- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Resveratrol Extraction: A Key to Unlocking Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential
2024-08-15

1. Introduction
Resveratrol, a natural polyphenol, has been the focus of extensive research in recent years due to its remarkable potential in the nutraceutical and pharmaceutical domains. It is found in various plant sources and has been associated with a wide range of health benefits. However, to fully realize its potential, effective extraction methods are crucial. This article aims to comprehensively explore Resveratrol extraction, covering different extraction techniques, its sources, and the associated health benefits, as well as how extraction can improve its bioavailability for therapeutic and preventive uses.
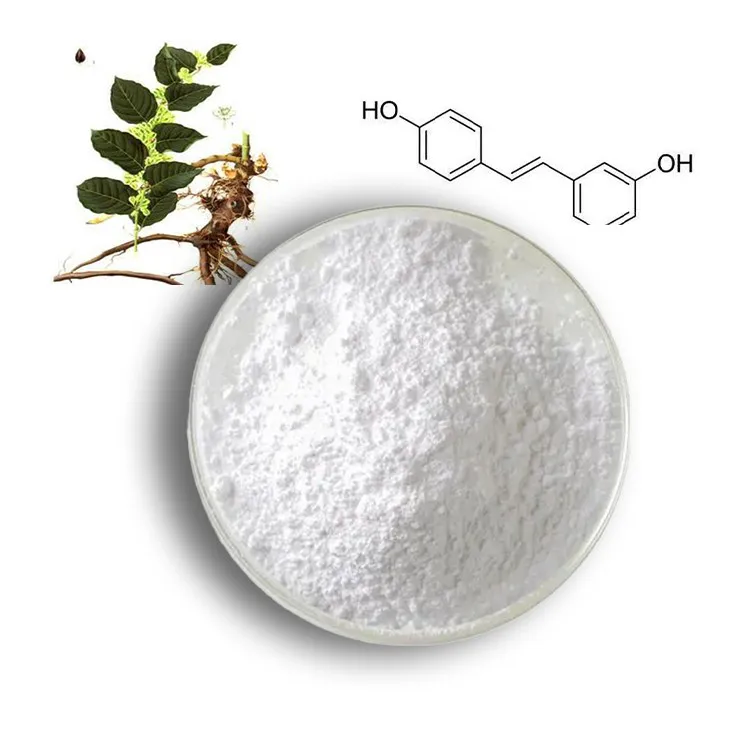
2. Sources of Resveratrol
2.1 Grape and Wine
- One of the most well - known sources of resveratrol is grapes, especially in their skins. Red grapes are particularly rich in resveratrol. During the winemaking process, resveratrol is transferred from the grape skins into the wine. Different grape varieties may contain varying amounts of resveratrol. For example, Pinot Noir is often considered to have a relatively high resveratrol content compared to some other grape varieties.
- The amount of resveratrol in wine can also be influenced by factors such as the grape - growing region, the winemaking techniques employed (e.g., fermentation time and temperature), and the storage conditions of the wine.
- Blueberries, raspberries, and cranberries are also sources of resveratrol. Although the concentration may be lower compared to grapes in some cases, they still contribute to the overall dietary intake of resveratrol. These berries are often consumed fresh or in processed forms such as jams, juices, and dried fruits.
- Berries are rich in other beneficial compounds as well, such as antioxidants and vitamins, which may work synergistically with resveratrol to provide health benefits.
- Peanuts contain resveratrol, although in relatively small amounts. Resveratrol in peanuts is mainly present in the skin. Peanut - based products, such as peanut butter, may also contain resveratrol, but the extraction and bioavailability can be affected by the processing methods used in their production.
3. Extraction Methods
3.1 Solvent Extraction
-
3.1.1 Organic Solvents
- Organic solvents such as ethanol, methanol, and ethyl acetate are commonly used for Resveratrol extraction. Ethanol is a popular choice as it is relatively safe and can effectively extract resveratrol from plant materials. For example, in the extraction from grape skins, a certain concentration of ethanol solution can be used to dissolve resveratrol. The extraction process typically involves soaking the plant material in the solvent for a period of time, followed by filtration and evaporation to obtain the resveratrol - rich extract.
