- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Extract quercetin by steam distillation.
2024-11-30

1. Introduction
Quercetin is a highly significant bioactive compound that has been the focus of numerous studies in recent years. It is a flavonoid with a wide range of potential health benefits, including antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anticancer properties. Steam distillation is one of the methods employed for its extraction, which offers several advantages over other techniques.
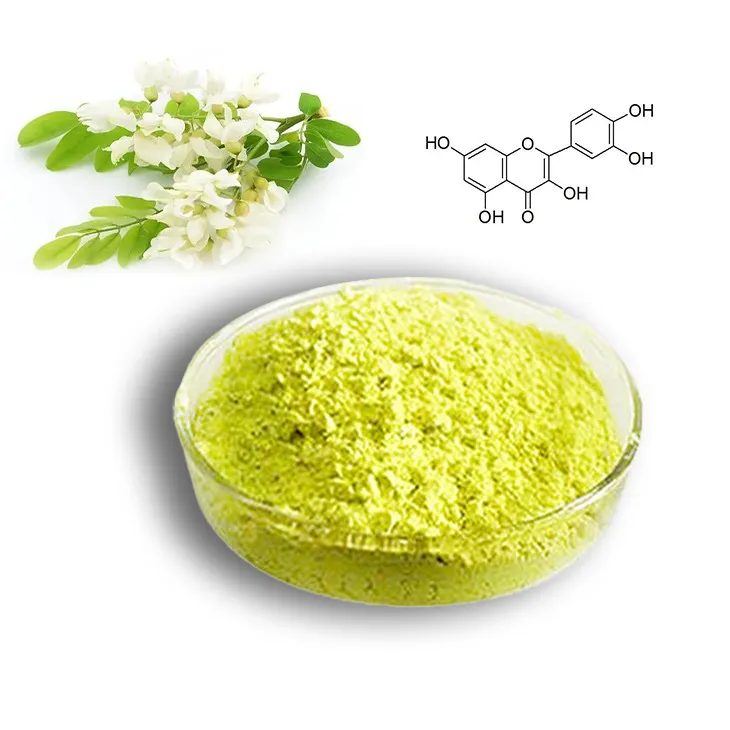

2. The Principle of Steam Distillation
2.1. Basics
Steam distillation is based on the principle that when a mixture of two immiscible liquids (in this case, the plant material containing Quercetin and water) is heated, the total vapor pressure above the mixture is equal to the sum of the vapor pressures of the individual components. As a result, the mixture boils at a lower temperature than the boiling point of either component alone. This allows for the extraction of Quercetin without subjecting it to extremely high temperatures that could potentially degrade it.
2.2. Role of Steam
The steam used in the distillation process has crucial characteristics. Purity of the steam is important as impurities in the steam can interfere with the extraction process. For example, if the steam contains dissolved minerals or other contaminants, they may react with the quercetin or the plant matrix, affecting the yield and quality of the extracted quercetin. The flow rate of the steam also plays a vital role. A too - slow flow rate may not effectively carry the quercetin vapors, resulting in a lower yield. On the other hand, an extremely high flow rate may cause turbulence and incomplete condensation, also leading to losses in the extraction process.
3. The Steam Distillation Process for Quercetin Extraction
3.1. Preparation of the Plant Material
The first step in the extraction process is the proper preparation of the plant material that contains quercetin. This may involve harvesting the plant at the appropriate stage of growth, drying it to a suitable moisture content, and grinding it to an appropriate particle size. Different plants may have different optimal conditions for these steps. For example, some plants may need to be harvested when the quercetin content is at its peak, which may be determined through prior analysis or by following established agricultural practices. Drying should be done carefully to avoid degradation of quercetin. If the drying temperature is too high, it can lead to a loss of quercetin content. Grinding the plant material to a fine powder can increase the surface area available for interaction with the steam, facilitating better extraction.
3.2. The Distillation Setup
A typical steam distillation setup consists of a distillation flask, a condenser, and a collection vessel. The plant material is placed in the distillation flask. Steam is then introduced into the flask, usually through a steam inlet. As the steam passes through the plant material, it causes the quercetin to vaporize along with the steam. The vapors then travel through the condenser, where they are cooled and condensed back into a liquid. The condensed liquid, which contains the extracted quercetin along with water, is collected in the collection vessel.
