- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
The extraction process of diosmin.
2024-11-30

1. Introduction
Diosmin is a flavonoid glycoside that has attracted significant attention in the field of medicine due to its various beneficial properties. It has been found to have antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and vascular - protective effects, among others. These properties make it a valuable compound in the treatment of conditions such as venous insufficiency, hemorrhoids, and capillary fragility. The extraction of Diosmin from natural sources is a crucial step in obtaining a pure and usable form of this compound for pharmaceutical applications.
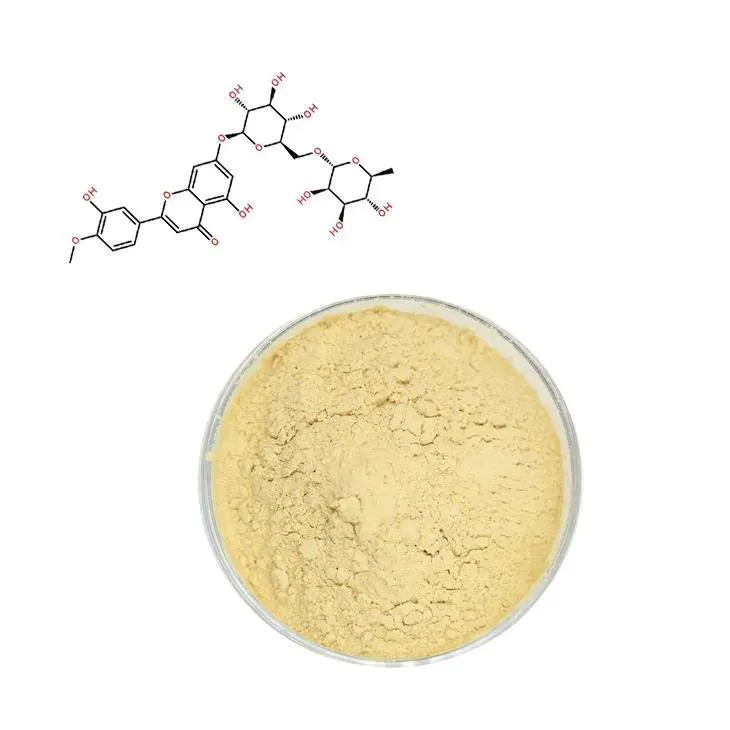
2. Selection of Raw Materials
2.1 Plant Sources
Diosmin is commonly found in certain plant sources. Citrus fruits are among the most well - known sources of diosmin. These fruits are rich in flavonoids, including diosmin. Other plant sources may also contain diosmin, but citrus fruits are often preferred due to their relatively high content and wide availability.2.2 Criteria for Selection
When selecting the raw materials, several factors need to be considered. Firstly, the quality of the plant material is crucial. This includes factors such as the maturity of the fruits, as the diosmin content may vary depending on the stage of ripeness. Secondly, the absence of contaminants such as pesticides and heavy metals is essential to ensure the safety and purity of the final product. Additionally, the source of the plant material should be traceable to meet regulatory requirements.3. Pretreatment of Plant Material
3.1 Cleaning
The first step in the pretreatment process is cleaning the plant material. This is necessary to remove any dirt, debris, or foreign matter that may be present on the surface of the fruits. Simple washing with clean water can be effective in removing most of the surface contaminants. However, in some cases, more thorough cleaning methods may be required, especially if the fruits are heavily soiled or have been treated with pesticides.3.2 Drying
After cleaning, the plant material needs to be dried. Drying helps to reduce the moisture content of the fruits, which is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to prevent the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi during storage and further processing. Secondly, it can also make the grinding process easier. The drying process can be carried out using natural methods such as air - drying or artificial methods such as using a drying oven. The choice of drying method depends on factors such as the quantity of plant material, the available resources, and the required drying time.3.3 Grinding
Once the plant material is dry, it is ground to a suitable particle size. Grinding is necessary to increase the surface area of the plant material, which in turn improves the efficiency of the extraction process. The particle size should be small enough to allow for effective contact with the solvent during extraction, but not too small that it causes problems such as clogging during filtration. A common grinding method is to use a grinder or a mill, and the resulting powder should have a uniform particle size distribution.4. Solvent Extraction
4.1 Choice of Solvent
The choice of solvent is a critical factor in the extraction of diosmin. Organic solvents such as ethanol and methanol are often used due to their high solubility for diosmin. Ethanol is a particularly popular choice as it is relatively safe, has a relatively low toxicity, and is also easily available. Methanol, on the other hand, has a higher solubility for some flavonoids but is more toxic and requires more careful handling. In addition to ethanol and methanol, other solvents or solvent mixtures may also be considered depending on the specific requirements of the extraction process.4.2 Extraction Conditions
The extraction conditions also play an important role in the efficiency of the extraction process. Factors such as the solvent - to - material ratio, the extraction temperature, and the extraction time need to be optimized. A higher solvent - to - material ratio generally results in a higher extraction yield, but it also increases the cost and may require more complex separation processes later. The extraction temperature can affect the solubility of diosmin in the solvent as well as the rate of extraction. Typically, a moderately elevated temperature can increase the extraction rate, but too high a temperature may cause degradation of diosmin or other components in the plant material. The extraction time should be long enough to ensure sufficient extraction of diosmin, but not overly long to avoid unnecessary extraction of impurities.4.3 Extraction Methods
There are several methods for carrying out solvent extraction. One common method is maceration, where the ground plant material is soaked in the solvent for a period of time, usually several hours to days. During this time, the solvent penetrates the plant material and dissolves the diosmin. Another method is percolation, where the solvent is continuously passed through a column filled with the plant material. This method can be more efficient as it allows for a continuous extraction process and better mass transfer. Soxhlet extraction is also a well - known method, which is suitable for extracting diosmin from plant material with a relatively low diosmin content. In this method, the plant material is repeatedly extracted with fresh solvent until the extraction is complete.5. Purification of the Extract
