- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Is astaxanthin better than green tea extract?
2025-04-29
In the realm of nutritional supplements, the quest for potent antioxidants is a driving force as consumers look for ways to optimize health, prevent disease, and enhance overall well-being. Astaxanthin and Green Tea Extract are two popular options, each boasting a range of health benefits and a robust antioxidant profile. But when comparing the two, one may wonder: is Astaxanthin better than Green Tea Extract? This professional article explores the properties, potential benefits, and distinctions between these two supplements, helping readers make informed decisions.
Understanding Astaxanthin
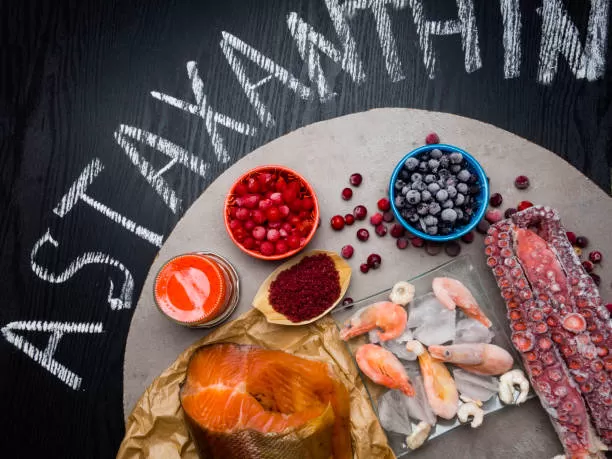
Astaxanthin is a red pigment classified as a carotenoid, famously found in algae, salmon, shrimp, and flamingos. Its powerful antioxidant capabilities are due to its unique molecular structure, which allows it to neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and exert anti-inflammatory effects within the body. Astaxanthin is fat-soluble, enabling it to integrate into cell membranes and provide protection against lipid peroxidation.
Several studies suggest that astaxanthin offers benefits for skin health, eye health, cardiovascular function, and muscle endurance. Athletes often turn to astaxanthin for its reported ability to combat exercise-induced oxidative stress and improve recovery times.
Understanding Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant. Known for its high content of polyphenolic compounds, particularly catechins like epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), green tea extract is celebrated for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardiovascular benefits. These compounds are water-soluble, making them easily absorbed and utilized by the body.
Green tea extract is widely recognized for its role in supporting metabolic health, enhancing fat oxidation, and promoting aerobic performance. Additionally, green tea extract contains L-theanine, an amino acid that offers calming effects and has been associated with improved cognitive function.
Comparing Astaxanthin and Green Tea Extract
Antioxidant Potency
When comparing antioxidant potency, astaxanthin is often regarded as one of the most powerful antioxidants available. Its ability to neutralize free radicals is purportedly stronger than many other commonly used antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and even catechins found in green tea. Astaxanthin's unique structure allows it to span cell membranes, offering comprehensive protection to cells.
Green tea extract, though not as potent as astaxanthin per molecule, provides a broad spectrum of polyphenolic compounds that collectively offer strong antioxidant activity. EGCG, the most abundant catechin in green tea, is particularly effective at scavenging free radicals and reducing the risk of oxidative damage.
Health Benefits
Both astaxanthin and green tea extract offer overlapping and distinct health benefits:
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Both supplements exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to overall health and chronic disease prevention. Astaxanthin has been shown to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, while green tea extract helps modulate inflammatory pathways.
Cardiovascular Health: Green tea extract is known to support heart health by improving lipid profiles and reducing blood pressure. Astaxanthin also contributes to cardiovascular function, though its primary focus is more on oxidative stress reduction within the vascular system.
Skin Health: Astaxanthin's affinity for cellular membranes makes it particularly effective for skin health, reducing UVA-induced damage and improving elasticity and hydration. Green tea extract offers photoprotective effects that can mitigate UV damage.
Metabolic Support: While green tea extract is often linked with metabolism acceleration and weight reduction due to increased fat oxidation, astaxanthin can aid endurance by combatting exercise-induced oxidative stress.
Bioavailability and Absorption
Astaxanthin, being a fat-soluble compound, requires dietary fat for optimal absorption. It integrates well into cell membranes, providing extended antioxidant protection. Conversely, green tea extract is water-soluble, allowing for more efficient absorption and utilization through aqueous bodily fluids.
Personal Health Goals
Ultimately, determining whether astaxanthin is better than green tea extract depends on individual health goals:
For those seeking potent antioxidant protection and targeting skin health and muscle performance, astaxanthin may be preferable.
Individuals focusing more on metabolic health, cardiovascular support, and cognitive improvements may benefit from green tea extract, which offers these specialized benefits.
Considerations for Supplementation
When considering supplementation, several factors should be kept in mind:
Source and Quality: Opt for high-quality, reputable brands to ensure purity and efficacy of supplements.
Dosage and Safety: Follow recommended dosage guidelines to avoid adverse effects. Consult healthcare providers for personalized advice, especially if pre-existing health conditions or other medications are involved.
Lifestyle Integration: Integrate supplements into a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle for maximum benefits.
Conclusion
Astaxanthin and green tea extract both offer remarkable benefits, each with unique strengths relative to antioxidant protection, health support, and disease prevention. While astaxanthin boasts superior antioxidant potency, green tea extract covers a broad range of health applications, especially concerning metabolism and cardiovascular health. Rather than determining a definitive winner, consider personal health priorities and choose the supplement that aligns best with those goals. By understanding the capabilities of each, individuals can make informed choices that enhance their overall health and well-being.
-
What are the benefits of astaxanthin?
2025-04-29
-
What is astaxanthin made from?
2025-04-29
-
What Is Astaxanthin Supplement
2025-04-29
-
What Is The Function Of Astaxanthin
2025-04-29
-
what is astareal astaxanthin
2025-04-29