- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Quercetin: An Antioxidant Champion from Natural Plants.
2024-12-14

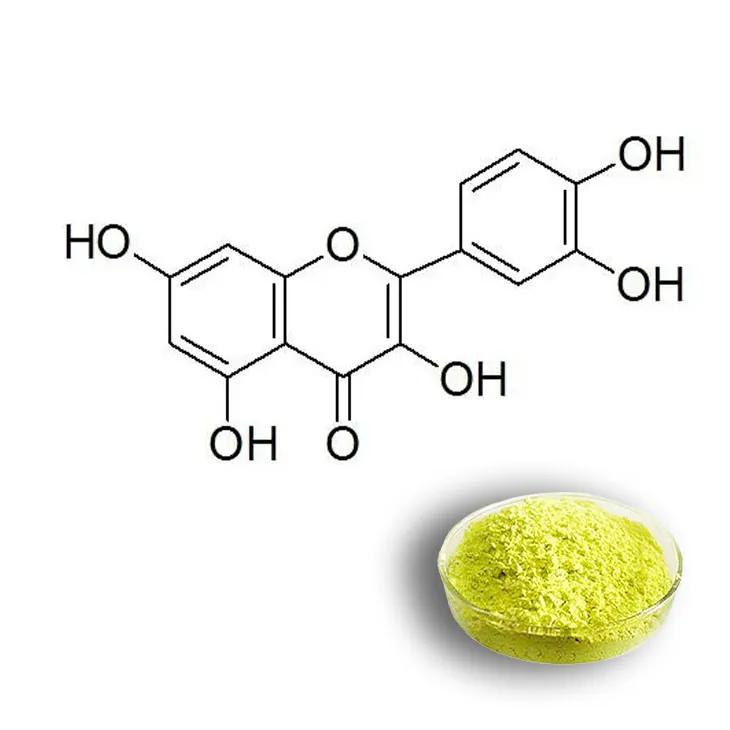
1. Introduction to Quercetin
Quercetin is a remarkable flavonoid that is widely distributed in the plant kingdom. It is a naturally occurring compound with a diverse range of biological activities. Flavonoids, in general, are known for their health - promoting properties, and Quercetin stands out as one of the most important representatives. This compound can be found in various parts of plants, including the leaves, fruits, and bark.
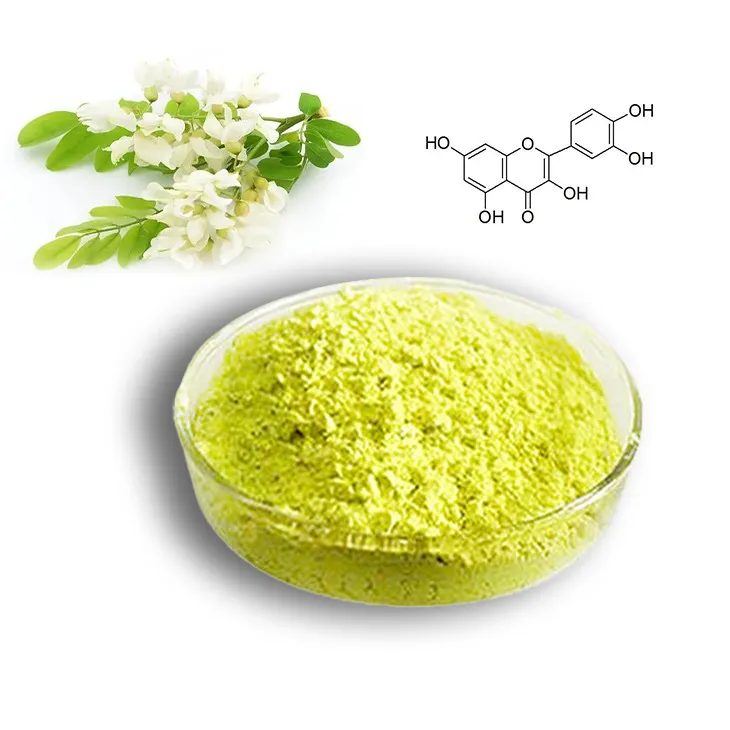

2. The Role of Antioxidants
Antioxidants play a crucial role in maintaining our health. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that are constantly formed in our bodies as a result of normal metabolic processes, as well as exposure to environmental factors such as pollution, radiation, and certain chemicals. These free radicals can cause damage to our cells, proteins, and DNA. If left unchecked, this damage can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Antioxidants, like quercetin, work by scavenging these free radicals. They donate an electron to the free radical, thereby neutralizing it and preventing it from causing further damage. This process is essential for protecting our cells and maintaining the overall health of our body.

