- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Quercetin extraction technology and production process
2024-11-30

1. Introduction
Quercetin is a flavonoid compound that has attracted significant attention in recent years due to its numerous bioactive properties. It is found in a variety of plant sources and has potential applications in the fields of nutraceuticals, functional foods, and pharmaceuticals. Understanding the extraction technology and production process of Quercetin is crucial for its large - scale production and commercial utilization.
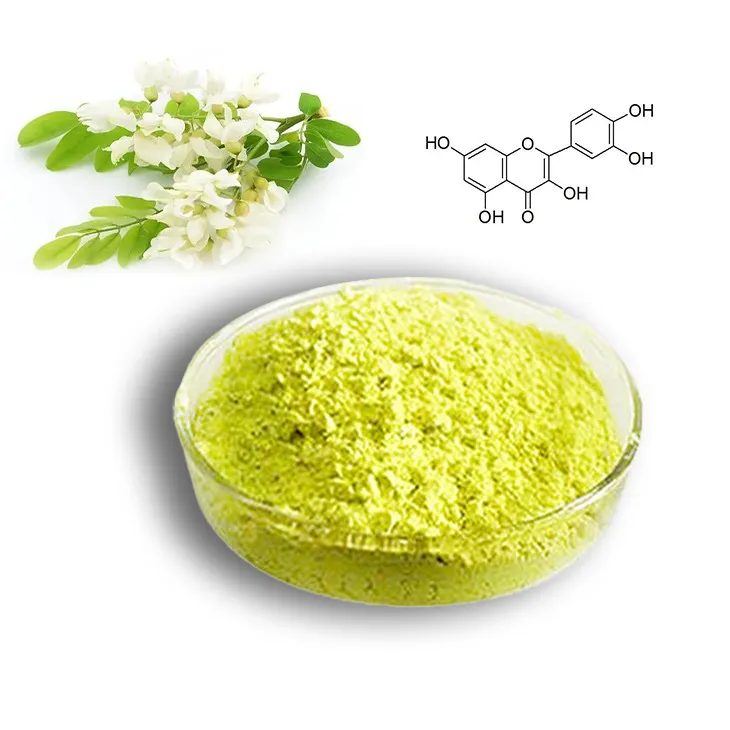

2. Factors Influencing Quercetin Extraction
2.1 Solvent Choice
The choice of solvent is one of the most critical factors in quercetin extraction. Different solvents have different affinities for quercetin and other components in the plant material.
- Ethanol is a commonly used solvent. It is relatively safe, has a good solubility for quercetin, and is suitable for extraction from many plant sources. Ethanol - based extraction can be carried out at different concentrations, with higher concentrations often leading to more efficient extraction in some cases.
- Acetone is also an effective solvent. However, it is more volatile and potentially more hazardous compared to ethanol. The use of acetone may require more careful handling in the extraction process.
- Water can be used as a solvent, especially in combination with other solvents or in the form of aqueous extracts. Water - based extraction is considered more environmentally friendly, but it may also extract a large number of other water - soluble compounds along with quercetin, which may require additional purification steps.
2.2 Extraction Time
The extraction time significantly affects the yield of quercetin. Longer extraction times generally lead to higher yields up to a certain point.
- In the initial stage of extraction, as time progresses, more quercetin is released from the plant matrix into the solvent. However, after a certain optimal time, further increasing the extraction time may not significantly increase the quercetin yield. Instead, it may lead to the extraction of more impurities or degradation of quercetin.
- The optimal extraction time can vary depending on factors such as the plant source, solvent used, and extraction temperature. For example, in the extraction of quercetin from onion skins using ethanol, an extraction time of 2 - 4 hours may be optimal under certain temperature and solvent concentration conditions.
2.3 Extraction Temperature
Temperature also plays an important role in quercetin extraction.
- At higher temperatures, the solubility of quercetin in the solvent generally increases, which can lead to faster extraction rates. However, excessive heat can also cause degradation of quercetin or other bioactive compounds in the plant material.
- For example, in some cases, extraction at temperatures between 40 - 60°C may be optimal. Temperatures below this range may result in slow extraction, while temperatures above may cause degradation. It is essential to find the right balance to ensure high - quality quercetin extraction.
2.4 Nature of Raw Materials
The nature of the raw materials, including the plant species, part of the plant used, and its pretreatment, affects quercetin extraction.
- Different plant species contain different amounts of quercetin. For example, buckwheat, onions, and apples are known to be rich sources of quercetin. The concentration of quercetin can vary within different parts of the same plant, such as in the peel, leaves, or fruits.
- Pretreatment of the raw materials can also impact extraction. Drying, grinding, or milling the plant materials can increase the surface area available for extraction, thereby improving the extraction efficiency. However, improper pretreatment may also cause loss of quercetin or introduce contaminants.

