- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Five Reasons for Using Quercetin in the Food Industry.
2024-12-31

1. Antioxidant Properties
Quercetin is highly regarded in the food industry for its antioxidant capabilities. Antioxidants play a crucial role in food by preventing oxidation. Oxidation is a chemical process that can lead to the spoilage of food. When food oxidizes, it can develop off - flavors, change in color, and lose its nutritional value. For example, fats in food can become rancid due to oxidation, which not only affects the taste but also poses a potential health risk if consumed.
Quercetin, as an antioxidant, acts as a scavenger of free radicals. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that are formed during normal metabolic processes in the body as well as during food processing and storage. These free radicals can initiate a chain reaction of oxidation in food. By reacting with free radicals, Quercetin halts this chain reaction, thereby slowing down the spoilage process. This property is especially valuable for foods that have a relatively long shelf - life, such as canned goods, dried fruits, and certain processed snacks.
In addition, in fresh produce, quercetin can help maintain the freshness and quality. Fruits and vegetables contain various nutrients and bioactive compounds that are sensitive to oxidation. The presence of quercetin can protect these valuable components, ensuring that consumers receive products with higher nutritional content and better sensory qualities. For instance, apples are known to contain quercetin, and this compound contributes to the preservation of the apple's color, flavor, and overall quality during storage.

2. Anti - Inflammatory Feature
Another significant reason for using quercetin in the food industry is its anti - inflammatory feature. Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can be associated with various health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
When incorporated into food products, quercetin can potentially reduce inflammation in the body. This is of great interest to consumers who are increasingly conscious of their health. Foods fortified with quercetin can be marketed as having health - promoting properties. For example, in the development of functional foods, such as yogurts or energy bars, the addition of quercetin can make these products more appealing to health - conscious consumers.
Moreover, anti - inflammatory foods are often recommended as part of a balanced diet. By using quercetin in food production, the food industry can contribute to the availability of a wider range of anti - inflammatory food options. This can have a positive impact on public health, as it encourages consumers to choose foods that may help prevent or manage chronic diseases.

3. Flavor Enhancement
Quercetin can also be used to enhance the flavor of various foods. It has a unique taste profile that can add depth and complexity to food products. In some cases, it can bring out the natural flavors of ingredients.
For example, in the brewing industry, quercetin - rich ingredients can contribute to the flavor of beer. It can enhance the bitterness, which is an important characteristic of many beer styles. Similarly, in the production of wine, quercetin - containing grape skins can influence the flavor profile. The presence of quercetin can add fruity, floral, or spicy notes to the wine, depending on the variety of grapes and the winemaking process.
In the realm of baked goods, quercetin can play a role in flavor development. It can interact with other ingredients such as sugars, fats, and starches during baking, resulting in a more appealing taste. This is especially important for products where flavor is a key selling point, such as artisanal breads, pastries, and cookies.
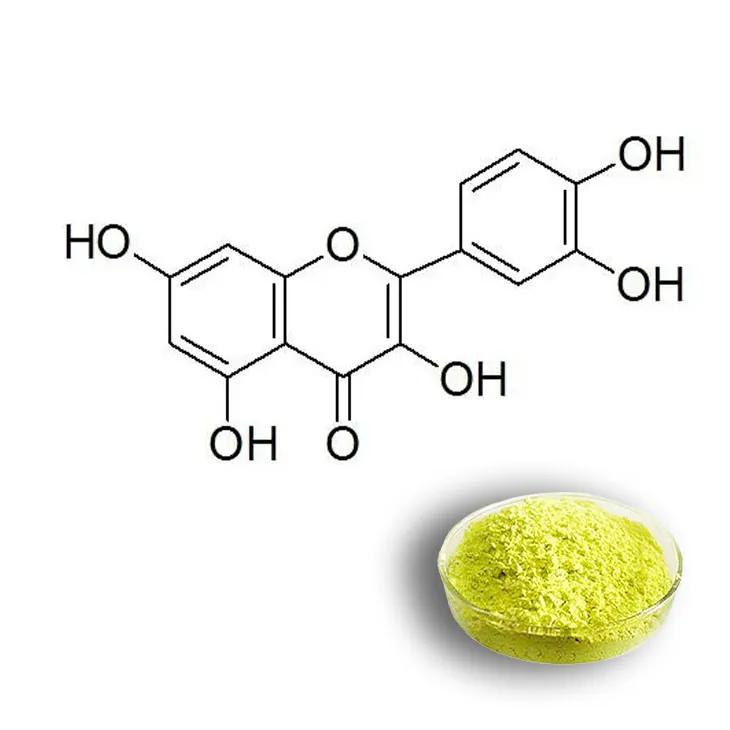
4. Food Fortification
Food fortification is an important aspect of the modern food industry, and quercetin is a good choice for this purpose. Fortification involves adding nutrients or bioactive compounds to food to improve its nutritional value.
Quercetin is a bioactive compound with potential health benefits. By adding it to staple foods such as cereals, breads, or dairy products, the food industry can enhance the nutritional profile of these products. For example, adding quercetin to breakfast cereals can provide an additional source of antioxidants and anti - inflammatory compounds, making the product more nutritious.
This is particularly relevant in the context of addressing nutritional deficiencies in the population. Some people may not consume enough fruits and vegetables, which are natural sources of quercetin. By fortifying commonly consumed foods with quercetin, it becomes easier for consumers to obtain the benefits of this compound without having to significantly change their diet.

