- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Astaxanthin vs. Vitamin C: Exploring Their Differences and Benefits
2025-04-29
In the realm of dietary supplements and natural health products, two compounds have garnered considerable attention for their antioxidant properties: Astaxanthin and vitamin C. Both are revered for their potential to enhance overall health and combat oxidative stress, but they are not the same and serve distinct roles within the body. As consumers look to bolster their wellness regimens, understanding the unique characteristics and benefits of these antioxidants is essential. This article delves into the differences between Astaxanthin and vitamin C, exploring their sources, mechanisms, and potential health impacts.
Understanding Astaxanthin
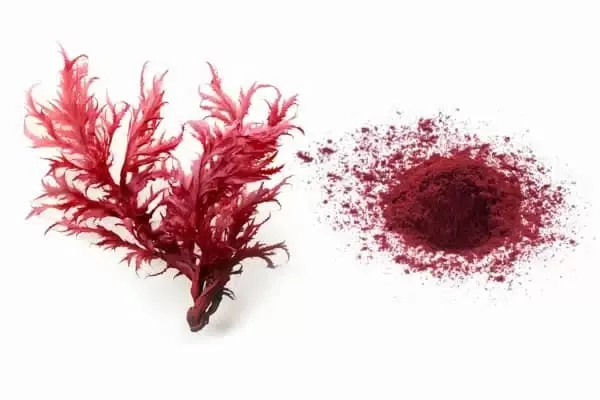
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid, which is a type of naturally occurring pigment found in various marine organisms. It is responsible for the reddish hue seen in salmon, shrimp, lobster, and other sea creatures. Often referred to as the "king of carotenoids," astaxanthin has a unique molecular structure that allows it to provide impressive antioxidant protection. Unlike many other antioxidants, astaxanthin sits within cell membranes, offering a protective shield against oxidative damage on both the inner and outer layers of cells.
Astaxanthin's powerful antioxidant activity is believed to be up to several times stronger than that of other carotenoids, such as beta-carotene, and even surpasses the potency of vitamin C in neutralizing certain types of free radicals. This makes astaxanthin particularly effective in protecting cells from oxidative stress, which is linked to a range of chronic diseases and aging processes.
Understanding Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is an essential nutrient well-known for its immune-boosting properties and pivotal role in maintaining skin, bone, and blood vessel health. It is a water-soluble vitamin, which means it is not stored in the body and must be consumed regularly through diet or supplementation. Vitamin C operates mainly in aqueous (water-based) environments within the body, such as blood and intracellular fluid, and it is a critical cofactor in the enzymatic production of collagen, a protein vital for skin integrity and wound healing.
In addition to its role in collagen synthesis, vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps combat oxidative stress by donating electrons to neutralize free radicals. It also aids the regeneration of other antioxidants, like vitamin E, enhancing their efficacy and contributing to a comprehensive antioxidant defense system.
Comparing Their Antioxidant Mechanisms
While both astaxanthin and vitamin C are antioxidants, their mechanisms of action and areas of influence differ significantly due to their chemical properties and solubility.
Astaxanthin, being fat-soluble, is predominantly active in lipid-rich areas of the body, including cell membranes. Its unique structure enables it to quench free radicals on both sides of the membrane, providing robust protection against lipid peroxidation—a major contributor to chronic disease and cellular damage. This property is particularly beneficial for protective roles in the brain, skin, and eyes, where fatty tissues are prevalent.
Vitamin C, on the other hand, being water-soluble, is primarily active in aqueous environments. It is crucial for neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in body fluids and inside cells, preventing oxidative damage to proteins and DNA. Its presence in the bloodstream allows vitamin C to quickly reach tissues and exert its protective effects, particularly in immune function and collagen maintenance.
Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
Research has highlighted several potential benefits of astaxanthin supplementation, largely attributed to its antioxidant capacity. These include:
1. Skin Health: Astaxanthin may improve skin hydration, elasticity, and overall complexion by protecting skin cells from UV-induced damage and reducing inflammation.
2. Eye Health: The antioxidant properties of astaxanthin help protect the eyes from oxidative damage, potentially improving visual acuity and reducing the risk of eye conditions such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
3. Cardiovascular Health: Astaxanthin may support heart health by improving blood lipid profiles, reducing inflammation, and enhancing endothelial function.
4. Exercise Recovery: Athletes may benefit from astaxanthin's ability to reduce muscle damage and enhance recovery following intense physical activity.
Health Benefits of Vitamin C
Vitamin C's myriad health benefits stem from its multifunctional role as an antioxidant and essential nutrient:
1. Immune Support: Vitamin C is widely known for enhancing immune defense, supporting various cellular functions, and facilitating the production of white blood cells.
2. Collagen Synthesis: Essential for collagen production, vitamin C supports skin health, wound healing, and structural maintenance of connective tissues.
3. Antioxidant Protection: As an effective free radical scavenger, vitamin C protects cells from oxidative damage and collaborates with other antioxidants to enhance overall defense.
4. Iron Absorption: Vitamin C enhances the absorption of non-heme iron from plant-based foods, helping prevent iron-deficiency anemia.
Conclusion
While astaxanthin and vitamin C share the commonality of being powerful antioxidants, they differ significantly in their structures, solubility, mechanisms, and functions within the body. Astaxanthin excels in protecting lipid-rich tissues with its superior antioxidant strength and has shown potential for addressing health concerns related to skin, eyes, and cardiovascular health. Vitamin C, vital for overall health, plays a critical role in immune support, collagen production, and the maintenance of various physiological processes.
Together, these antioxidants can complement each other in a balanced diet or supplementation regimen, supporting a wide range of health benefits. Understanding their distinct properties and applications allows individuals to tailor their wellness strategies effectively, harnessing the best of both natural compounds. As always, consulting with healthcare professionals before beginning any supplementation is recommended to ensure safety and efficacy.
-
What are the benefits of astaxanthin?
2025-04-29
-
What is astaxanthin made from?
2025-04-29
-
What Is Astaxanthin Supplement
2025-04-29
-
What Is The Function Of Astaxanthin
2025-04-29
-
what is astareal astaxanthin
2025-04-29