- The choice of solvent can affect the extraction efficiency and the quality of the extract. Different solvents may have different selectivity for resveratrol and other compounds present in the plant material. Methanol, for instance, may extract more impurities along with resveratrol compared to ethanol, which may require additional purification steps.
-
3.1.2 Aqueous Solvents
- Aqueous solvents, such as water, can also be used for Resveratrol extraction. However, resveratrol has relatively low solubility in water alone. To improve solubility, additives such as surfactants or cosolvents may be used. For example, a combination of water and a small amount of ethanol can be used to increase the extraction yield of resveratrol from plant sources. Aqueous solvent extraction has the advantage of being more environmentally friendly compared to organic solvents, but it may require more complex extraction procedures to achieve high extraction efficiencies.
- Supercritical fluid extraction uses supercritical fluids, such as supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO₂), as the extraction medium. scCO₂ has properties between those of a gas and a liquid at its supercritical state. It has high diffusivity, low viscosity, and can be easily removed from the extract, leaving behind a pure resveratrol product.
- The extraction process using SFE is typically carried out at high pressure and a specific temperature. The pressure and temperature conditions can be adjusted to optimize the extraction of resveratrol. For example, by varying the pressure, it is possible to selectively extract resveratrol while minimizing the extraction of other unwanted compounds. SFE is considered a "green" extraction method as carbon dioxide is non - toxic, non - flammable, and readily available.
- Microwave - assisted extraction utilizes microwave energy to enhance the extraction process. Microwaves can heat the plant material and the solvent rapidly and uniformly, which can increase the extraction efficiency. In the case of resveratrol extraction from plant sources, the plant material and solvent are placed in a microwave - transparent vessel and subjected to microwave irradiation for a specific period of time.
- The extraction time and power of the microwave can be optimized to achieve the highest yield of resveratrol. Compared to traditional extraction methods, MAE can significantly reduce the extraction time. However, it requires careful control of the microwave parameters to avoid over - heating and degradation of resveratrol.

4. Health Benefits of Resveratrol
4.1 Antioxidant Properties
- Resveratrol is a powerful antioxidant. It can scavenge free radicals in the body, which are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and tissues. By neutralizing free radicals, resveratrol helps to protect the body against oxidative stress, which is associated with various chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Oxidative stress can lead to the oxidation of lipids, proteins, and DNA. Resveratrol can prevent or reduce this oxidation, thereby maintaining the integrity of these biomolecules. For example, in vitro studies have shown that resveratrol can inhibit the oxidation of low - density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
- Resveratrol has anti - inflammatory properties. It can modulate the inflammatory response in the body by inhibiting the production of pro - inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin - 1β (IL - 1β), interleukin - 6 (IL - 6), and tumor necrosis factor - α (TNF - α). Inflammation is a key component of many diseases, including arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and autoimmune disorders.
- In animal models of arthritis, resveratrol has been shown to reduce joint inflammation and pain. It can also regulate the activity of immune cells, such as macrophages, which play a crucial role in the inflammatory process.
- As mentioned earlier, resveratrol can protect against LDL cholesterol oxidation. In addition, it can also improve endothelial function. The endothelium is the inner lining of blood vessels, and its proper function is essential for maintaining normal blood flow and preventing cardiovascular diseases. Resveratrol can stimulate the production of nitric oxide (NO) in endothelial cells, which causes vasodilation and helps to lower blood pressure.
- Resveratrol may also have anti - platelet aggregation effects. Platelet aggregation can lead to the formation of blood clots, which can block blood vessels and cause heart attacks or strokes. By inhibiting platelet aggregation, resveratrol can reduce the risk of these thrombotic events.
- Resveratrol has shown potential in cancer prevention and treatment. It can interfere with various stages of cancer development, including initiation, promotion, and progression. In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that resveratrol can induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells.
- Resveratrol can also target multiple signaling pathways involved in cancer, such as the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and the MAPK pathway. By modulating these pathways, resveratrol can inhibit the growth and survival of cancer cells. However, more research is needed to fully understand its anti - cancer mechanisms and to develop effective resveratrol - based cancer therapies.

5. Enhancing Bioavailability of Resveratrol
5.1 Nanoparticle - Based Delivery Systems
- One approach to enhance the bioavailability of resveratrol is through the use of nanoparticle - based delivery systems. Nanoparticles can protect resveratrol from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and improve its absorption. For example, polymeric nanoparticles can be designed to encapsulate resveratrol. These nanoparticles can be surface - modified to target specific cells or tissues in the body, increasing the specificity of resveratrol delivery.
