- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Best Answers to 7 Key Questions about Astaxanthin.
2024-12-16

1. What is Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is a red - colored pigment that belongs to the carotenoid family. It is a powerful antioxidant that is naturally produced by certain microorganisms, such as microalgae, and can also be found in some seafood, like salmon, shrimp, and krill. Its chemical structure gives it unique properties that make it highly effective in protecting cells from oxidative stress.
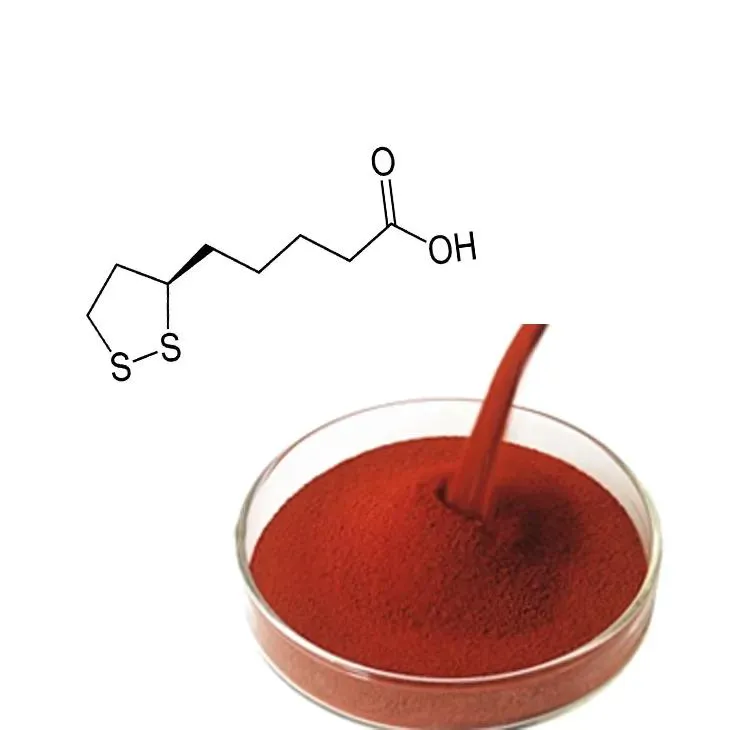
2. Where does Astaxanthin come from?
There are two main sources of astaxanthin:
- Natural Sources
- Microalgae, such as Haematococcus pluvialis, are the primary natural producers of astaxanthin. These microalgae produce astaxanthin as a protective mechanism against environmental stressors like excessive sunlight and nutrient depletion.
- As mentioned earlier, some marine animals also contain astaxanthin. They obtain it through their diet, which includes consuming microalgae that produce the pigment. For example, salmon get their characteristic pink color from astaxanthin in their diet.
- Synthetic Sources
- Chemically synthesized astaxanthin is also available on the market. However, there are some concerns regarding its purity and potential differences in biological activity compared to natural astaxanthin.

3. What are the health benefits of Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin offers a wide range of health benefits:
- Antioxidant Activity
- It is one of the most powerful antioxidants known. Astaxanthin can neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to various diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- By protecting cells from oxidative damage, it helps to maintain the integrity of cell membranes, DNA, and other cellular components.
- Skin Health
- Has been shown to improve skin elasticity and moisture. It can protect the skin from UV - induced damage, reducing the risk of sunburn, wrinkles, and skin aging.
- Some studies suggest that astaxanthin may also help in treating skin conditions such as acne and rosacea.
- Eye Health
- May protect the eyes from age - related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts. It accumulates in the retina, where it can act as a natural sunscreen, protecting the eye from harmful light.
- Can also improve visual acuity and reduce eye fatigue.
- Cardiovascular Health
- Helps to reduce inflammation in the blood vessels, which is a key factor in the development of heart disease. It can also lower blood lipid levels, such as triglycerides and LDL cholesterol.
- May improve endothelial function, which is important for maintaining normal blood flow and blood pressure.
- Muscle Endurance and Recovery
- Some athletes use astaxanthin to enhance their muscle endurance during exercise. It can reduce muscle fatigue and soreness, allowing for faster recovery after workouts.