3.3. Optimization of the Process
There are several factors that need to be optimized in the steam distillation process for quercetin extraction. Temperature is a crucial factor. Although steam distillation occurs at a lower temperature compared to some other extraction methods, the temperature still needs to be carefully controlled. Too low a temperature may not provide sufficient energy for the quercetin to vaporize effectively, while too high a temperature can cause degradation. The ratio of plant material to steam is also important. A higher amount of plant material relative to steam may not allow for complete extraction as there may not be enough steam to carry all the quercetin vapors. Conversely, too much steam relative to the plant material may be wasteful and can also cause issues in the condensation process.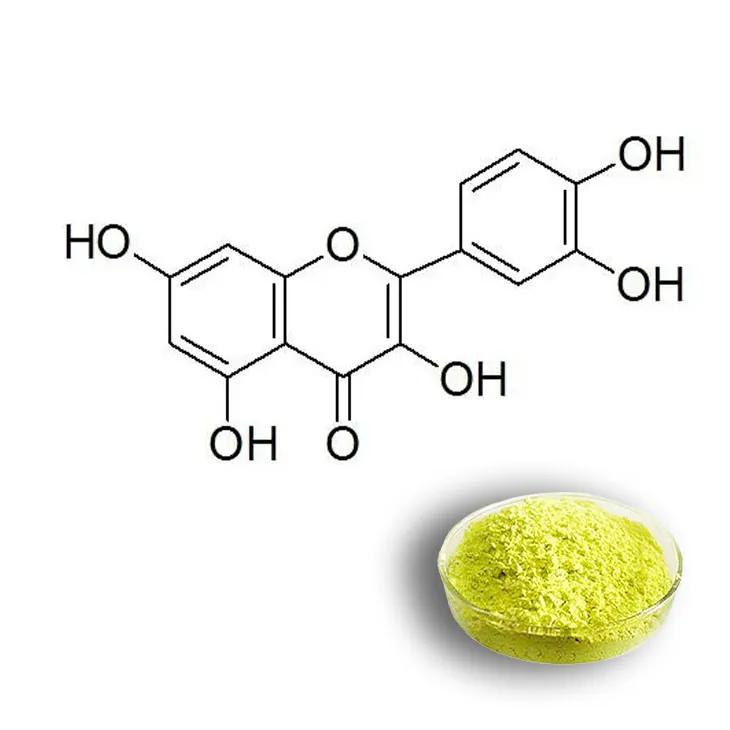
4. Post - extraction Purification
4.1. Importance of Purification
After the extraction by steam distillation, the obtained product is a mixture that contains quercetin along with other substances such as water, plant - derived impurities, and possibly some by - products of the extraction process. Post - extraction purification is essential to obtain high - quality quercetin that can be used in various applications. Pure quercetin is required for accurate research studies on its biological activities, and in commercial applications, it needs to meet certain quality standards.
4.2. Purification Methods
There are several methods available for purifying quercetin after steam distillation. One common method is solvent extraction. In this method, a suitable solvent is used to selectively dissolve quercetin from the mixture. The choice of solvent depends on the solubility properties of quercetin and the other components in the mixture. For example, ethyl acetate is often used as it has a good solubility for quercetin and can be easily separated from water. Another method is chromatography. Column chromatography or high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) can be used to separate quercetin from other components based on their differential affinities for the stationary and mobile phases in the chromatography system. Crystallization is also a possible purification method. By carefully controlling the conditions such as temperature and concentration, quercetin can be made to crystallize out of the solution, leaving behind the impurities.
5. Applications of Quercetin
5.1. Research Applications
Quercetin has been widely used in research studies due to its diverse biological activities. In antioxidant research, quercetin is studied for its ability to scavenge free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage. This is important in understanding the mechanisms of various diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, where oxidative stress is thought to play a significant role. In anti - inflammatory research, quercetin's effects on inflammatory pathways are investigated. It has been shown to modulate the production of inflammatory cytokines, which could have implications for the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as arthritis. In cancer research, quercetin's potential as an anticancer agent is explored. It may act through various mechanisms, including inhibiting cancer cell growth, inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, and interfering with cancer cell metastasis.
