- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Nature's Bounty: Unveiling the Origins and Synthesis of Diosmin
2024-07-04

1. Introduction
Diosmin, a flavonoid with remarkable properties, has been drawing increasing attention in various scientific and medical fields. It is a natural compound that has shown potential in treating a wide range of health conditions. Understanding its origins, both in terms of natural sources and the processes of synthesis, is crucial for further exploration of its applications. This article aims to comprehensively discuss the origins and synthesis of Diosmin, providing insights into how this knowledge can pave the way for new research and practical uses.
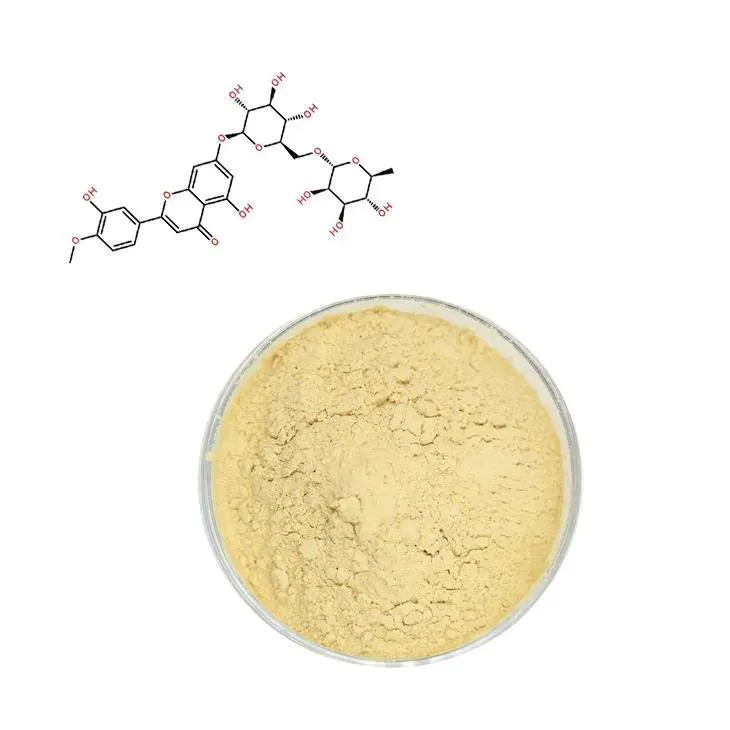
2. Origins of Diosmin in Nature
2.1 Plant Sources
Diosmin is found in various plant species. One of the well - known sources is Citrus fruits. In citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, diosmin is present in relatively small amounts but can be extracted through appropriate methods. The peel of these fruits is a particularly rich source. The biosynthesis within the citrus plants results in the production of diosmin as part of their secondary metabolite repertoire. Another important plant source is Hesperidin - rich plants. Hesperidin often co - exists with diosmin in nature. Some plants that are rich in Hesperidin also contain diosmin. These plants are often used in traditional medicine in different cultures, and the presence of diosmin may contribute to their medicinal properties.
2.2 Geographic Distribution of Diosmin - containing Plants
Plants containing diosmin are distributed worldwide. Citrus plants are widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions. For example, in countries like Brazil, the United States (Florida and California), and Spain, large - scale citrus cultivation is carried out. These regions not only produce a large quantity of citrus fruits for consumption but also serve as potential sources for diosmin extraction. In addition, some other diosmin - containing plants are native to specific regions. For instance, certain wild plants in Asia are known to contain diosmin, and these plants have been used in traditional Asian medicine for centuries.
3. Biosynthesis of Diosmin in Plants
3.1 The Basic Pathway
The biosynthesis of diosmin in plants involves a complex series of enzymatic reactions. It starts from the phenylpropanoid pathway. In this pathway, p - coumaroyl - CoA is an important intermediate. Through a series of reactions, including hydroxylation, methylation, and glycosylation reactions, the precursor molecules are gradually transformed into diosmin. The enzymes involved in these reactions play a crucial role. For example, cytochrome P450 enzymes are responsible for some of the hydroxylation steps. The biosynthesis is regulated by various factors such as plant hormones, environmental factors (such as light, temperature, and water availability), and the developmental stage of the plant.
3.2 Genetic Control of Diosmin Biosynthesis
Genes play a significant role in controlling the biosynthesis of diosmin. There are specific genes that encode the enzymes involved in the biosynthesis pathway. Mutations in these genes can lead to changes in the production of diosmin in plants. For example, some genetic studies have shown that certain gene mutations can result in either an increase or a decrease in the diosmin content in plants. Understanding the genetic control of diosmin biosynthesis can potentially allow for genetic engineering of plants to enhance the production of diosmin, which would be beneficial for both research and commercial extraction purposes.
4. Artificial Synthesis of Diosmin
4.1 Chemical Synthesis Routes
There are several chemical synthesis routes for diosmin. One common approach is through the modification of related flavonoid compounds. Starting from precursors such as rutin, chemical reactions are carried out to transform it into diosmin. These reactions typically involve hydrolysis, methylation, and glycosylation steps. Another approach is the total synthesis of diosmin from simpler organic compounds. However, this method is more complex and often requires multiple steps and the use of specific reagents. Chemical synthesis allows for the production of diosmin in larger quantities compared to extraction from natural sources, which is important for meeting the increasing demand in various industries such as pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
4.2 Challenges in Artificial Synthesis
Although artificial synthesis of diosmin is possible, there are several challenges. One of the main challenges is the selectivity of the reactions. Since the synthesis involves multiple steps and complex chemical transformations, achieving high selectivity for the desired product (diosmin) can be difficult. Side reactions may occur, leading to the formation of impurities. Another challenge is the cost - effectiveness of the synthesis. Some of the reagents used in the synthesis are expensive, and the overall process may be energy - intensive. Moreover, ensuring the safety of the synthesis process is also crucial, as some of the chemicals involved may be hazardous.
