- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
A Complete Guide to Quercetin Grinding Process: Key Points Step by Step
2024-12-17

1. Introduction
Quercetin, a prominent flavonoid, has been widely recognized for its numerous health benefits. These include antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and potential anti - cancer properties. However, to fully utilize its potential in various applications such as in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food industries, proper grinding is essential. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on the Quercetin grinding process, covering all the crucial aspects from equipment selection to quality control.

2. Equipment Selection
2.1. Mortar and Pestle
The most basic and traditional equipment for grinding Quercetin is the mortar and pestle. This is suitable for small - scale grinding, especially in laboratory settings or for home - made preparations.
- Advantages:
- It allows for precise control over the grinding process. You can easily monitor the particle size and texture of the quercetin as you grind.
- It is a relatively inexpensive option, making it accessible for small - budget operations or individual users.
- Disadvantages:
- Grinding with a mortar and pestle can be time - consuming, especially when dealing with larger quantities of quercetin.
- The consistency of the grind may not be as uniform as with more advanced equipment.
2.2. Ball Mills
Ball mills are commonly used in industrial settings for grinding quercetin. They consist of a rotating cylinder filled with grinding media, usually balls, and the quercetin sample.
- Advantages:
- Capable of handling larger quantities of quercetin at once, making it suitable for large - scale production.
- Can achieve a relatively uniform particle size distribution, which is crucial for consistent product quality.
- Disadvantages:
- They are more expensive to purchase and maintain compared to a mortar and pestle.
- Requires more space due to their larger size.
2.3. Hammer Mills
Hammer mills are another option for grinding quercetin. They use high - speed rotating hammers to break down the material.
- Advantages:
- Very efficient in reducing the particle size quickly, which can save time in the grinding process.
- Can be adjusted to different settings to achieve the desired particle size.
- Disadvantages:
- The high - speed operation may generate heat, which could potentially affect the stability of quercetin if not properly controlled.
- May cause some degree of mechanical stress on the quercetin particles, which could also impact its properties.

3. Grinding Techniques
3.1. Pre - Grinding Preparation
Before starting the actual grinding process, proper pre - grinding preparation is necessary.
- Drying: Quercetin should be dried to an appropriate moisture level. Excessive moisture can make the grinding process difficult and may also affect the quality of the final product. The drying process can be carried out using methods such as air - drying or using a desiccator, depending on the quantity and available facilities.
- Sieving: Sieving the quercetin before grinding can remove any large particles or impurities that may interfere with the grinding process. A fine - mesh sieve can be used to ensure a more uniform starting material.
3.2. Grinding Speed and Time
The grinding speed and time are critical factors in achieving the desired particle size and quality of quercetin.
- Mortar and Pestle: When using a mortar and pestle, a slow and steady grinding speed is recommended. This allows for better control over the particle size. The grinding time can vary depending on the quantity and the desired fineness, but it usually takes longer compared to other equipment. For example, for a small amount (about 1 - 2 grams) of quercetin, it may take 10 - 15 minutes of continuous grinding to achieve a moderately fine powder.
- Ball Mills: In ball mills, the rotation speed of the cylinder needs to be optimized. Too slow a speed may result in inefficient grinding, while too high a speed can cause excessive wear on the grinding media and the cylinder. The grinding time also depends on the initial particle size, the desired final particle size, and the quantity of quercetin. Generally, for a batch of 100 grams of quercetin, it may take several hours to a day of continuous grinding in a ball mill to achieve a fine and uniform powder.
- Hammer Mills: Hammer mills operate at high speeds, but the time of operation needs to be carefully controlled. A short grinding time may not achieve the desired particle size reduction, while an overly long time can lead to over - grinding and potential degradation of quercetin. For a 50 - gram sample of quercetin in a hammer mill, a grinding time of 2 - 5 minutes may be appropriate, depending on the specific settings of the mill.
3.3. Cooling during Grinding
As mentioned earlier, some grinding equipment, such as hammer mills, can generate heat during operation. This heat can have a negative impact on quercetin. Therefore, cooling during grinding is an important consideration.
- Air - Cooling: One simple method is air - cooling. This can be achieved by having a proper ventilation system around the grinding equipment. For example, in a hammer mill, fans can be installed to blow cool air over the grinding chamber to dissipate the heat generated during the grinding process.
- Liquid - Cooling: In some cases, liquid - cooling may be necessary, especially for more intensive grinding operations. A coolant can be circulated around the grinding equipment to maintain a low temperature. However, this requires more complex equipment and careful handling to prevent any contact between the coolant and the quercetin.
4. Quality Control
4.1. Particle Size Analysis
After grinding, it is essential to analyze the particle size of the quercetin powder. This helps to ensure that the grinding process has been successful and that the product meets the required specifications.
