- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Quercetin Manufacturers.
2024-11-30

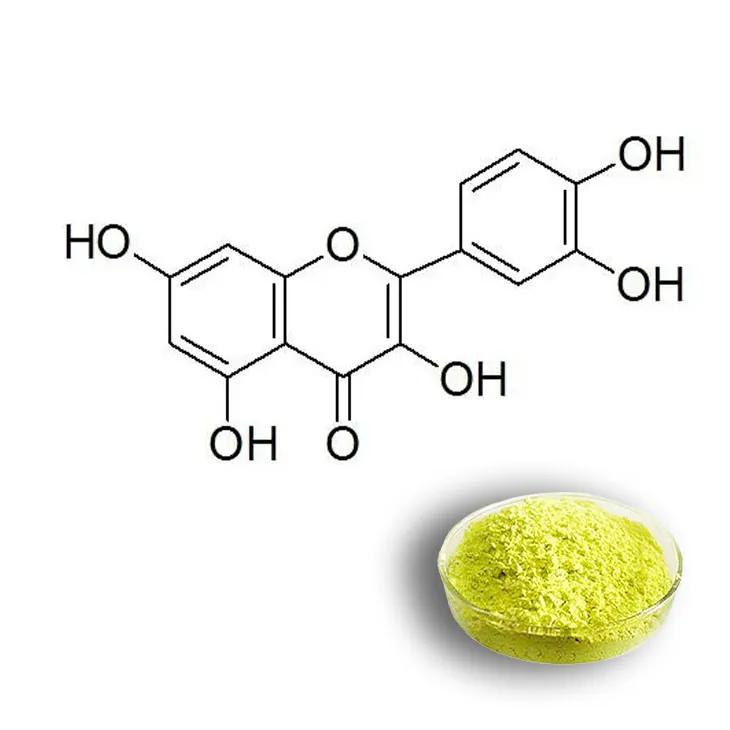
Introduction to Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid compound that has been receiving increasing attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits. It is naturally occurring in a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and grains. For example, apples, onions, and buckwheat are rich sources of Quercetin. This compound has been the subject of extensive scientific research for its medicinal properties, which include antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anti - cancer effects among others.

The Role of Quercetin Manufacturers
Quercetin manufacturers play a crucial role in bringing this beneficial compound to the market. Their activities span from the initial extraction from plant sources to the final marketing of quercetin - based products.
Extraction
The extraction of quercetin from plant matrices is a complex process. Manufacturers use state - of - - art equipment to ensure efficient extraction. Different plants may require different extraction methods. For instance, when extracting quercetin from onions, they might use solvent extraction methods. The choice of solvent is critical as it can affect the purity and yield of the extracted quercetin. Some of the commonly used solvents are ethanol and methanol. Manufacturers need to optimize the extraction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and extraction time to maximize the amount of quercetin obtained while minimizing the extraction of unwanted compounds.
Purification
Once the quercetin is extracted, the purification process begins. The goal of purification is to remove impurities and increase the concentration of quercetin. This is typically achieved through various chromatography techniques. Column chromatography, for example, can separate quercetin from other flavonoids and impurities based on their different affinities for the stationary and mobile phases. Another purification method is crystallization, which can further purify quercetin by forming pure crystals. Manufacturers must ensure that the purification process is carried out under strict quality control to produce high - quality quercetin products.
Formulation
After purification, quercetin manufacturers are involved in formulating the compound into different product forms. Quercetin can be formulated into tablets, capsules, powders, or even incorporated into functional foods and beverages. When formulating into tablets or capsules, manufacturers need to consider factors such as the stability of quercetin, the appropriate dosage, and the excipients to be used. For example, they may add fillers like cellulose to ensure proper tablet formation and disintegration. In the case of formulating quercetin into functional foods and beverages, they need to ensure that the taste, solubility, and stability of quercetin are maintained while also meeting the regulatory requirements for food and beverage products.

Marketing Strategies of Quercetin Manufacturers
Marketing is a vital aspect for quercetin manufacturers as they need to promote their products in a competitive market. They have to not only inform consumers about the benefits of quercetin but also differentiate their products from competitors.
Targeting Different Sectors
- Health - conscious consumer market: This is a large and growing market segment. Manufacturers target these consumers by highlighting the antioxidant and anti - inflammatory properties of quercetin. They promote quercetin - based products as a natural way to support overall health and well - being. For example, they may market quercetin supplements as a means to boost the immune system or reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Sports nutrition: Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are also a target group. Quercetin has been shown to have potential benefits for athletic performance, such as improving endurance and reducing muscle fatigue. Manufacturers in this sector may market quercetin - containing products as pre - workout or post - workout supplements. They may also collaborate with sports teams or fitness influencers to promote their products.
- Medical community: Quercetin's potential medicinal properties have attracted the attention of the medical community. Manufacturers may target healthcare professionals by providing scientific evidence on the effectiveness of quercetin in treating or preventing certain diseases. They may also develop quercetin - based products for specific medical conditions, such as quercetin - enriched formulations for patients with cardiovascular diseases.
Keeping up with Scientific Research
To stay competitive, quercetin manufacturers need to keep up with the latest scientific research on quercetin. New research findings can provide opportunities for product innovation and improvement. For example, if a new study discovers a previously unknown benefit of quercetin, manufacturers can use this information to develop new products or modify their existing product formulations. They can also use scientific research to support their marketing claims. However, they must ensure that their marketing claims are based on reliable scientific evidence and comply with regulatory requirements.
Quality Control in Quercetin Manufacturing
Quality control is essential throughout the quercetin manufacturing process. From the raw materials used in extraction to the final formulated products, manufacturers must adhere to strict quality standards.
Raw Material Selection
The quality of the raw materials used for quercetin extraction directly affects the quality of the final product. Manufacturers need to source high - quality plant materials that are rich in quercetin. They should also ensure that the raw materials are free from contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, and mycotoxins. For example, when sourcing onions for quercetin extraction, they should select onions that are grown organically or have been tested and found to be free of harmful substances.
Manufacturing Process Monitoring
During the extraction, purification, and formulation processes, manufacturers need to monitor various parameters to ensure product quality. In the extraction process, they should monitor the extraction efficiency, solvent consumption, and temperature stability. During purification, they need to check the purity of the quercetin at each stage of the chromatography or crystallization process. In the formulation stage, they must ensure that the dosage accuracy, tablet hardness (in the case of tablets), and powder flowability (for powders) are within the acceptable range. Any deviation from the set parameters should be immediately addressed to prevent the production of sub - standard products.
Final Product Testing
Before the quercetin - based products are released to the market, they must undergo comprehensive final product testing. This includes testing for purity, potency, and stability. For example, high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) can be used to accurately determine the purity and concentration of quercetin in the final product. Stability testing is also crucial to ensure that the product maintains its quality over its shelf life. Manufacturers should test the product under different storage conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure to determine its stability.

