- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Extract quercetin by the natural wood log method.
2024-12-01

1. Introduction to Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid compound that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its numerous health - promoting properties. It is widely distributed in the plant kingdom and can be found in various fruits, vegetables, and grains. Quercetin has antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anti - cancer properties, among others. In the field of medicine, it is being studied for its potential role in preventing and treating chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. In the food industry, it is also of interest as a natural preservative and antioxidant additive.

2. Natural Log Wood as a Source for Quercetin Extraction
2.1 Characteristics of Log Wood
The use of natural log wood for quercetin extraction is based on several important characteristics. Log wood often contains a variety of compounds that are related to quercetin biosynthesis. For example, some trees may produce precursor molecules that can be converted into quercetin during the extraction process. The porosity and surface area of the log wood play crucial roles in the extraction. A high porosity allows for better penetration of solvents, which is essential for efficient extraction. The larger the surface area, the more contact there is between the wood and the extraction solvent, facilitating the release of quercetin. Different types of log wood may vary in their suitability for quercetin extraction based on these characteristics. For instance, hardwoods may have different properties compared to softwoods, and some species may be more rich in quercetin - related compounds.
2.2 Comparison with Other Sources
Compared to other traditional sources of quercetin such as fruits and vegetables, log wood offers several advantages. Firstly, it is a more sustainable source as it does not compete with the food supply. Secondly, log wood can often be sourced locally, reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation. However, it also presents some challenges. For example, the extraction process from log wood may be more complex compared to simple extraction from plant tissues like fruits. The composition of log wood is more complex, containing lignin, cellulose, and other compounds that need to be carefully managed during extraction to ensure high - quality quercetin extraction.

3. The Extraction Procedure
3.1 Pre - treatment of the Wood
Before extraction, the log wood needs to be pre - treated. This may involve processes such as drying, chopping, or grinding. Drying the wood helps to reduce the moisture content, which can affect the extraction efficiency. Chopping or grinding the wood increases the surface area, making it more accessible to the extraction solvent. However, care must be taken during these pre - treatment steps to avoid damaging the compounds related to quercetin biosynthesis. For example, excessive heat during drying may cause the degradation of some precursor molecules. Grinding too finely may also lead to the loss of some volatile components that are important for the extraction process.
3.2 Extraction with Different Solvents
- Ethanol - based solvents are commonly used for quercetin extraction from log wood. Ethanol is a relatively safe and effective solvent. It can dissolve quercetin and its related compounds well. The concentration of ethanol in the solvent can vary depending on the specific requirements of the extraction. A higher concentration of ethanol may be more effective in extracting quercetin, but it may also extract other unwanted compounds. For example, a 70% ethanol solution is often a good compromise, as it can extract quercetin efficiently while minimizing the extraction of excessive lignin or other impurities.
- Other solvents such as methanol and water - ethanol mixtures have also been explored. Methanol can be a more aggressive solvent and may extract quercetin more quickly, but it is more toxic and requires more careful handling. Water - ethanol mixtures offer the advantage of being more environmentally friendly, but they may require more complex extraction procedures to achieve high yields of quercetin.
3.3 Purification Steps
After extraction, the resulting solution contains not only quercetin but also other compounds. Purification is necessary to obtain pure quercetin. One common method is chromatography. Column chromatography can be used to separate quercetin from other components based on their different affinities for the stationary and mobile phases. Another method is crystallization. By carefully controlling the temperature and concentration conditions, quercetin can be crystallized out of the solution, leaving behind the impurities. However, crystallization may require multiple steps and careful optimization of the conditions to ensure high - purity quercetin.
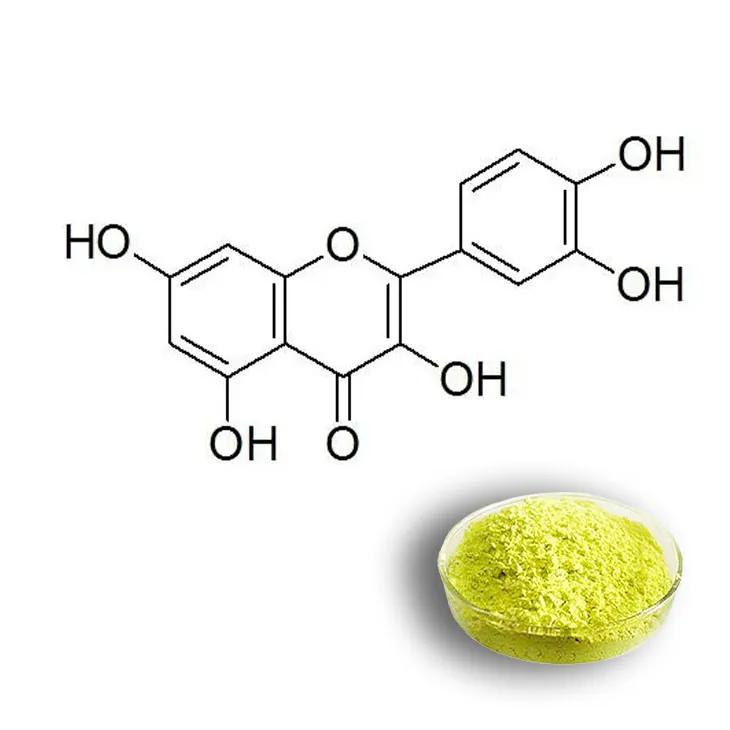
4. Quality Control of the Extracted Quercetin
4.1 Identification Methods
- Spectroscopic methods are widely used for the identification of quercetin. UV - Vis spectroscopy can be used to detect the characteristic absorption peaks of quercetin. Quercetin has a specific absorption pattern in the ultraviolet and visible regions, which can be used to confirm its presence. Infrared spectroscopy (IR) can also provide information about the functional groups present in quercetin, helping to further confirm its identity.
- Mass spectrometry (MS) is another powerful tool for identification. MS can determine the molecular weight of quercetin and its fragmentation pattern, which is unique to the compound. By comparing the mass spectra of the extracted sample with that of a known quercetin standard, the identity of the extracted quercetin can be verified.
4.2 Quantification Methods
- High - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a commonly used method for quantifying quercetin. HPLC can separate quercetin from other components in the sample and measure its concentration accurately. By using a standard curve of known quercetin concentrations, the amount of quercetin in the extracted sample can be determined.
- Enzyme - linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) can also be used for quercetin quantification in some cases. ELISA is based on the specific binding of antibodies to quercetin. Although it may be less accurate than HPLC in some situations, it can be a more cost - effective and rapid method, especially for screening large numbers of samples.