- Laser Diffraction: Laser diffraction is a commonly used method for particle size analysis. It measures the scattering of light by the particles in the powder. This method can provide accurate and detailed information about the particle size distribution, allowing for precise control over the grinding process.
- Sieving Analysis: Sieving analysis is a more traditional method. It involves passing the quercetin powder through a series of sieves with different mesh sizes. The amount of powder retained on each sieve can be measured, and from this, the particle size distribution can be determined. Although it is less precise than laser diffraction, it is a relatively simple and inexpensive method, especially suitable for small - scale operations.
4.2. Purity and Contamination Checks
Ensuring the purity of the quercetin powder is crucial for its various applications.
- Spectroscopic Methods: Spectroscopic techniques such as infrared spectroscopy (IR) and ultraviolet - visible spectroscopy (UV - Vis) can be used to check the purity of quercetin. These methods can detect any impurities or contaminants that may have been introduced during the grinding process. For example, IR spectroscopy can identify the presence of foreign organic compounds based on the characteristic absorption bands in the infrared region.
- Chemical Analysis: Chemical analysis methods like high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) can be used to determine the exact composition of the quercetin powder. HPLC can separate and quantify the quercetin and any potential impurities, providing a detailed analysis of the product's purity.
4.3. Stability Testing
Since quercetin may be affected by the grinding process in terms of its stability, stability testing is necessary.
- Storage Stability: The ground quercetin powder should be stored under different conditions (such as different temperatures and humidities) to assess its long - term stability. Samples can be taken at regular intervals and analyzed for any changes in the chemical composition or physical properties. For example, if stored at high temperatures and high humidities, quercetin may degrade more rapidly, which can be detected through spectroscopic or chemical analysis methods.
- Process - Induced Stability Changes: Stability changes induced during the grinding process can also be investigated. This can be done by comparing the stability of the quercetin before and after grinding under the same storage conditions. If the grinding process has a negative impact on the stability, appropriate measures such as adjusting the grinding parameters or adding stabilizers may be required.

5. Conclusion
In conclusion, the grinding process of quercetin is a complex but crucial step for its optimal use in various applications. By carefully selecting the appropriate equipment, applying the correct grinding techniques, and implementing strict quality control measures, high - quality quercetin powder can be obtained. This not only ensures the effectiveness of quercetin in its intended applications but also guarantees the safety and consistency of the final product. As the demand for quercetin - based products continues to grow in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food industries, a proper understanding of the grinding process will become even more important.
FAQ:
What are the important factors to consider when selecting equipment for quercetin grinding?
When choosing equipment for quercetin grinding, several factors are crucial. Firstly, the precision of the grinding is essential as quercetin may need to be ground to a specific particle size for different applications. Secondly, the material of the equipment should be non - reactive with quercetin to avoid any chemical contamination. For example, stainless steel is often a good choice. Additionally, the capacity of the equipment should match the required production scale. If only small - scale grinding is needed, a small - capacity grinder may be sufficient, but for large - scale production, a more powerful and high - capacity grinder is required.
What are the common grinding techniques for quercetin?
There are several common grinding techniques for quercetin. One is mechanical grinding, which uses devices like ball mills or mortar and pestle. Ball mills are effective for achieving a relatively uniform particle size. Mortar and pestle can be used for small - scale or more precise grinding, especially when a finer texture is desired. Another technique is cryogenic grinding. This involves cooling quercetin to a very low temperature before grinding. It can be beneficial as it makes the material more brittle and easier to grind, especially for quercetin which may be difficult to grind under normal conditions.
How can we ensure the quality during the quercetin grinding process?
To ensure quality during the quercetin grinding process, regular sampling and analysis are necessary. The particle size distribution should be monitored to ensure it meets the required specifications. Contamination control is also vital. This includes preventing the introduction of foreign particles during grinding, such as dust or debris from the grinding equipment. The grinding environment should be clean and well - maintained. Additionally, the temperature and humidity during grinding may affect the quality of quercetin, so these parameters need to be controlled within an appropriate range.
What are the applications of well - ground quercetin?
Well - ground quercetin has various applications. In the pharmaceutical industry, it can be used in the formulation of drugs due to its antioxidant and anti - inflammatory properties. In the food and beverage industry, it can be added as a dietary supplement. For example, it may be incorporated into functional foods or drinks. In the cosmetic industry, quercetin can be used in skincare products as it may help protect the skin from oxidative damage.
Are there any safety precautions to take during quercetin grinding?
