- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Quercetin: Their production methods and the reasons for their popularity.
2024-12-17

1. Introduction
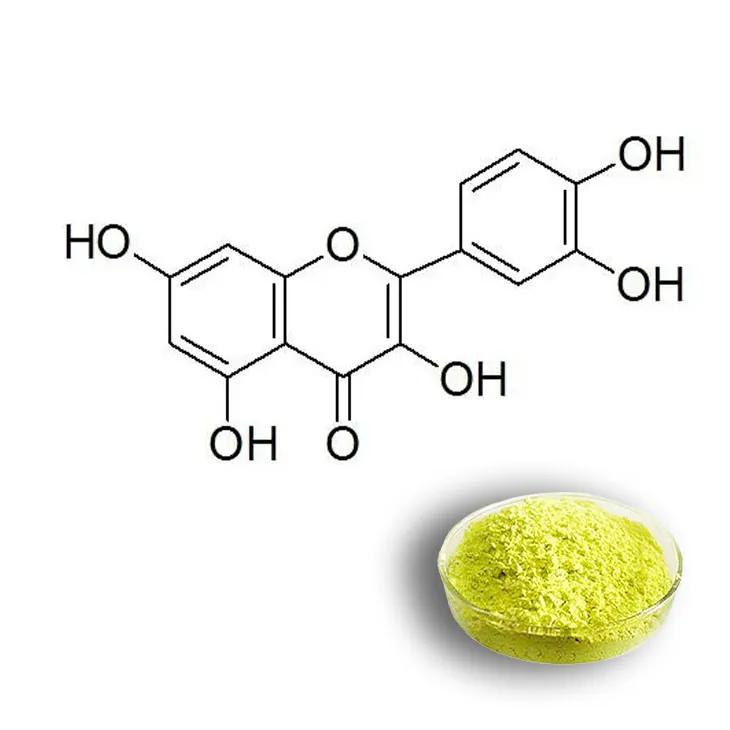
Quercetin is a flavonoid that has attracted a great deal of attention in recent years. Flavonoids are a large class of plant - derived compounds that are known for their various biological activities. Quercetin, in particular, stands out due to its unique properties and potential health benefits. This article will explore the production methods of Quercetin and the reasons behind its growing popularity.
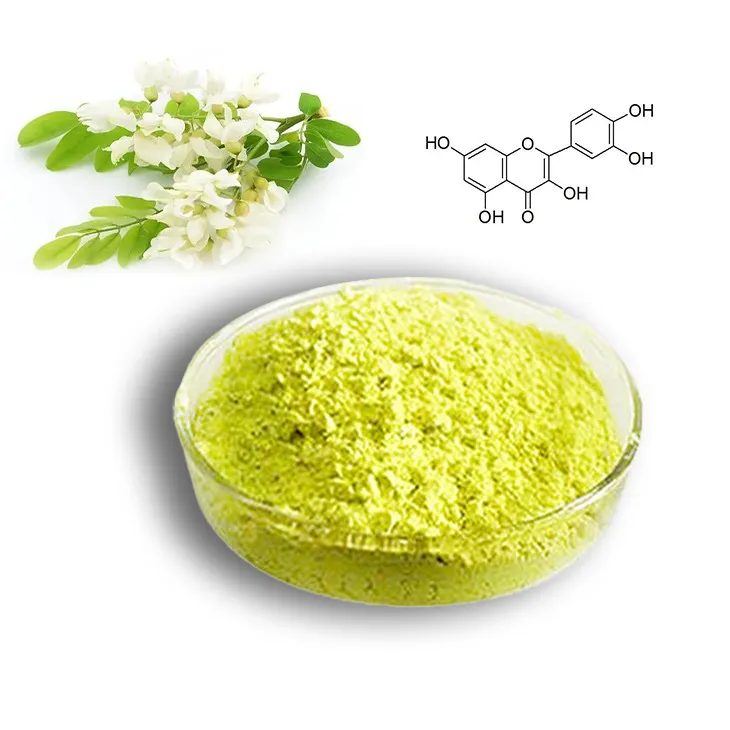

2. Production Methods of Quercetin
2.1 Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction is one of the most common methods for producing quercetin. This process involves using suitable solvents to isolate quercetin from plant materials. The choice of solvent is crucial as it can affect the efficiency and purity of the extraction.
- Typical solvents used for quercetin extraction include ethanol, methanol, and acetone. These solvents are able to dissolve the flavonoid compounds present in the plant tissues.
- The extraction process usually begins with the preparation of the plant material. The plants, which are rich sources of quercetin such as onions, apples, and buckwheat, are first dried and ground into a fine powder. This increases the surface area of the plant material, allowing for better solvent penetration.
- After that, the powdered plant material is mixed with the solvent in a suitable container. The mixture is then stirred or shaken for a certain period of time, usually several hours to days, depending on the nature of the plant material and the solvent used. This helps to ensure that the quercetin is fully dissolved in the solvent.
- Once the extraction is complete, the mixture is filtered to separate the liquid extract containing quercetin from the solid plant residue. The filtrate can then be further processed to purify the quercetin, for example, through evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain a concentrated quercetin extract.
2.2 Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Enzymatic hydrolysis is another method for quercetin production. This technique can enhance the yield of quercetin compared to traditional extraction methods.
- Enzymes are used to break down the complex structures in the plant material that may be binding the quercetin. For example, some plant polysaccharides or proteins may be associated with quercetin, and enzymes can specifically target these components and hydrolyze them.
- Commonly used enzymes in quercetin production include cellulases, hemicellulases, and pectinases. These enzymes are often derived from microorganisms such as fungi or bacteria.
- The process typically starts with the addition of the enzyme preparation to the plant material suspension. The reaction is carried out under specific conditions of temperature, pH, and reaction time. For instance, the optimal pH for cellulase activity may be around 4.5 - 5.5, and the temperature may be in the range of 40 - 50 °C. These conditions need to be carefully controlled to ensure the maximum activity of the enzymes.
- After enzymatic hydrolysis, the resulting mixture can be further processed using solvent extraction as described above to isolate and purify the quercetin.