3. Sources of Quercetin in Plants
3.1 Tea
Tea is one of the most popular sources of quercetin. Both green tea and black tea contain significant amounts of this flavonoid. Green tea, in particular, is known for its high antioxidant content. The quercetin in tea is thought to contribute to its many health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease and improving cognitive function.
3.2 Grapes
Grapes are another rich source of quercetin. This compound is found in the skins of grapes, which is why red wine, which is made from fermented grape skins, also contains quercetin. In addition to its antioxidant properties, the quercetin in grapes may also have anti - inflammatory effects, which could be beneficial for people with conditions such as arthritis.
3.3 Broccoli
Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable that is well - known for its health - promoting properties. It contains a variety of nutrients, including quercetin. The quercetin in broccoli is thought to play a role in its anti - carcinogenic effects. Studies have shown that consuming broccoli regularly may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast cancer and prostate cancer.
4. Health Benefits of Quercetin
4.1 Antioxidant Effects
As mentioned earlier, quercetin is a powerful antioxidant. It can neutralize a wide range of free radicals, including those that are particularly harmful to our cells. By reducing oxidative stress, quercetin may help to prevent the development of many chronic diseases. For example, it may protect against the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries, which can lead to heart disease.
4.2 Anti - inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can be a contributing factor to many diseases, such as diabetes, obesity, and autoimmune disorders. Quercetin has been shown to have anti - inflammatory properties. It can inhibit the production of certain inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and prostaglandins. This may help to reduce inflammation in the body and improve overall health.
4.3 Anti - carcinogenic Effects
Quercetin has also been studied for its potential anti - carcinogenic effects. It can interfere with the growth and spread of cancer cells in several ways. For example, it may induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, or it may inhibit the angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) that is necessary for tumor growth. While more research is needed, the evidence so far suggests that quercetin may be a promising compound for cancer prevention and treatment.

5. Absorption and Bioavailability of Quercetin
The absorption and bioavailability of quercetin in the human body are important factors to consider when evaluating its health benefits. Quercetin is not easily absorbed in its native form. However, it can be modified by the body's digestive enzymes, which can improve its absorption. Additionally, certain factors such as the presence of other nutrients in the diet can affect the bioavailability of quercetin. For example, consuming quercetin - rich foods with a source of fat may enhance its absorption.
6. Quercetin in Dietary Supplements
Due to its potential health benefits, quercetin is also available as a dietary supplement. These supplements can be a convenient way to increase your intake of quercetin, especially if you do not consume enough of the foods that are rich in this flavonoid. However, it is important to note that dietary supplements are not regulated in the same way as drugs, and the quality and purity of quercetin supplements can vary. It is advisable to choose a reputable brand and consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
7. Conclusion
Quercetin is a versatile and valuable compound that is abundantly found in natural plants. Its antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anti - carcinogenic properties make it a promising candidate for promoting health and preventing disease. By including quercetin - rich foods in our diet, such as tea, grapes, and broccoli, or by considering the use of a high - quality dietary supplement, we can take advantage of the many benefits that this flavonoid has to offer. However, more research is still needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action of quercetin and to determine the optimal dosage for different health conditions.
FAQ:
What is quercetin?
Quercetin is a flavonoid that is widely present in natural plants. It is known for its powerful antioxidant properties, which enable it to combat free radicals effectively.
Which plants contain quercetin?
Plants like tea, grapes, and broccoli contain quercetin. This makes it possible for people to obtain quercetin through their diet.
How does quercetin act as an antioxidant?
Quercetin can scavenge free radicals. Free radicals are related to many diseases and the aging process, and quercetin's ability to neutralize them is what makes it a strong antioxidant.
What are the health benefits of quercetin?
Quercetin may have antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anti - carcinogenic effects. These benefits contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Can quercetin prevent diseases?
While research has shown that quercetin has positive effects such as antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anti - carcinogenic ones, it cannot be simply said that it can prevent diseases. However, its properties may play a role in reducing the risk of certain diseases associated with free radicals, inflammation, and cancer development.
Related literature
- Quercetin and Its Role in Health: A Review"
- "Quercetin: A Promising Antioxidant from Plant Sources for Human Health"
- "The Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin in Natural and Processed Foods"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Eucommia Ulmoides Extract
2024-12-14
-
Citrus Aurantii Extract
2024-12-14
-
Clove Powder
2024-12-14
-
Jujube Extract
2024-12-14
-
Marigold Extract
2024-12-14
-
Tinospora cordifolia extract
2024-12-14
-
Kidney Bean Extract
2024-12-14
-
Resveratrol extract
2024-12-14
-
Curcuma Longa Extract/Turmeric extract
2024-12-14
-
Carrageenan Extract Powder
2024-12-14





