5. Significance of Understanding Diosmin's Origins and Synthesis
5.1 For Research Purposes
Understanding the origins and synthesis of diosmin is of great significance for research. Knowledge of its natural biosynthesis can help in studying plant metabolism and the regulation of secondary metabolite production. This can provide insights into the evolution of plants and their adaptation mechanisms. In artificial synthesis, understanding the chemical reactions involved can lead to the development of more efficient and cost - effective synthesis methods. This, in turn, can facilitate the study of diosmin's structure - activity relationships. By having a better understanding of how diosmin is synthesized, researchers can also design and synthesize analogues of diosmin, which may have improved or novel properties.
5.2 For Practical Applications
In practical applications, knowledge of diosmin's origins and synthesis can have a wide range of impacts. In the pharmaceutical industry, it can help in the production of high - quality diosmin - based drugs. Since diosmin has been shown to have potential in treating various health conditions such as venous insufficiency and hemorrhoids, efficient production methods are crucial. In the cosmetics industry, diosmin can be used in skin - care products for its antioxidant and anti - inflammatory properties. Understanding its synthesis can ensure a stable supply of diosmin for these applications. Moreover, in the field of agriculture, knowledge of diosmin biosynthesis in plants can be used to develop strategies for enhancing the production of diosmin - rich plants, which may have implications for plant breeding and crop improvement.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, diosmin, a valuable compound from nature, has its origins in various plant species. The understanding of its natural biosynthesis and artificial synthesis is gradually deepening. By unveiling the origins and synthesis of diosmin, we open doors to new research opportunities and practical applications. Future research should focus on further exploring the biosynthesis mechanisms at the molecular level, improving artificial synthesis methods to overcome the existing challenges, and expanding the practical uses of diosmin in different industries. With continued research, diosmin is likely to play an even more important role in improving human health, enhancing agricultural productivity, and contributing to the development of the cosmetics industry.
FAQ:
What are the main plant species where diosmin is found?
Diosmin can be found in various plant species. Some of the common ones include citrus fruits. The peels of oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are rich sources of diosmin. It is also present in certain medicinal plants.
How does the natural biosynthesis of diosmin occur?
The natural biosynthesis of diosmin involves a series of enzymatic reactions within the plant cells. It starts with the synthesis of precursor molecules through primary metabolic pathways. These precursors are then modified by specific enzymes. The exact mechanism is complex and may vary depending on the plant species. For example, in citrus plants, it is related to the biosynthesis of flavonoids, of which diosmin is a part. The plants use their genetic machinery to regulate these enzymatic steps and ensure the production of diosmin.
What are the common artificial synthesis techniques for diosmin?
One of the common artificial synthesis techniques for diosmin is chemical synthesis. This typically involves starting from simple chemical compounds and using a series of chemical reactions to build the diosmin molecule. Another approach could be semi - synthetic methods, where natural precursors are chemically modified to obtain diosmin. However, the artificial synthesis needs to be carefully controlled to ensure the purity and quality of the synthesized diosmin, as it is intended for various applications such as in pharmaceuticals.
Why is understanding the origins of diosmin important for new research?
Understanding the origins of diosmin is crucial for new research. Firstly, it helps in identifying potential new sources of diosmin. If we know which plants produce it, we can explore those plants further for extraction and purification. Secondly, knowledge of its origin can give insights into its natural function in plants. This can then be related to its potential functions in other organisms, including humans. For example, if diosmin has a certain role in protecting plants from oxidative stress, it may have similar antioxidant properties in humans. Thirdly, it can aid in understanding the evolution of the molecule and related compounds, which can inspire new research directions.
How can the knowledge of diosmin's synthesis be applied in practical uses?
The knowledge of diosmin's synthesis can be applied in several practical uses. In the pharmaceutical industry, understanding the synthesis can help in developing more efficient and cost - effective production methods. This can lead to increased availability of diosmin - based drugs. In the cosmetic industry, if the synthesis can be optimized, it can be used to produce skincare products with diosmin more easily. Also, in the field of food additives, knowing the synthesis can ensure the quality and safety of diosmin when it is added to foods for its potential health - promoting properties.
Related literature
- Diosmin: A Review of Its Pharmacological Properties"
- "The Biosynthesis of Flavonoids and Diosmin in Plants"
- "Advances in Artificial Synthesis of Diosmin"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Yohimbine Bark Extract
2024-07-04
-
Tongkat Ali Extract Powder
2024-07-04
-
Scutellaria Extract
2024-07-04
-
Lycopene
2024-07-04
-
Mulberry leaf Extract
2024-07-04
-
Chaste Berry Extract
2024-07-04
-
Licorice Root Extract Powder
2024-07-04
-
Peppermint Oil
2024-07-04
-
Genistein
2024-07-04
-
Shikone Extract
2024-07-04





