Yes, there are safety precautions during quercetin grinding. Since quercetin may be in powder form during grinding, proper ventilation is required to prevent inhalation of the powder, which could potentially cause respiratory irritation. Workers should wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as masks and gloves. Also, the grinding equipment should be operated according to the manufacturer's instructions to avoid any mechanical hazards.
Related literature
- Quercetin: Chemistry, Dietary Sources, Bioavailability, and Health Benefits"
- "Optimization of Quercetin Extraction and Its Application in the Food Industry"
- "The Role of Quercetin in Pharmaceutical Research: A Review"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Apricot Powder
2024-12-17
-
Giant Knotweed Extract
2024-12-17
-
Purple Sweet Potato Extract
2024-12-17
-
Chaste Berry Extract
2024-12-17
-
Kupilu Extract
2024-12-17
-
Dan Shen Root Extract/Salvia Root Extract
2024-12-17
-
Motherwort Extract
2024-12-17
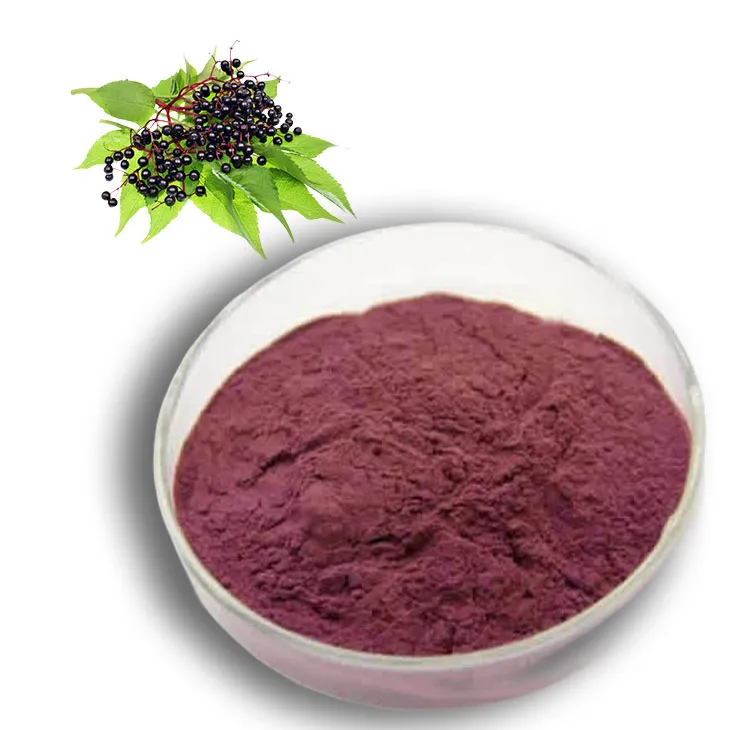
-
Elderberry Extract
2024-12-17
-
Red Vine Extract
2024-12-17
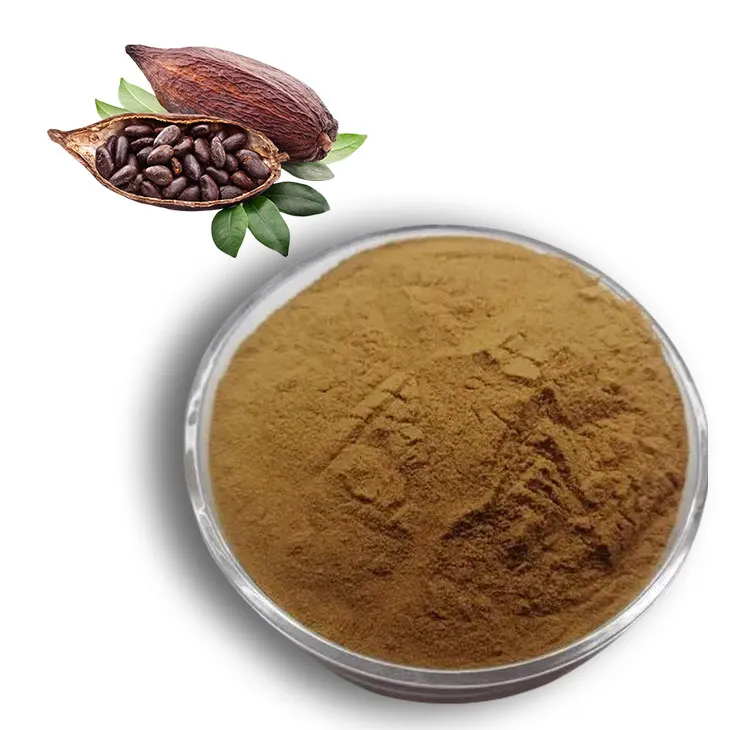
-
Cocoa Extract
2024-12-17





