3. Reasons for the Popularity of Quercetin
3.1 Antioxidant Properties
One of the main reasons for the popularity of quercetin is its antioxidant properties. Oxidative stress is a major factor in many diseases and the aging process.
- Quercetin is able to scavenge free radicals in the body. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can cause damage to cells, proteins, and DNA. By donating an electron to the free radicals, quercetin stabilizes them and prevents them from causing further harm.
- It can also enhance the activity of the body's endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a crucial role in the body's defense against oxidative stress by catalyzing the conversion of reactive oxygen species into less harmful products.
- Compared to other antioxidants, quercetin has a relatively high antioxidant capacity. This makes it a valuable compound in the prevention and treatment of oxidative - stress - related diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.
3.2 Anti - inflammatory Effects
Anti - inflammatory effects of quercetin also contribute to its popularity. Chronic inflammation is associated with a wide range of health problems.
- Quercetin can inhibit the production of pro - inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin - 1β (IL - 1β), interleukin - 6 (IL - 6), and tumor necrosis factor - α (TNF - α). These cytokines are key mediators in the inflammatory response and their overproduction can lead to excessive inflammation.
- It can also suppress the activation of nuclear factor - κB (NF - κB), a transcription factor that regulates the expression of many inflammatory genes. By inhibiting NF - κB activation, quercetin can down - regulate the expression of numerous pro - inflammatory proteins.
- In addition, quercetin has been shown to modulate the activity of immune cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes. It can promote the anti - inflammatory phenotype of macrophages and regulate the function of T - cells, which are important for maintaining immune homeostasis.
3.3 Role in Cardiovascular Health
Quercetin is also believed to play an important role in cardiovascular health.
- It can help to lower blood pressure. Quercetin may act on the smooth muscle cells of blood vessels, causing them to relax. This vasodilation effect can reduce the resistance in the blood vessels and thus lower blood pressure.
- Quercetin has been shown to improve lipid profiles. It can reduce the levels of low - density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL - C), also known as "bad" cholesterol, and increase the levels of high - density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL - C), or "good" cholesterol. This lipid - modulating effect can help to prevent the development of atherosclerosis, a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
- Furthermore, quercetin has anti - platelet aggregation properties. Platelets are cells in the blood that play a key role in blood clotting. Excessive platelet aggregation can lead to the formation of blood clots, which can block blood vessels and cause heart attacks or strokes. By inhibiting platelet aggregation, quercetin can reduce the risk of thrombosis.
3.4 Immune System Modulation
Another aspect of quercetin's popularity is its role in immune system modulation.
- As mentioned before, quercetin can regulate the function of immune cells. It can enhance the phagocytic activity of macrophages, which are responsible for engulfing and destroying foreign pathogens. This helps to improve the body's first line of defense against infections.
- Quercetin can also stimulate the production of antibodies by B - cells. Antibodies are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific antigens on the surface of pathogens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells.
- In addition, quercetin may have a role in modulating the balance between the different subsets of T - cells, such as helper T - cells and cytotoxic T - cells. This balance is crucial for a proper immune response, as an imbalance can lead to autoimmune diseases or immunodeficiency.
4. Conclusion
Quercetin, with its diverse production methods and numerous potential health benefits, has become a highly popular compound. The production methods, including solvent extraction and enzymatic hydrolysis, allow for the efficient isolation and purification of quercetin from natural sources. Its popularity is mainly due to its antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, cardiovascular - protective, and immune - modulating properties. As research continues to uncover more about quercetin, it is likely that its applications in the health and wellness industry will continue to expand.

FAQ:
1. What are the main natural sources for quercetin production?
Fruits, vegetables, and certain herbs are the main natural sources for quercetin production. These plant - based sources contain quercetin which can be extracted through different methods.
2. How does solvent extraction work in quercetin production?
In solvent extraction for quercetin production, suitable solvents are used. These solvents are capable of dissolving quercetin from the plant materials. By this process, quercetin can be separated from other components in the plant matter.
3. What is the advantage of enzymatic hydrolysis in quercetin production?
The advantage of enzymatic hydrolysis in quercetin production is that it can enhance the yield. Enzymes are used to break down certain components in the plant materials, which helps to release more quercetin and thus increase the amount that can be obtained.
4. Why is quercetin considered beneficial for cardiovascular health?
Research has suggested that quercetin may play a role in cardiovascular health. However, the exact mechanisms are still being studied. It may be related to its antioxidant and anti - inflammatory properties which can have positive impacts on the heart and blood vessels.
5. How does quercetin modulate the immune system?
Quercetin's role in immune system modulation is an area of ongoing research. It may interact with immune cells and signaling pathways in the body. Its antioxidant and anti - inflammatory effects are also thought to contribute to its influence on the immune system.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Promising Molecule for Health Benefits"
- "The Production and Bioactivity of Quercetin: A Review"
- "Quercetin in Natural Sources and Its Role in Human Health"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Wheat Germ Extract
2024-12-17
-
Plantain extract
2024-12-17
-
Resveratrol extract
2024-12-17
-
Withania Somnifera Extract
2024-12-17
-
Hesperidin
2024-12-17
-
Troxerutin
2024-12-17
-
Green Tea Extract
2024-12-17
-
Phyllanthus Emblica Extract
2024-12-17
-
Tormentil Extract
2024-12-17
-
Pomegranate Extract
2024-12-17





