5. Future Prospects
The extraction of quercetin from natural log wood has promising future prospects. As the demand for natural and sustainable sources of bioactive compounds continues to grow, log wood may become an increasingly important source. Research efforts are likely to focus on optimizing the extraction process to increase the yield and purity of quercetin. This may involve the development of new solvents or extraction techniques. In addition, there is potential for the valorization of the by - products of the extraction process. For example, the lignin and cellulose remaining after quercetin extraction could be used for other applications such as biofuel production or the development of new composite materials. However, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. Regulatory requirements for the use of quercetin extracted from log wood in food and pharmaceutical applications need to be established. There is also a need for more comprehensive environmental impact assessments to ensure that the extraction process is truly sustainable.
FAQ:
What are the characteristics of log wood suitable for quercetin extraction?
The log wood suitable for quercetin extraction may have certain characteristics. For example, it contains specific compounds related to quercetin biosynthesis. These compounds can play an important role in the extraction process. Also, the structure of the log wood, such as its porosity and surface area, can affect the extraction. A proper porosity and large surface area can facilitate the contact between the wood and the extraction solvents, thus promoting the extraction of quercetin.
What solvents are commonly used in the quercetin extraction from natural log wood?
Ethanol - based solvents are commonly used in the quercetin extraction from natural log wood. Ethanol is a relatively safe and effective solvent. It can dissolve quercetin and other related compounds in the log wood well. Besides ethanol - based solvents, other solvents may also be explored depending on different research and practical requirements.
What are the purification steps in the quercetin extraction process?
The purification steps in the quercetin extraction process typically involve removing impurities from the initial extract. This may include filtration to remove large particles, and then using techniques such as chromatography. Chromatography can separate quercetin from other similar compounds based on their different chemical properties, such as polarity. Through these purification steps, a relatively pure quercetin product can be obtained.
How is the quality of the extracted quercetin controlled?
The quality control of the extracted quercetin mainly involves identification and quantification methods. Identification methods can use techniques like spectroscopy to determine whether the extracted compound is indeed quercetin. Quantification methods can measure the exact amount of quercetin in the extract. These methods ensure that the quercetin product meets certain quality standards, for example, in terms of purity and concentration.
What are the future prospects of this extraction method?
With the growing demand for natural and sustainable sources of bioactive compounds, the extraction of quercetin from natural log wood has promising future prospects. It provides a natural and potentially more sustainable alternative to traditional extraction methods. This method may be further optimized and scaled up in the future. It could also be integrated into the development of new products in fields such as pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, as quercetin has important applications in these areas.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Promising Bioactive Compound from Natural Sources"
- "Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Wood: New Approaches and Technologies"
- "The Role of Quercetin in Modern Medicine and its Sustainable Extraction"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Alisma Extract
2024-12-01
-
Tormentil Extract
2024-12-01
-
Kupilu Extract
2024-12-01
-
Nettle Root Extract
2024-12-01
-
Moringa powder
2024-12-01
-
Thunder God Vine Extract
2024-12-01
-
Saffron Extract Powder
2024-12-01
-
Okra Extract
2024-12-01
-
White Peony Extract
2024-12-01
-
Curcumin Extract
2024-12-01





