- Lipid - based nanoparticles, such as liposomes, are also used for resveratrol delivery. Liposomes are composed of phospholipids and can mimic the cell membrane structure. Resveratrol - loaded liposomes can enhance the solubility of resveratrol and promote its uptake by cells. Nanoparticle - based delivery systems can also control the release of resveratrol, allowing for a sustained release over time, which can further improve its therapeutic efficacy.
- Formulating resveratrol with other compounds can also enhance its bioavailability. For example, combining resveratrol with piperine, a compound found in black pepper, has been shown to increase the absorption of resveratrol in the body. Piperine can inhibit the enzymes responsible for the metabolism of resveratrol in the intestine, thereby increasing its bioavailability.
- Resveratrol can also be combined with other antioxidants or bioactive compounds to achieve synergistic effects. For instance, when combined with vitamin C or E, resveratrol may have enhanced antioxidant activity, which can contribute to better health benefits.
6. Conclusion
Resveratrol extraction is a complex but crucial process for unlocking its potential in the nutraceutical and pharmaceutical fields. Understanding the different sources of resveratrol, the various extraction methods, and its health benefits is essential for further research and development. By improving the extraction techniques and enhancing the bioavailability of resveratrol, we can better utilize this natural compound for therapeutic and preventive applications, potentially leading to the development of new drugs and nutraceutical products. However, more research is still needed to fully explore the mechanisms of resveratrol's action and to optimize its use in human health.
FAQ:
What are the common sources of resveratrol?
Resveratrol can be sourced from various plants. One of the most well - known sources is grapes, especially in the skins and seeds. It is also present in berries such as blueberries, cranberries, and raspberries. Additionally, peanuts are a source of resveratrol.
What are the main extraction methods for resveratrol?
There are several extraction methods. Solvent extraction is a common one, where solvents like ethanol are used to extract resveratrol from plant materials. Supercritical fluid extraction is another method that uses supercritical fluids, such as carbon dioxide, which offers advantages like better selectivity and reduced solvent residue. Microwave - assisted extraction and ultrasonic - assisted extraction are also used, which can enhance the extraction efficiency by using microwave or ultrasonic energy respectively.
How does resveratrol extraction enhance its bioavailability?
During extraction, certain techniques can modify the physical and chemical properties of resveratrol. For example, encapsulation during extraction can protect resveratrol from degradation in the body and improve its solubility. Nanoparticle - based extraction methods can also enhance its bioavailability by facilitating better absorption at the cellular level.
What are the potential health benefits of resveratrol?
Resveratrol has been associated with numerous health benefits. It has antioxidant properties, which can help in reducing oxidative stress in the body. It may also have anti - inflammatory effects, potentially useful in treating various inflammatory diseases. There is also evidence suggesting that it could play a role in cardiovascular health by reducing cholesterol levels and improving blood vessel function. In addition, resveratrol has been studied for its potential anti - cancer properties, although more research is needed in this area.
Are there any challenges in resveratrol extraction?
Yes, there are challenges. One challenge is achieving high purity. Since resveratrol is often present in complex plant matrices, separating it from other compounds can be difficult. Another challenge is cost - effectiveness. Some extraction methods may be expensive, especially those involving advanced technologies. Also, ensuring the stability of resveratrol during extraction and subsequent storage is a concern.
Related literature
- Resveratrol: Sources, Bioavailability, and Potential Health Benefits"
- "Advances in Resveratrol Extraction and Its Application in Nutraceuticals"
- "The Role of Resveratrol in Pharmaceutical Research: Extraction and Therapeutic Potential"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Tamarind extract powder
2024-08-15
-
Cocoa Extract
2024-08-15
-
Chia Seed Powder
2024-08-15
-
Phyllanthus Emblica Extract
2024-08-15
-
Berberis aristata Extract
2024-08-15
-
White Willow Bark Extract
2024-08-15
-
Plantain extract
2024-08-15
-
Boswellia Serrata Extract
2024-08-15
-
Polygonum Cuspidatum Extract
2024-08-15
-
Alfalfa Meal
2024-08-15





















