- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
The process of extracting pure resveratrol from resveratrol extract.
2024-12-02

1. Introduction
Resveratrol, a natural phenolic compound, has attracted significant attention due to its potential health benefits, including antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anti - cancer properties. Resveratrol is found in various plants, such as grapes, berries, and peanuts. However, the extraction of pure resveratrol from resveratrol - containing sources is a complex process. This article will detail the main steps involved in obtaining high - purity resveratrol from Resveratrol extracts.
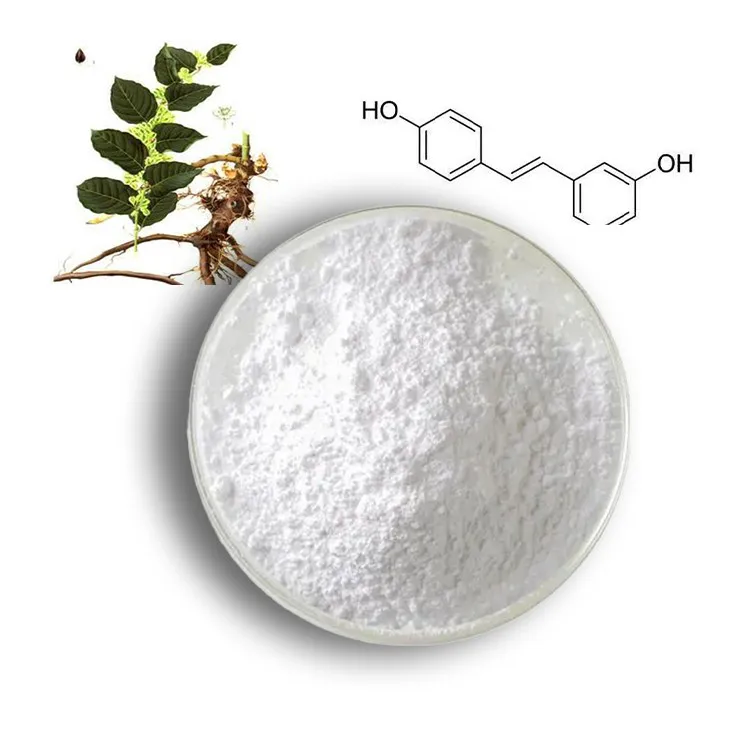
2. Source of Resveratrol extracts
Grape skins and seeds: Grape is one of the richest sources of resveratrol. During winemaking, resveratrol is present in the skins and seeds of grapes. The extraction of resveratrol from grape by - products can be an economical way to obtain Resveratrol extracts.
Berries: Berries like blueberries, raspberries, and cranberries also contain resveratrol. Their extracts can be used as a source for further purification of resveratrol.
Peanuts: Peanuts are another source of resveratrol. Although the concentration is relatively lower compared to grapes, it can still be a potential source for resveratrol extraction.
3. Solvent Extraction
3.1 Selection of Solvents
The choice of solvents is crucial in the extraction process.- Ethanol: Ethanol is a commonly used solvent for resveratrol extraction. It has several advantages. It is relatively safe, and has a good solubility for resveratrol. Moreover, it can be easily removed during the subsequent purification steps. Ethanol - based extraction can be carried out at different concentrations, typically ranging from 50% to 95% ethanol in water.
- Methanol: Methanol is also effective in extracting resveratrol. However, it is more toxic than ethanol. Special care must be taken when using methanol to ensure safety during the extraction process.
- Other solvents: Organic solvents like ethyl acetate can also be used for extraction. Each solvent has its own characteristics in terms of solubility and selectivity for resveratrol extraction.
3.2 Extraction Procedure
- First, the plant material (such as grape skins or seeds) containing resveratrol is dried and ground into a fine powder. This increases the surface area available for extraction.
- The powdered material is then mixed with the selected solvent in a suitable ratio. For example, a ratio of 1:10 (plant material: solvent) can be used.