- Immune System Support
- Boosts the immune system by enhancing the function of immune cells. It can help the body fight off infections and diseases more effectively.
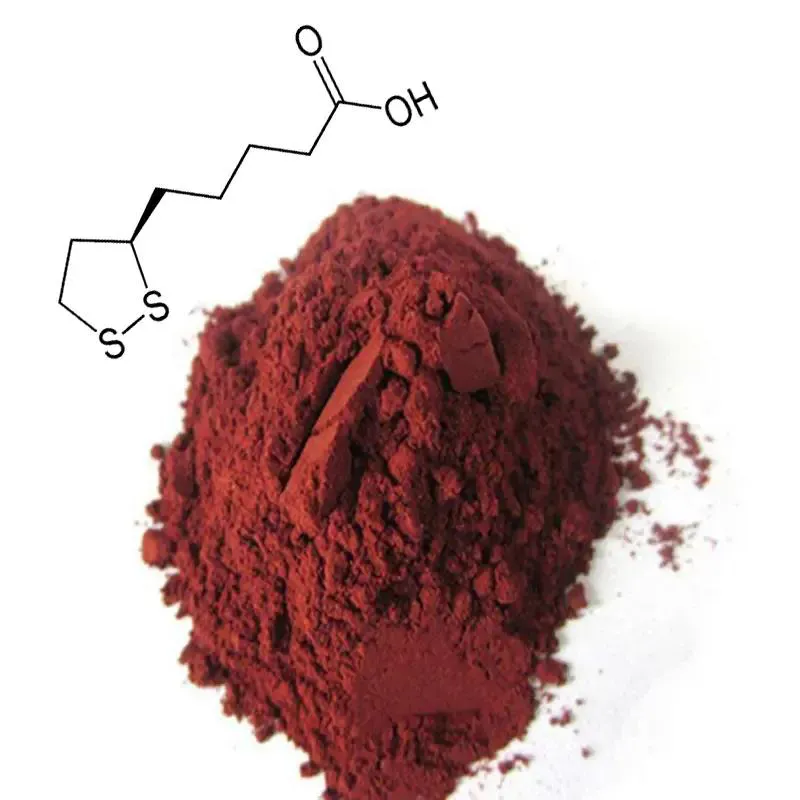
4. How does Astaxanthin work in the body?
Once ingested, astaxanthin is absorbed in the small intestine. It is then transported in the bloodstream to various tissues and organs throughout the body.
- At the cellular level, astaxanthin inserts itself into cell membranes. This unique property allows it to protect the cell membrane from oxidative damage. It can also interact with other antioxidants in the body, such as vitamins C and E, to enhance their antioxidant activity.
- In the case of skin health, for example, astaxanthin can penetrate the skin layers and protect skin cells from both internal and external sources of oxidative stress. In the eyes, it accumulates in the retina and lens, where it provides protection against light - induced damage.
- For muscle endurance, it may work by reducing oxidative stress in muscle cells during exercise, thereby delaying the onset of fatigue. In the immune system, it can stimulate the production and activity of immune cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes.
5. What is the proper dosage of Astaxanthin?
The proper dosage of astaxanthin can vary depending on several factors:
- General Health Maintenance
- For general health benefits, a dosage of 2 - 4 mg per day is often recommended. This amount can help to provide antioxidant protection and support overall health.
- Specific Health Conditions
- For skin health, some studies suggest a dosage of 4 - 6 mg per day. In cases of eye health or cardiovascular health, a dosage of 6 - 12 mg per day may be more appropriate, although more research is needed to determine the exact optimal dosages for these conditions.
- For athletes looking to improve muscle endurance and recovery, dosages of 8 - 12 mg per day have been used in some studies, but individual responses may vary.
- Safety Considerations
- While astaxanthin is generally considered safe, high - dose supplementation should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Excessive intake may potentially cause side effects, although these are rare.
6. Are there any side effects of Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is generally well - tolerated, but in some cases, there may be potential side effects:
- Digestive Issues
- Some people may experience mild digestive problems such as stomach upset, diarrhea, or nausea. However, these side effects are not very common and usually occur at higher dosages.
- Skin Reactions
- In rare cases, there may be skin reactions such as itching or a rash. If this occurs, it is advisable to stop taking astaxanthin and consult a doctor.