5.1 Chromatography
Chromatography is a widely used technique for purifying the diosmin extract. There are different types of chromatography that can be applied, such as column chromatography, high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and thin - layer chromatography (TLC). In column chromatography, the extract is passed through a column filled with a stationary phase, and the different components in the extract are separated based on their different affinities for the stationary and mobile phases. HPLC is a more advanced and efficient form of chromatography that can provide high - resolution separation of diosmin from other impurities. TLC is a simple and inexpensive method that can be used for preliminary analysis and purification on a small scale.5.2 Recrystallization
Recrystallization is another purification method that can be used for diosmin. In this method, the crude extract is dissolved in a suitable solvent at a high temperature, and then the solution is slowly cooled. As the solution cools, the diosmin crystallizes out of the solution, leaving behind the impurities in the mother liquor. The crystals can be separated from the mother liquor by filtration or centrifugation, and further purified if necessary. Recrystallization can be repeated several times to obtain a highly pure form of diosmin.6. Final Product and its Applications
6.1 Characteristics of the Final Product
After the purification steps, the final product is pure diosmin. The pure diosmin should have a high purity level, typically above 95% or even higher depending on the requirements of the pharmaceutical applications. It should also have a consistent chemical composition and physical properties, such as a specific melting point and solubility.6.2 Pharmaceutical Applications
Diosmin has a wide range of pharmaceutical applications. It is commonly used in the treatment of venous disorders, where it can improve venous tone, reduce venous stasis, and relieve symptoms such as leg swelling and pain. It is also used in the treatment of hemorrhoids, where it can reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation in the anal area, and promote the healing of hemorrhoidal tissue. Additionally, diosmin has potential applications in the prevention and treatment of other conditions related to vascular health, such as capillary fragility and microcirculation disorders.7. Conclusion
The extraction process of diosmin is a complex but well - defined process that involves several crucial steps. From the selection of raw materials to the final purification of the product, each step needs to be carefully carried out to ensure the production of high - quality diosmin for pharmaceutical applications. With the increasing demand for natural and effective medicinal compounds, the extraction of diosmin will continue to be an important area of research and development in the pharmaceutical industry.
FAQ:
What are the common plant sources for diosmin extraction?
Citrus fruits are among the common plant sources for diosmin extraction as they are rich in diosmin.
Why are ethanol and methanol often used in the solvent extraction of diosmin?
Ethanol and methanol are often used in the solvent extraction of diosmin because they have the ability to dissolve diosmin effectively.
What is the purpose of the pretreatment process in diosmin extraction?
The pretreatment process in diosmin extraction, which may include cleaning, drying, and grinding to a suitable particle size, is to prepare the plant material for the subsequent extraction process. Cleaning removes dirt and impurities, drying helps in preservation and proper handling, and grinding to an appropriate particle size increases the surface area for better extraction.
What purification techniques are used in the extraction of diosmin?
Chromatography is one of the purification techniques used in the extraction of diosmin. It helps to separate diosmin from other impurities in the extract.
What are the pharmaceutical applications of diosmin?
Diosmin has various medicinal properties and can be used in pharmaceutical applications for treating conditions such as venous insufficiency, hemorrhoids, and other related vascular disorders. However, specific pharmaceutical applications may vary depending on further research and development.
Related literature
- “Diosmin: A Review of Its Pharmacological and Therapeutic Applications”
- “Optimization of Diosmin Extraction from Plant Sources”
- “The Role of Diosmin in Vascular Health: A Comprehensive Study”
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
The best lemon juice powder in nature.
2024-11-30
-
Organic Vitamin K2 Powder Suppliers
2024-11-30
-
Bulk purchase of L - tyrosine.
2024-11-30
-
Vitamin K2 Manufacturers
2024-11-30
-
100% Pure Natural Rutin.
2024-11-30
-
Chinese Citrus Bioflavonoid Suppliers.
2024-11-30
-
Yam Extract
2024-11-30
-
Lavender Extract
2024-11-30
-
Centella Asiatica Extract
2024-11-30
-
Polygonum Cuspidatum Extract
2024-11-30
-
Nettle leaf extract
2024-11-30
-
Sugarcane Extract
2024-11-30
-
Polygonum multiflorum extract
2024-11-30
-
Bilberry Extract
2024-11-30
-
Black Garlic Extract
2024-11-30
-
Beta Carotene
2024-11-30





















