- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Quercetin: Uses, Advantages, and Manufacturing Processes
2024-11-13

1. Introduction
Quercetin is a flavonoid compound that has been the subject of increasing scientific research in recent years. Flavonoids are a diverse group of plant - based compounds known for their various biological activities. Quercetin stands out due to its potential health - promoting properties and its relatively widespread occurrence in nature.

2. Uses of Quercetin
2.1 Anti - cancer Potential
One of the most studied uses of quercetin is its anti - cancer potential. Cancer is a complex disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. Quercetin may interfere with the growth of cancer cells through multiple mechanisms.
- It can induce cell cycle arrest, preventing cancer cells from dividing and multiplying. For example, in some types of breast cancer cells, quercetin has been shown to block the cell cycle at specific phases, thereby inhibiting their growth.
- Quercetin also has the ability to promote apoptosis, which is the programmed cell death of cancer cells. This is crucial as many cancer cells develop mechanisms to avoid normal apoptosis, allowing them to survive and proliferate. Studies on prostate cancer cells have demonstrated that quercetin can activate certain apoptotic pathways within the cells.
- Furthermore, it may inhibit angiogenesis, the process by which new blood vessels are formed to supply nutrients and oxygen to tumors. By blocking angiogenesis, quercetin can starve tumors and limit their growth. In experiments with lung cancer models, quercetin has been observed to reduce the formation of new blood vessels around the tumors.
2.2 Anti - inflammatory Properties
Quercetin has significant anti - inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can be harmful and is associated with many diseases.
- In the case of arthritis, which is characterized by joint inflammation, quercetin can help reduce pain and swelling. It does this by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and prostaglandins. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis patients, quercetin supplementation may potentially decrease the levels of inflammatory markers in the blood.
- Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis can also benefit from quercetin. It can modulate the gut microbiota and reduce the inflammatory response in the intestinal mucosa. Research has shown that quercetin can increase the population of beneficial bacteria in the gut while decreasing the harmful ones, which in turn can help in reducing intestinal inflammation.
- Moreover, in skin inflammation, quercetin can protect the skin cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation. It can be used topically or taken orally to improve skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis.
2.3 Enhancing the Antioxidant Defense System
The body has its own antioxidant defense system to protect against free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can cause damage to cells and DNA. Quercetin can enhance this antioxidant defense system.
- Quercetin itself is a powerful antioxidant. It can directly scavenge free radicals, such as superoxide anions and hydroxyl radicals. By doing so, it helps prevent oxidative damage to cells, which is linked to various diseases including heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging.
- It also has the ability to regenerate other antioxidants in the body. For instance, it can recycle vitamin C and vitamin E, allowing them to continue their antioxidant functions. This synergy between quercetin and other antioxidants is important for maintaining the overall antioxidant balance in the body.

3. Advantages of Quercetin
3.1 Wide Availability in Nature
One of the main advantages of quercetin is its wide availability in nature. It is present in many common fruits and vegetables, which makes it relatively easy to obtain through diet.
- Apples are a rich source of quercetin. The skin of apples contains a significant amount of this flavonoid. Eating apples regularly can provide a natural source of quercetin, along with other beneficial nutrients such as fiber and vitamins.
- Onions are another common food item that contains quercetin. Red onions, in particular, have a relatively high concentration of this compound. Whether consumed raw in salads or cooked in various dishes, onions can contribute to the intake of quercetin.
- Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, also contain quercetin. These delicious fruits are not only rich in quercetin but also in other antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Incorporating berries into the diet can be an excellent way to boost the intake of quercetin and other health - promoting substances.
3.2 Multiple Health Benefits
As mentioned earlier, quercetin offers multiple health benefits. This multifaceted nature of quercetin is a significant advantage.
- Its anti - cancer, anti - inflammatory, and antioxidant properties all work together to promote overall health. For example, by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, it can potentially lower the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
- Quercetin may also have benefits for cardiovascular health. It can help improve blood vessel function by reducing inflammation and oxidative damage in the blood vessels. This can lead to better blood flow, lower blood pressure, and a reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- In addition, its potential role in modulating the immune system can help the body better defend against infections and diseases. By enhancing the antioxidant defense system and reducing chronic inflammation, it can support a healthy immune response.
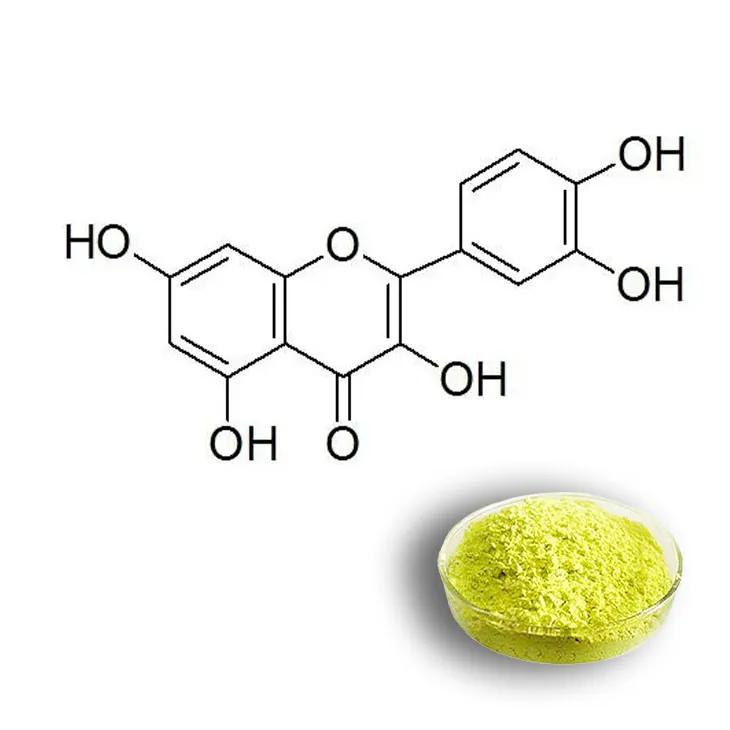
4. Manufacturing Processes of Quercetin
4.1 Selection of Plant Materials
The manufacturing process of quercetin typically begins with the selection of plant materials rich in this flavonoid.
- Botanical identification is crucial. The plants need to be accurately identified to ensure that they are indeed a good source of quercetin. For example, certain species of oak trees are known to contain quercetin in their bark, but proper identification is necessary to avoid using the wrong plant.
- Quality assessment of the plant materials is also important. Factors such as the age of the plant, the environmental conditions in which it was grown, and any potential contaminants need to be considered. Older plants may have a different quercetin content compared to younger ones, and plants grown in polluted environments may contain harmful substances that need to be removed during the manufacturing process.
4.2 Extraction Techniques
Once the appropriate plant materials are selected, extraction techniques are employed to obtain quercetin.
- Solvent extraction is a commonly used method. Organic solvents such as ethanol or methanol are often used. The plant material is soaked in the solvent, which helps to dissolve the quercetin and other compounds. For example, in the extraction of quercetin from onions, the chopped onions may be soaked in ethanol for a certain period to extract the quercetin.
- Supercritical fluid extraction is another technique. Supercritical carbon dioxide can be used as a solvent - like medium. It has the advantage of being a relatively clean and efficient method. In this process, carbon dioxide is brought to a supercritical state (where it has properties of both a liquid and a gas) and is passed through the plant material to extract quercetin. This method is often preferred for high - value applications as it can produce a purer extract.
- After extraction, purification steps are usually required. This may involve processes such as filtration, chromatography, or crystallization. Filtration can remove solid particles from the extract, while chromatography can separate quercetin from other compounds based on their chemical properties. Crystallization can be used to obtain quercetin in a pure crystalline form, which is suitable for use in various applications such as in the pharmaceutical or nutraceutical industries.

