- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
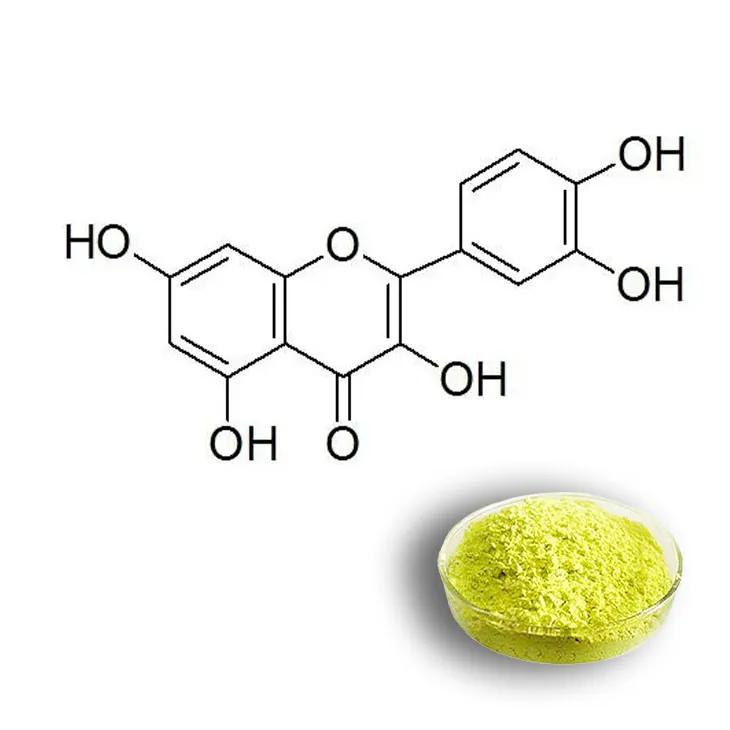
All about Quercetin.
2024-12-31

1. Introduction to Quercetin
Quercetin is a remarkable natural flavonol that is widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom. It can be found in a diverse range of plants, including but not limited to onions, apples, berries, and tea. This ubiquity in the plant world makes it relatively accessible in our diet, either through consuming these plant - based foods directly or in some cases, through dietary supplements.

2. The Antioxidant Power of Quercetin
One of the most significant aspects of quercetin is its role as a powerful antioxidant. Antioxidants are substances that are crucial for maintaining our health as they neutralize free radicals.
What are Free Radicals?
Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that are produced in our bodies as a by - product of normal metabolic processes. However, they can also be generated due to external factors such as exposure to pollution, radiation, and certain chemicals. These free radicals have unpaired electrons, which makes them unstable and highly reactive. As a result, they can cause damage to our cells, proteins, and DNA.
How Quercetin Combats Free Radicals
Quercetin is able to donate electrons to these free radicals, thereby stabilizing them and preventing them from causing further damage. By neutralizing free radicals, quercetin helps to protect our cells from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress has been linked to a variety of health problems, including aging and numerous diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.

3. Quercetin's Anti - Viral Properties
Quercetin has also been the subject of extensive research regarding its anti - viral potential. Scientists have found that it may interfere with the replication of certain viruses.
Mechanisms of Action Against Viruses
- One proposed mechanism is that quercetin can inhibit the enzymes that viruses need for their replication process. For example, some viruses require specific proteases to cleave their proteins during replication, and quercetin may be able to bind to and inhibit these proteases.
- It may also enhance the body's immune response against viruses. By modulating the immune system, quercetin can help the body better recognize and eliminate virus - infected cells.
Examples of Viruses Affected
Studies have suggested that quercetin may have an impact on viruses such as influenza viruses. While more research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness and potential applications in antiviral therapy, the initial findings are promising.
4. Role in Diabetes Management
Quercetin shows great promise in the area of diabetes management as well. It may play a role in helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
How it Affects Blood Sugar
- Quercetin may improve insulin sensitivity. Insulin is a hormone that is essential for regulating blood sugar levels. In individuals with diabetes, the body may become resistant to insulin, meaning that cells do not respond properly to the insulin signal. Quercetin may help to enhance the cells' ability to respond to insulin, thereby improving blood sugar control.
- It may also affect the absorption and metabolism of carbohydrates. By influencing the enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion and metabolism, quercetin can potentially slow down the release of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels.
Research Findings in Diabetes
Several studies have been conducted on the relationship between quercetin and diabetes. In animal models, quercetin supplementation has been shown to have beneficial effects on blood sugar levels. While human studies are still in progress, the results so far suggest that quercetin could be a valuable addition to diabetes management strategies.

