- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
What is Quercetin? Definition, Types, History and Nutritional Value
2024-12-18

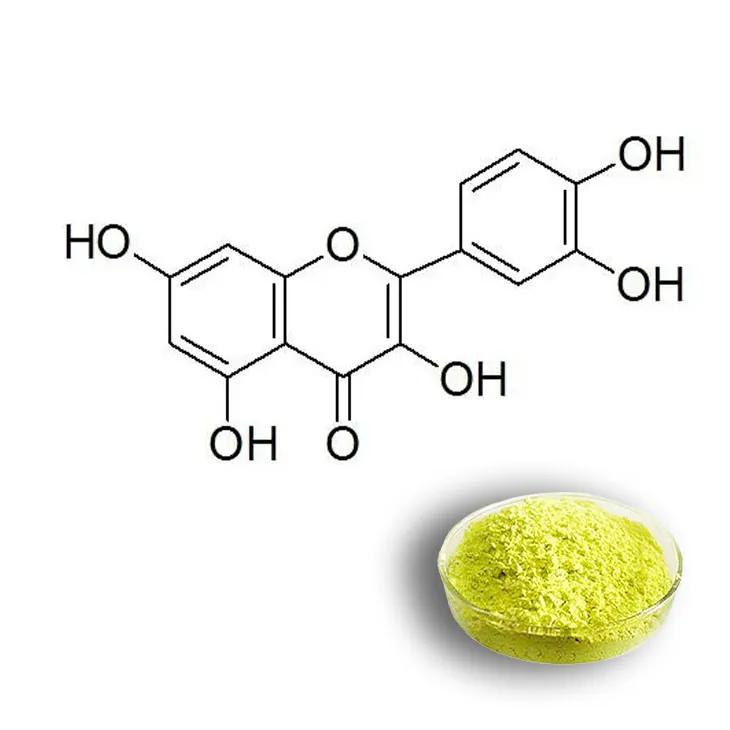
1. Definition of Quercetin
Quercetin is a natural flavonoid that is widely distributed in the plant kingdom. It belongs to the class of polyphenolic compounds. Structurally, it consists of a flavone backbone with multiple hydroxyl groups, which contribute to its various biological activities. Flavonoids are known for their diverse functions in plants, including roles in pigmentation, UV protection, and defense against pathogens. In the context of human health, Quercetin has emerged as a compound of significant interest due to its potential beneficial effects.
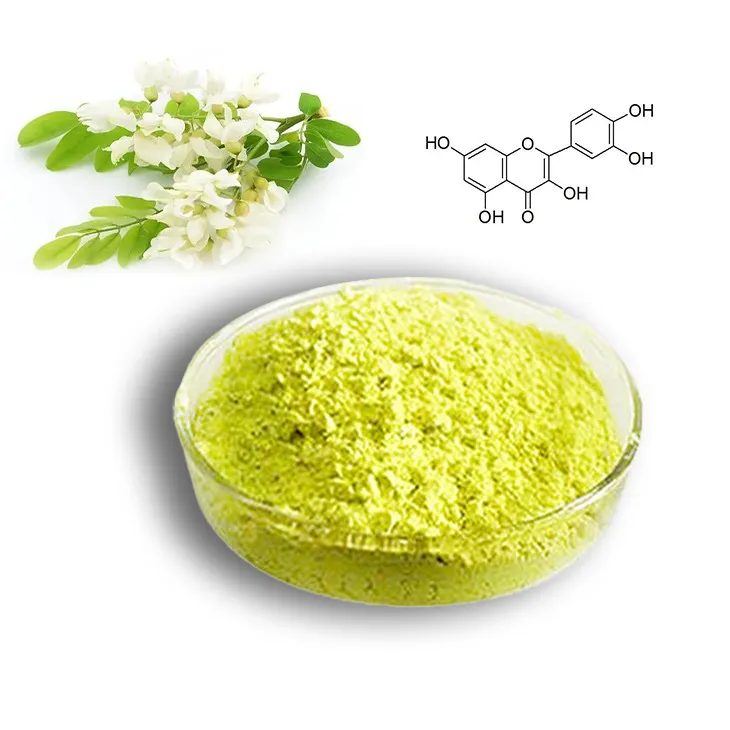

2. Types of Quercetin
2.1 Based on Sources
- Fruits: Quercetin can be found in apples, especially in the skin. Apples are a common source, and the quercetin content may vary depending on the variety. For example, some heirloom apple varieties may contain higher levels compared to mass - produced commercial varieties.
- Berries: Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries also contain quercetin. Blueberries, in particular, are rich in flavonoids, including quercetin. The presence of quercetin in these berries contributes to their antioxidant properties and potential health benefits.
- Onions: Onions are a significant source of quercetin, with the highest concentrations found in the outer layers. Different types of onions, such as red onions, yellow onions, and shallots, may have varying levels of quercetin. Red onions, for instance, are known to have relatively high levels of this flavonoid.
- Leafy Greens: Some leafy green vegetables like kale and spinach contain quercetin. These greens are already recognized for their high nutritional value, and the presence of quercetin adds to their health - promoting properties.
2.2 Based on Chemical Modifications
- Quercetin glycosides are a common form. In these compounds, quercetin is attached to a sugar molecule. This modification can affect its solubility, bioavailability, and biological activity. For example, quercetin - 3 - O - glucoside is one such glycoside form that has been studied for its antioxidant and anti - inflammatory properties.
- There are also ester - modified forms of quercetin. These modifications can occur in nature or be synthesized in the laboratory. They may alter the way quercetin interacts with biological molecules, potentially leading to different physiological effects.