Regulatory Considerations for Quercetin Manufacturers
Quercetin manufacturers must operate within the framework of regulatory requirements. These regulations vary from country to country and also depend on the type of product being manufactured.
Food Supplements
If quercetin is being manufactured as a food supplement, manufacturers need to comply with the regulations governing food supplements. In many countries, this includes requirements for product labeling, such as clearly stating the ingredients, dosage instructions, and any potential side effects. They may also need to register their products with the relevant regulatory authorities. For example, in the United States, food supplement manufacturers must comply with the regulations of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which includes Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements for ensuring product quality and safety.
Pharmaceutical Products
If quercetin is being developed as a pharmaceutical product, the regulatory requirements are even more stringent. Pharmaceutical manufacturers need to conduct extensive pre - clinical and clinical trials to prove the safety and efficacy of quercetin for specific medical indications. They also need to follow strict GMP guidelines during the manufacturing process. In addition, the approval process for pharmaceutical products is much more complex and time - consuming compared to food supplements. For example, in the European Union, pharmaceutical companies need to submit a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for approval.
Future Trends in Quercetin Manufacturing
As the demand for natural health products continues to grow, quercetin manufacturers are likely to face new opportunities and challenges in the future.
New Extraction and Purification Technologies
Research is ongoing to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly extraction and purification technologies. For example, supercritical fluid extraction, which uses supercritical fluids such as carbon dioxide, is being explored as a potential alternative to traditional solvent extraction methods. This technology has the advantage of being more selective and producing less waste. Similarly, new purification techniques based on membrane separation or ionic liquids are being investigated to improve the purity and yield of quercetin.
Product Diversification
Manufacturers are expected to diversify their product portfolios. In addition to traditional tablets, capsules, and powders, they may develop more innovative products such as quercetin - loaded nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery or quercetin - fortified functional foods with enhanced bioavailability. They may also explore the combination of quercetin with other bioactive compounds to create synergistic effects. For example, combining quercetin with vitamin C or other antioxidants may enhance its antioxidant activity.
Global Market Expansion
The global market for quercetin - based products is likely to expand. Manufacturers may look to enter new international markets, especially in emerging economies where the awareness of natural health products is growing. However, they will need to adapt to the different regulatory requirements and cultural preferences in these markets. For example, in Asian markets, there may be a greater preference for quercetin - based functional foods in traditional forms such as herbal teas or tinctures.
FAQ:
What are the main steps in quercetin production by manufacturers?
The main steps in quercetin production include extraction, purification, and formulation. In the extraction phase, manufacturers use advanced equipment to extract quercetin from plant matrices. Then, purification processes are carried out to remove impurities and increase the concentration of quercetin. Finally, they formulate the purified quercetin into various products.
How do quercetin manufacturers market their products?
Quercetin manufacturers market their products by educating consumers about the benefits of quercetin. They also differentiate their products in a competitive market. They target different sectors such as the health - conscious consumer market, sports nutrition, and the medical community.
Why is purification important in quercetin manufacturing?
Purification is important in quercetin manufacturing because it helps to remove impurities from the extracted quercetin. This not only increases the concentration of quercetin but also ensures the quality and safety of the final product.
How do quercetin manufacturers stay competitive?
Quercetin manufacturers stay competitive by keeping up with the latest scientific research on quercetin. Based on this research, they can adapt their production and marketing strategies accordingly. For example, if new benefits of quercetin are discovered, they can highlight these in their marketing and adjust their production to meet potential new demands.
What sources do quercetin manufacturers use to extract quercetin?
Quercetin manufacturers extract quercetin from many natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, and grains where quercetin occurs naturally.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Versatile Flavonoid with Potential Health Benefits"
- "The Production and Applications of Quercetin in the Pharmaceutical Industry"
- "Quercetin: Extraction, Purification and Analysis"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Dandelion Leaf Extract
2024-11-30
-
Hops Extract
2024-11-30
-
Resveratrol extract
2024-11-30
-
Curcuma Longa Extract
2024-11-30
-
Honeysuckle Pollen
2024-11-30
-
Giant Knotweed Extract
2024-11-30
-
Citrus Aurantii Extract
2024-11-30
-
Tongkat Ali Extract
2024-11-30
-
Aguaje Extract
2024-11-30
-
Europen Bilberry Extract
2024-11-30





















