-
Pomegranate Extract
2024-11-26
-
Genistein
2024-11-26
-
Tongkat Ali Extract
2024-11-26





