- Interactions with Medications
- There is a possibility of interactions with certain medications. For example, it may enhance the blood - thinning effects of anticoagulant medications. Therefore, it is important to inform your healthcare provider if you are taking astaxanthin, especially if you are on other medications.
7. How can one choose a high - quality Astaxanthin supplement?
When choosing an astaxanthin supplement, consider the following factors:
- Source of Astaxanthin
- Opt for supplements that are derived from natural sources, such as microalgae - based astaxanthin. Natural astaxanthin is often considered to be of higher quality and more bioavailable than synthetic versions.
- Form of the Supplement
- There are different forms of astaxanthin supplements, including softgels, capsules, and powders. Softgels are a popular choice as they can protect the astaxanthin from degradation and ensure better absorption.
- Brand Reputation
- Choose a well - known and reputable brand. Look for brands that have a good track record in terms of product quality, safety, and customer satisfaction. You can check online reviews and ratings to get an idea of the brand's reputation.
- Third - Party Testing
- Supplements that have been third - party tested for purity, potency, and quality are generally more reliable. Look for products that display seals or logos from independent testing organizations, such as USP (United States Pharmacopeia) or NSF (National Sanitation Foundation).
FAQ:
Question 1: What is the main source of astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is mainly sourced from two primary sources. One is microalgae, specifically Haematococcus pluvialis, which is a very rich natural source of astaxanthin. The other source is some marine organisms like salmon, shrimp, and krill. These organisms accumulate astaxanthin through their diet which contains the microalgae that produce it.
Question 2: What are the major health benefits of astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin offers several health benefits. It is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. This may potentially reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain cancers. It also has anti - inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for those with inflammatory conditions like arthritis. Additionally, it may improve skin health by reducing wrinkles, protecting against UV damage, and enhancing skin elasticity.
Question 3: How much astaxanthin should one take daily?
The proper dosage of astaxanthin can vary depending on various factors such as individual health goals and overall health status. However, in general, for general health maintenance, a dosage of around 4 - 12 mg per day is often recommended. For specific health conditions or for those seeking more pronounced benefits, higher dosages may be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Question 4: Is astaxanthin safe for everyone?
Astaxanthin is generally considered safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as stomach upset or changes in skin color (a slightly orange tint in the skin, which is rare). Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before taking astaxanthin supplements, as there is limited research on its safety during these periods.
Question 5: Can astaxanthin interact with medications?
There is currently limited evidence of significant interactions between astaxanthin and medications. However, as with any supplement, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider if you are taking medications, especially blood - thinning medications or medications for diabetes, as astaxanthin may potentially have an impact on blood sugar levels or blood clotting in some cases.
Question 6: How does astaxanthin compare to other antioxidants?
Astaxanthin is considered one of the most powerful antioxidants. Compared to other common antioxidants like vitamin C and E, it has a unique molecular structure that allows it to more effectively scavenge free radicals. It can cross cell membranes and the blood - brain barrier more easily, providing broader protection to cells and tissues throughout the body. Its antioxidant capacity is much higher than that of many other antioxidants on a per - molecule basis.
Question 7: How long does it take to see the effects of astaxanthin?
The time it takes to see the effects of astaxanthin can vary from person to person. For some, improvements in skin health such as reduced redness or a more even skin tone may be noticed within a few weeks of starting supplementation. However, for more systemic benefits like reduced inflammation or improved cardiovascular health, it may take several months of consistent use to observe significant changes.
Related literature
- The Role of Astaxanthin in Health and Disease"
- "Astaxanthin: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits"
- "Astaxanthin Sources and Their Impact on Human Health"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Kupilu Extract
2024-12-16
-
Acerola Juice Powder
2024-12-16
-
Chasteberry Extract
2024-12-16
-
Eucommia Ulmoides Extract
2024-12-16
-
Okra Extract
2024-12-16
-
Beta Carotene
2024-12-16
-
Honeysuckle Pollen
2024-12-16
-
Passionflower Extract
2024-12-16
-
Sophora Flavescens Root Extract
2024-12-16
-
Polygonum Cuspidatum Extract
2024-12-16





