5. Food Preservation
The impact of quercetin on food preservation is yet another reason for its use in the food industry. Ensuring food safety and extending the shelf - life of food products are major concerns for food manufacturers.
Quercetin can inhibit the growth of certain microorganisms. Microbial growth in food can lead to spoilage, foodborne illness, and economic losses. By preventing the growth of bacteria, yeasts, or molds, quercetin helps to keep food safe and fresh for a longer period. In the case of refrigerated or packaged foods, the addition of quercetin can act as an additional layer of protection against microbial contamination.
For example, in the preservation of meat products, quercetin can be used in combination with other preservatives to slow down the growth of spoilage - causing bacteria. This not only helps to maintain the quality of the meat but also reduces the risk of foodborne diseases associated with meat consumption.
FAQ:
Question 1: How does quercetin prevent food from going bad quickly?
Quercetin is an antioxidant. Antioxidants work by neutralizing free radicals in food. Free radicals can cause oxidative reactions that lead to spoilage, such as rancidity in fats and browning in fruits and vegetables. By scavenging these free radicals, quercetin helps to slow down these oxidative processes and thus prevent food from going bad quickly.
Question 2: In what ways can the anti - inflammatory feature of quercetin be beneficial for food production?
The anti - inflammatory feature of quercetin can be beneficial in food production in multiple ways. For example, it can be added to products like functional foods or nutraceuticals. In these types of foods, the anti - inflammatory property can help consumers who may have chronic inflammatory conditions. Also, it can be used in the production of foods aimed at promoting overall health, as inflammation is related to many health problems. By including quercetin, food manufacturers can produce foods with added health benefits.
Question 3: Which types of foods can quercetin enhance the flavor of?
Quercetin can enhance the flavor of a variety of foods. It can be used in fruit - based products like jams and juices, where it may enhance the natural fruit flavors. In baked goods, it can potentially add a unique flavor note. It can also be beneficial in savory products such as certain types of sauces or seasonings, adding a depth of flavor that might not be present otherwise.
Question 4: How does quercetin make foods more nutritious in the context of food fortification?
When used for food fortification, quercetin adds its own nutritional value to foods. It contains properties that are beneficial for human health, such as antioxidant and anti - inflammatory capabilities. By adding quercetin to foods, manufacturers can increase the overall nutrient profile of the product. For example, in a cereal product, the addition of quercetin can provide an extra health - promoting component along with other vitamins and minerals already present.
Question 5: What specific mechanisms does quercetin use for food preservation?
Quercetin uses multiple mechanisms for food preservation. Besides its antioxidant function which reduces oxidative spoilage, it may also have antimicrobial properties. This means it can inhibit the growth of certain microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, and molds that can cause food to spoil. By preventing the growth of these spoilage - causing agents, quercetin helps to ensure food safety and prolong the shelf - life of food products.
Question 6: Are there any potential drawbacks or limitations to using quercetin in the food industry?
There can be some potential drawbacks or limitations. One aspect is cost. The extraction and purification of quercetin can be expensive, which may limit its widespread use in some food products. Also, there may be regulatory issues regarding the amount of quercetin that can be added to foods in different regions. Additionally, some people may be allergic or sensitive to quercetin, although this is relatively rare. These factors need to be considered when using quercetin in the food industry.
Related literature
- The Role of Quercetin in Food and Nutrition"
- "Quercetin: A Promising Ingredient in the Food Industry - A Review"
- "Antioxidant and Functional Properties of Quercetin in Food Systems"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Cassia Seed Extract
2024-12-31
-
Garcinia Cambogia Extract
2024-12-31
-
Alfalfa Meal
2024-12-31
-
Saponin Extract
2024-12-31
-
Motherwort Extract
2024-12-31
-
Astaxanthin
2024-12-31
-
melatonin extract
2024-12-31
-
Baicalin
2024-12-31
-
Passionflower Extract
2024-12-31
-
Marigold Extract
2024-12-31





