- The mixture is stirred or shaken for a certain period, usually several hours to overnight, at a specific temperature. The temperature can range from room temperature to a slightly elevated temperature (e.g., 40 - 50°C) to enhance the extraction efficiency.
- After extraction, the mixture is filtered to separate the liquid extract (containing resveratrol) from the solid residue. Filtration can be carried out using filter paper, a Buchner funnel, or other filtration devices.

4. Purification by Column Chromatography
4.1 Column Preparation
- First, a suitable chromatography column is selected. Silica gel columns are often used for resveratrol purification. The column is filled with the stationary phase, which is usually silica gel. The size of the column and the amount of silica gel depend on the scale of the purification process.
- Before use, the silica gel is activated by heating at a high temperature (e.g., 100 - 120°C) for a certain period to remove moisture and other impurities.
4.2 Sample Loading
- The resveratrol - containing extract obtained from solvent extraction is concentrated if necessary. This can be done by evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure using a rotary evaporator.
- The concentrated extract is then dissolved in a small amount of a suitable solvent (e.g., a low - polarity solvent like hexane or chloroform) and carefully loaded onto the top of the prepared chromatography column.
4.3 Elution
- Different solvents or solvent mixtures are used for elution. A gradient elution method is often employed. For example, a less polar solvent can be used first to elute non - target compounds, and then a more polar solvent is used to elute resveratrol. Commonly used elution solvents include hexane/ethyl acetate mixtures with different ratios.
- The eluate is collected in fractions. Each fraction can be analyzed by techniques such as thin - layer chromatography (TLC) or high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to determine which fractions contain resveratrol.

5. Crystallization
5.1 Concentration of Resveratrol - Rich Fractions
The fractions containing resveratrol obtained from column chromatography are combined and concentrated. This is usually done by evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure. The resulting concentrated solution should have a relatively high concentration of resveratrol.5.2 Crystallization Conditions
- The concentrated resveratrol solution is then cooled slowly. Slow cooling is important as it allows the resveratrol molecules to form crystals gradually. The cooling rate can be adjusted according to the specific experimental conditions.
- Sometimes, a small amount of a seed crystal of resveratrol can be added to the solution to initiate the crystallization process. The seed crystal provides a nucleation site for the growth of resveratrol crystals.
- The solvent used for crystallization also plays a role. A solvent in which resveratrol has relatively low solubility at low temperatures is preferred. For example, ethyl acetate can be a suitable solvent for crystallization of resveratrol.
5.3 Isolation of Crystals
Once the crystals have formed, they can be isolated by filtration. The crystals are then washed with a small amount of a cold solvent to remove any impurities adsorbed on the crystal surface. After washing, the crystals are dried under vacuum or at a low - humidity environment to obtain pure resveratrol.6. Quality Control and Analysis
6.1 Spectroscopic Methods
- UV - Vis Spectroscopy: UV - Vis spectroscopy can be used to detect the presence of resveratrol based on its characteristic absorption peaks. Resveratrol has absorption maxima in the UV region, typically around 306 - 310 nm. This method can provide a quick indication of the presence and approximate concentration of resveratrol in a sample.
- IR Spectroscopy: Infrared spectroscopy can be used to identify the functional groups in resveratrol. The characteristic absorption bands corresponding to phenolic - OH groups, C = C double bonds, etc. can be observed in the IR spectrum of resveratrol.
6.2 Chromatographic Methods
- High - Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): HPLC is a powerful technique for the quantitative and qualitative analysis of resveratrol. It can separate resveratrol from other compounds in a sample with high resolution. By comparing the retention time of the sample peak with that of a standard resveratrol, the identity of resveratrol can be confirmed, and its concentration can be accurately measured.
- Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry (GC - MS): Although resveratrol is a relatively polar compound and requires derivatization before GC - MS analysis, this method can provide detailed information about the structure of resveratrol. The mass spectrum obtained can be used to identify the molecular weight and fragmentation pattern of resveratrol.