5.2. Commercial Applications
In the commercial realm, quercetin is used in the food and beverage industry as a natural antioxidant. It can be added to products such as juices, wines, and processed foods to extend their shelf - life and prevent oxidative spoilage. In the nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry, quercetin - containing products are marketed for their potential health benefits. Consumers are increasingly interested in natural products that can support their health, and quercetin fits this trend. Additionally, quercetin may also find applications in the cosmetic industry, for example, in skin - care products due to its antioxidant properties that can help protect the skin from environmental damage.6. Challenges and Future Directions
6.1. Challenges in Steam Distillation and Purification
One of the main challenges in steam distillation for quercetin extraction is achieving high yields while maintaining the quality of the quercetin. As mentioned earlier, optimizing the process parameters such as temperature, steam flow rate, and the ratio of plant material to steam can be difficult. In purification, the main challenge is to develop cost - effective and efficient methods that can produce highly pure quercetin. Some purification methods, such as HPLC, can be expensive and time - consuming, which may limit their use on a large - scale.
6.2. Future Directions
Future research could focus on improving the steam distillation process for quercetin extraction. This could involve the development of new distillation techniques or the modification of existing ones to enhance the extraction efficiency. In terms of purification, there is a need to explore alternative, more cost - effective purification methods. Additionally, more research is needed to fully understand the biological activities of quercetin and to develop new applications for it. For example, further studies could explore its potential in the prevention and treatment of emerging diseases or its use in combination with other bioactive compounds for enhanced health benefits.FAQ:
What are the key factors in steam distillation for quercetin extraction?
The key factors include the properties of the steam, such as its purity and flow rate. These factors can affect the efficiency of isolating quercetin while maintaining its integrity.
Why is post - extraction purification necessary in quercetin extraction by steam distillation?
Post - extraction purification is necessary to ensure the high - quality of the quercetin obtained. Through purification, impurities can be removed, making the quercetin suitable for different research and commercial applications.
How can the purity of steam affect quercetin extraction?
If the steam has a high purity, it is less likely to introduce contaminants during the extraction process. This helps in better isolating quercetin in its pure form and maintaining its bioactive properties.
What are the potential commercial applications of quercetin obtained by steam distillation?
Quercetin can be used in various commercial applications such as in the pharmaceutical industry for drug development, in the food industry as a natural antioxidant, and in the cosmetic industry for its potential anti - aging properties.
How can the flow rate of steam be optimized in quercetin extraction?
The optimal flow rate of steam can be determined through experimental studies. It may depend on factors such as the amount of the source material containing quercetin, the design of the distillation apparatus, and the desired extraction efficiency. Generally, a flow rate that allows for sufficient contact between the steam and the quercetin - containing material without causing excessive turbulence or incomplete extraction is preferred.
Related literature
- Steam Distillation: Principles and Applications in Natural Product Extraction"
- "Quercetin: Properties, Extraction Methods, and Bioactivities"
- "Enhancing Quercetin Extraction Efficiency through Steam Distillation Optimization"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
-
Best - brand Skullcap Extract Gluten - free.
2024-11-30
-
The Best Thunder God Vine Extract in 2024.
2024-11-30
-
100% Pure Natural Rosemary Extract.
2024-11-30
-
Active components in beetroot powder.
2024-11-30
-
The best sea - buckthorn oil on the market.
2024-11-30
-
The Best Avocado Extract Powder in 2024.
2024-11-30
-
Pomegranate Extract
2024-11-30
-
Honeysuckle Pollen
2024-11-30
-
Propolis Extract Powder
2024-11-30
-
Cranberry Extract
2024-11-30
-
Eucommia Ulmoides Extract
2024-11-30
-
Beta Carotene
2024-11-30
-
Lavender Extract
2024-11-30
-
Yohimbine Bark Extract
2024-11-30
-
American Ginseng Root Extract
2024-11-30
-
Moringa powder
2024-11-30





