5. Quercetin in the Cosmetic Industry
Quercetin is increasingly being explored in the cosmetic industry for its skin - protecting and anti - aging properties.
Protecting Skin Cells from Environmental Damage
Our skin is constantly exposed to environmental factors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pollution, and chemicals. These factors can cause damage to skin cells, leading to premature aging, wrinkles, and skin disorders. Quercetin has the ability to protect skin cells from such environmental damage. It can act as a shield against UV radiation, reducing the formation of free radicals in the skin that are caused by UV exposure. Additionally, it can help to detoxify the skin by neutralizing harmful pollutants and chemicals that may come into contact with the skin.
Anti - Aging Effects on the Skin
- Quercetin can stimulate the production of collagen in the skin. Collagen is a protein that provides structural support to the skin, keeping it firm and elastic. As we age, collagen production naturally declines, leading to the appearance of wrinkles and sagging skin. By promoting collagen production, quercetin can help to maintain the skin's youthful appearance.
- It also has anti - inflammatory properties. Inflammation in the skin can contribute to the aging process. Quercetin can reduce skin inflammation, thereby slowing down the signs of aging.
6. Sources of Quercetin
As mentioned earlier, quercetin is found in a variety of plants. Here are some of the main sources:
Fruits
- Apples are a good source of quercetin, especially in the skin. The peel of an apple contains a relatively high concentration of this flavonol.
- Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries also contain quercetin. These colorful fruits are not only delicious but also rich in antioxidants, including quercetin.
Vegetables
- Onions are one of the richest sources of quercetin. The outer layers of onions tend to have a higher concentration of this compound. Different types of onions, such as red onions, may contain even more quercetin compared to white onions.
- Leafy greens like kale and spinach also contain quercetin, albeit in smaller amounts. These vegetables are already known for their high nutritional value, and the presence of quercetin adds to their health - promoting properties.
Other Sources
- Tea, especially green tea, contains quercetin. Green tea is renowned for its numerous health benefits, and quercetin is one of the components that contribute to its antioxidant and health - promoting effects.
- Citrus fruits, while not as high in quercetin as some of the other sources mentioned above, still contain a certain amount of this flavonol. The peel of citrus fruits may have a relatively higher concentration of quercetin.
7. Supplementation and Considerations
Quercetin is available as a dietary supplement for those who may not be able to obtain sufficient amounts from their diet alone. However, there are several important considerations when it comes to quercetin supplementation.
Recommended Dosage
The appropriate dosage of quercetin can vary depending on factors such as age, health status, and the specific purpose of supplementation. In general, research studies have used dosages ranging from 500mg to 1000mg per day. However, it is always best to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the appropriate dosage for an individual.
Potential Side Effects
- Some people may experience mild side effects such as stomach upset, nausea, or headaches when taking quercetin supplements. These side effects are usually relatively mild and may subside over time.
- There is also a concern about potential interactions with medications. Quercetin may interact with certain drugs, such as blood - thinning medications or some antibiotics. It is crucial to inform your doctor if you are taking any medications before starting quercetin supplementation.
8. Future Research Directions
While much has been discovered about quercetin, there are still many areas that require further research.
Clinical Trials in Humans
Most of the current research on quercetin has been conducted in laboratory settings or in animal models. There is a need for more comprehensive clinical trials in humans to fully understand its effectiveness in treating various diseases, its long - term safety, and the optimal dosage for different applications.
Combination Therapies
Exploring the potential of quercetin in combination with other drugs or natural compounds could be an interesting area of research. For example, combining quercetin with other antioxidants or antiviral agents may enhance its therapeutic effects. Additionally, studying how quercetin interacts with different medications in combination therapies could help to optimize treatment strategies.
FAQ:
What is quercetin?
Quercetin is a natural flavonol that is widely distributed in various plants.
What are the health benefits of quercetin?
Quercetin has multiple health benefits. It is a powerful antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals related to aging and diseases. It also has potential anti - viral effects as it may interfere with virus replication, and shows promise in diabetes management by helping regulate blood sugar levels. In addition, it has skin - protecting and anti - aging properties in the cosmetic industry as it can protect skin cells from environmental damage.
How does quercetin act as an antioxidant?
Quercetin acts as an antioxidant by neutralizing free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells, and quercetin can react with them to make them stable, thus reducing the risk of aging and various diseases associated with free radical damage.
What viruses may quercetin interfere with?
Research has been done on quercetin's anti - viral potential, but specific viruses that it may interfere with are still being explored in more detail. However, it has shown the ability to potentially disrupt the replication processes of some viruses.
How can quercetin help in diabetes management?
Quercetin may help in diabetes management by playing a role in regulating blood sugar levels. It might influence the body's mechanisms related to glucose metabolism, although the exact pathways are still under study.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Promising Natural Compound for Health"
- "The Role of Quercetin in Antioxidant Defense and Disease Prevention"
- "Quercetin and Its Potential in Skin Health"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Giant Knotweed Extract
2024-12-31
-
Cocoa Extract
2024-12-31
-
Yellow Pine Extract
2024-12-31
-
Red Vine Extract
2024-12-31
-
Rosemary extract
2024-12-31
-
Lycopene
2024-12-31
-
Shikone Extract
2024-12-31
-
Epimedium extract powder
2024-12-31
-
Hesperidin
2024-12-31
-
Plantain extract
2024-12-31





