7. Conclusion
The extraction of pure resveratrol from resveratrol extracts is a multi - step process that involves solvent extraction, column chromatography purification, and crystallization. Each step requires careful control of parameters such as solvent selection, extraction conditions, chromatography elution, and crystallization conditions. Quality control and analysis methods are also essential to ensure the purity and quality of the final resveratrol product. With the increasing demand for resveratrol in the fields of pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics, the development of efficient and reliable extraction methods is of great significance.
FAQ:
What are the common solvents used in solvent extraction for resveratrol?
Common solvents used in solvent extraction for resveratrol include ethanol, methanol, and ethyl acetate. These solvents are chosen because they can effectively dissolve resveratrol from the extract based on its solubility properties. Ethanol, for example, is a relatively safe and efficient solvent often used in natural product extraction processes. Methanol also has good solubility for resveratrol but is more toxic and requires careful handling. Ethyl acetate is another option that can be used to selectively extract resveratrol.
How does column chromatography work in the purification of resveratrol?
Column chromatography works by passing the resveratrol - containing extract through a column filled with a stationary phase, such as silica gel or an ion - exchange resin. The different components in the extract have different affinities for the stationary phase. As the mobile phase (a solvent or solvent mixture) is passed through the column, the components move at different rates. Resveratrol, with its specific chemical properties, will interact differently with the stationary phase compared to other impurities. This allows it to be separated and purified as it elutes from the column at a different time or under different solvent conditions compared to the unwanted substances.
What factors affect the crystallization of resveratrol?
Several factors affect the crystallization of resveratrol. Temperature is an important factor. A suitable temperature range is often required to promote the formation of crystals. If the temperature is too high, the resveratrol may remain in solution, and if it is too low, it may lead to the formation of amorphous solids or the precipitation of other impurities along with resveratrol. The concentration of resveratrol in the solution also matters. A proper concentration ensures that there are enough molecules to form stable crystals. Additionally, the choice of solvent and the presence of impurities can influence crystallization. Impurities may either inhibit or promote crystal growth depending on their nature and interaction with resveratrol.
Why is it necessary to extract pure resveratrol from resveratrol extract?
It is necessary to extract pure resveratrol from resveratrol extract for several reasons. Firstly, pure resveratrol is required for accurate scientific research on its biological activities and potential health benefits. Impurities in the extract may interfere with the results of in - vitro and in - vivo studies. Secondly, in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries, pure resveratrol is needed to ensure the safety and efficacy of products. Impurities may cause unwanted side effects or reduce the effectiveness of resveratrol - based formulations. Moreover, pure resveratrol has a more defined chemical and physical profile, which is important for quality control and standardization in various applications.
What are the challenges in the process of extracting pure resveratrol?
There are several challenges in the process of extracting pure resveratrol. One challenge is the presence of structurally similar compounds in the resveratrol extract, which can be difficult to separate from resveratrol during purification steps like column chromatography. Another challenge is the potential degradation of resveratrol during the extraction and purification processes. Resveratrol is sensitive to factors such as heat, light, and oxygen, and improper handling can lead to its decomposition. Additionally, achieving high yields of pure resveratrol while maintaining cost - effectiveness is also a challenge. The extraction and purification methods often require expensive equipment and solvents, and finding a balance between purity, yield, and cost is crucial.
Related literature
- Improved Extraction and Purification of Resveratrol from Natural Sources"
- "Recent Advances in Resveratrol Extraction Technologies"
- "Purification of Resveratrol: A Comprehensive Review"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Artichoke Extract
2024-12-02
-
Hawthorn powder
2024-12-02
-
Moringa powder
2024-12-02
-
Reishi mushroom extract
2024-12-02
-
Curcumin
2024-12-02
-
Licorice Root Extract Powder
2024-12-02
-
Eyebright Extract
2024-12-02
-
Dandelion Leaf Extract
2024-12-02
-
Diosmin
2024-12-02
-
Nettle leaf extract
2024-12-02





