3. History of Quercetin
Quercetin has a long history in traditional medicine systems around the world.
3.1 In Asian Traditional Medicine
In traditional Chinese medicine, herbs and plants containing quercetin have been used for centuries. These plants were often used to treat various ailments, including inflammation - related conditions. Although the concept of quercetin as a specific compound was not known at that time, the therapeutic effects of the plants were recognized and passed down through generations. For example, some herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine formulas for treating joint pain or respiratory infections may have contained quercetin - rich plants.
3.2 In European Traditional Medicine
In European traditional medicine, plants with quercetin were also utilized. For instance, certain herbal remedies for digestive problems or skin disorders may have included quercetin - containing plants. In the Middle Ages, local plants were often the primary source of medicine, and knowledge of their medicinal properties was passed down within communities. The presence of quercetin in these plants likely contributed to their effectiveness in treating certain conditions, although the scientific understanding of its role was not developed until much later.
4. Nutritional Value of Quercetin
4.1 Antioxidant Activity
Quercetin is a powerful antioxidant. It has the ability to scavenge free radicals in the body. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can cause oxidative damage to cells. This damage is associated with various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. Quercetin's antioxidant activity is due to its chemical structure, which allows it to donate electrons to neutralize free radicals. By doing so, it helps protect cells from oxidative stress, maintaining the integrity of cell membranes, DNA, and other cellular components.
4.2 Anti - Inflammatory Properties
Quercetin has been shown to possess anti - inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to serious health problems. Quercetin can modulate the inflammatory response by interfering with the signaling pathways involved in inflammation. It can inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines, which are small proteins that play a key role in promoting inflammation. For example, in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that quercetin can reduce inflammation in conditions such as arthritis and colitis.
4.3 Cardiovascular Health Benefits
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Quercetin may contribute to reducing blood pressure. It can act on the smooth muscle cells in blood vessels, causing them to relax. This relaxation leads to an increase in the diameter of blood vessels, thereby reducing blood pressure. Some studies have shown that supplementation with quercetin can result in a modest but significant decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in individuals with hypertension.
- Cholesterol Level Management: Quercetin can also affect cholesterol metabolism. It has been shown to inhibit the absorption of dietary cholesterol in the intestines and can also promote the excretion of cholesterol from the body. Additionally, it may have an impact on the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver. By influencing these processes, quercetin can help in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, which is crucial for cardiovascular health.
4.4 Other Potential Health Benefits
- Cancer Prevention: While more research is needed, some studies suggest that quercetin may have anti - cancer properties. It can interfere with the growth and proliferation of cancer cells by affecting various cellular processes, such as cell cycle regulation and apoptosis (programmed cell death). For example, in some pre - clinical studies, quercetin has been shown to inhibit the growth of cancer cells in vitro.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Quercetin may also have neuroprotective potential. It can cross the blood - brain barrier and exert antioxidant and anti - inflammatory effects in the brain. This may be beneficial in preventing or delaying the onset of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Some animal studies have indicated that quercetin can improve cognitive function and protect neurons from damage.

FAQ:
What are the main sources of quercetin?
Quercetin is widely found in many plants. Some common sources include onions, apples, berries (such as blueberries, cranberries), and green tea. These plants are rich in quercetin and are part of our daily diet.
How does quercetin act as an antioxidant?
Quercetin has a chemical structure that allows it to donate electrons to free radicals. By doing so, it neutralizes the free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative damage to cells. This antioxidant activity helps in maintaining the health of cells and protecting them from damage caused by factors like pollution, UV radiation, and normal metabolic processes.
Can quercetin be used to treat inflammatory diseases?
While quercetin has anti - inflammatory properties, it cannot be considered a sole treatment for inflammatory diseases. However, it may play a supportive role. Its anti - inflammatory effects are due to its ability to inhibit certain enzymes and signaling pathways involved in the inflammatory response. For example, it may help reduce inflammation in conditions like arthritis, but more research is needed to fully understand its potential in treating such diseases.
What are the different chemical types of quercetin?
The different types of quercetin can be classified based on their sources and chemical modifications. For instance, quercetin glycosides are a common form where quercetin is bound to a sugar molecule. The type and number of sugar molecules attached can vary, resulting in different quercetin glycosides. Another aspect is the isomeric forms of quercetin, which have the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms in space.
How does quercetin contribute to cardiovascular health?
Quercetin contributes to cardiovascular health in multiple ways. Firstly, it can help reduce blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels. Secondly, it has the potential to lower cholesterol levels, particularly LDL (bad) cholesterol. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the blood vessels, it also helps in preventing the development of atherosclerosis, a condition that can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Flavonoid with Multiple Health Benefits"
- "The Role of Quercetin in Plant and Human Health"
- "Quercetin: From Dietary Sources to Therapeutic Applications"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Soy Extract
2024-12-18
-
Ginger Extract
2024-12-18
-
Uridine-5'-monophosphate Disodium salt
2024-12-18
-
Shikone Extract
2024-12-18
-
Berberis aristata Extract
2024-12-18
-
Hericium erinaceus extract powder
2024-12-18
-
Saw Palmetto Extract
2024-12-18
-
Kelp Extract Powder
2024-12-18
-
Avocado Extract Powder
2024-12-18
-
Cranberry Extract
2024-12-18





