5. Conclusion
Quercetin is a flavonoid compound with significant potential in various aspects of health promotion. Its uses in anti - cancer, anti - inflammation, and enhancing the antioxidant defense system are well - studied. The advantages of its wide availability in nature and multiple health benefits make it an attractive compound for further research and potential applications. The manufacturing processes, starting from the selection of plant materials to extraction and purification, are crucial in obtaining high - quality quercetin for these applications. Continued research on quercetin is likely to uncover more of its potential benefits and lead to its wider use in the fields of medicine, nutrition, and health.
FAQ:
What are the potential anti - cancer mechanisms of quercetin?
Quercetin may interfere with the growth of cancer cells. It might act on various cellular pathways involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis (programmed cell death), and angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow). However, the exact mechanisms are still under extensive research.
Which plant materials are commonly used in the manufacturing process of quercetin?
Many plants can be used as sources for quercetin extraction. For example, onions, apples, berries, and tea leaves are rich in quercetin. These plant materials are selected based on their relatively high quercetin content.
How does quercetin enhance the body's antioxidant defense system?
Quercetin itself has antioxidant properties. It can scavenge free radicals in the body, which are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells. By neutralizing these free radicals, quercetin helps protect cells from oxidative stress and thus enhances the overall antioxidant defense system of the body.
Can quercetin be used as a sole treatment for arthritis?
While quercetin has anti - inflammatory properties that can be beneficial for arthritis, it is not typically used as a sole treatment. Arthritis is a complex condition, and current medical approaches often involve a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. However, quercetin may be used as a complementary therapy to help manage inflammation associated with arthritis.
What are the challenges in the manufacturing process of quercetin?
One challenge in the manufacturing process is the efficient extraction of quercetin from plant materials. Different extraction techniques need to be optimized to obtain a high yield of pure quercetin. Another challenge can be the purification process to remove other compounds present in the plant extract. Additionally, ensuring the stability of quercetin during processing and storage is also important.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Versatile Flavonoid with Potential Health Benefits"
- "The Role of Quercetin in Cancer Prevention and Treatment"
- "Manufacturing and Purification of Quercetin: Current Trends and Future Perspectives"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Organic Tongkat Ali extract powder factory.
2024-11-13
-
How to make powder with ashwagandha extract.
2024-11-13
-
Rosehip extract manufacturers from China.
2024-11-13
-
The best cat's claw extract in nature.
2024-11-13
-
Chinese Dandelion Leaf Extract Suppliers.
2024-11-13
-
Oat Straw Extract Powder
2024-11-13
-
Beetroot juice Powder
2024-11-13
-
Curcuma Longa Extract
2024-11-13
-
Peppermint Extract Powder
2024-11-13
-
Apricot Powder
2024-11-13
-
Rose Hip Extract
2024-11-13
-
Withania Somnifera Extract
2024-11-13
-
American Ginseng Root Extract
2024-11-13
-
Bamboo Leaf extract
2024-11-13
-
Wheat Germ Extract
2024-11-13





