3. Production Process of Quercetin
3.1 Identification and Preparation of Plant Sources
The first step in the production of quercetin is to identify suitable plant sources. As mentioned earlier, plants rich in quercetin such as buckwheat, onions, and apples are commonly used.
- Once the plant source is identified, proper harvesting techniques need to be employed. For example, in the case of onions, they should be harvested at the appropriate maturity stage to ensure a high quercetin content in the skins.
- After harvesting, the plant materials need to be prepared for extraction. This may involve cleaning to remove dirt, debris, and pesticides if present. Then, the materials are usually dried to reduce moisture content, which can help in subsequent extraction steps and prevent spoilage.
3.2 Extraction Methods
There are several extraction methods available for quercetin extraction.
- Solvent Extraction: This is the most common method. As discussed earlier, a suitable solvent such as ethanol or a solvent mixture is used. The plant material is immersed in the solvent for a specific period (extraction time) at a certain temperature. After extraction, the solvent containing quercetin is separated from the solid plant residue, usually by filtration or centrifugation.
- Supercritical Fluid Extraction: This method uses supercritical fluids, such as supercritical carbon dioxide. Supercritical fluids have properties between those of a gas and a liquid, which can provide unique extraction capabilities. Supercritical carbon dioxide is non - toxic, non - flammable, and can be easily removed from the extract. However, this method requires specialized equipment and higher operating costs compared to solvent extraction.
- Microwave - Assisted Extraction: In this method, microwave energy is used to heat the plant - solvent mixture. Microwave heating can lead to more rapid and efficient extraction compared to traditional heating methods. It is thought to work by enhancing the mass transfer of quercetin from the plant matrix to the solvent. However, careful control of microwave power and exposure time is required to avoid overheating and degradation of quercetin.
3.3 Purification Steps
After extraction, the obtained extract usually contains quercetin along with other impurities. Purification steps are necessary to obtain high - purity quercetin.
- Filtration and Centrifugation: These are initial steps to remove large particles and solid residues from the extract. Filtration can be carried out using filter papers or membranes, while centrifugation helps to separate heavier particles by spinning the extract at high speeds.
- Chromatographic Purification: Chromatography techniques such as column chromatography or high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are often used for further purification. In column chromatography, the extract is passed through a column filled with a stationary phase, and different components are separated based on their affinities for the stationary and mobile phases. HPLC is a more advanced and precise chromatographic method that can separate quercetin from other closely related compounds with high resolution.
- Crystallization: Crystallization can be used to obtain pure quercetin crystals. By adjusting the temperature, solvent concentration, and other conditions, quercetin can be made to crystallize out of the solution. The crystals can then be separated from the mother liquor by filtration or other means.
3.4 Packaging
Once the quercetin has been purified, it needs to be packaged properly for storage and distribution.
- The packaging material should be selected based on the stability requirements of quercetin. For example, quercetin may be sensitive to light, oxygen, and moisture. Therefore, packaging materials that can protect against these factors, such as amber - colored glass bottles or vacuum - sealed foil pouches, are often used.
- Proper labeling is also essential, indicating the purity, quantity, and other relevant information about the quercetin product. This helps in ensuring the quality control and proper use of the quercetin in various applications.
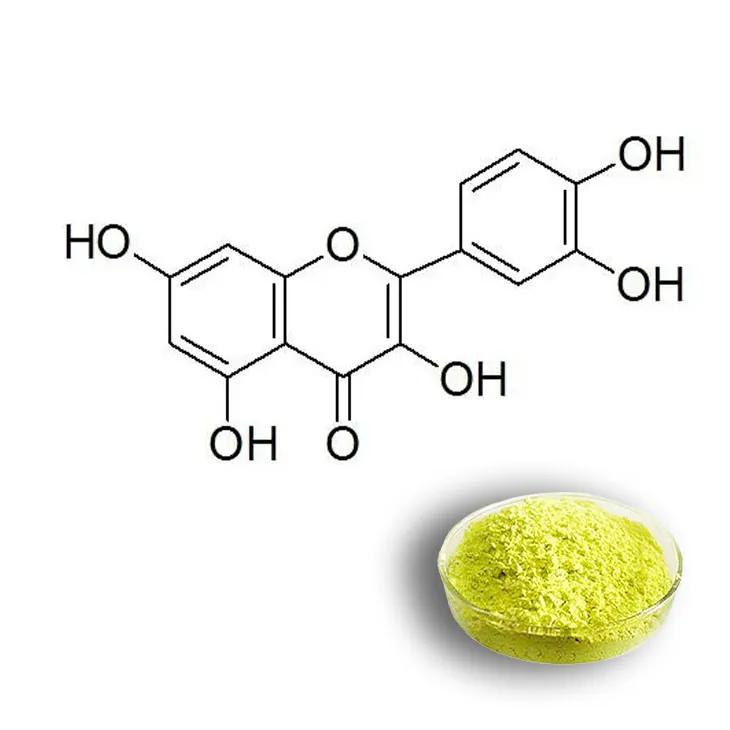
4. Conclusion
The extraction technology and production process of quercetin are complex and multi - faceted. The successful production of high - quality quercetin on a large scale requires careful consideration of factors such as solvent choice, extraction time, temperature, and the nature of raw materials. Each step in the production process, from plant source identification to packaging, plays a crucial role in ensuring the purity, yield, and commercial viability of quercetin. With the increasing demand for quercetin in the fields of nutraceuticals and functional foods, continuous research and improvement in these extraction and production technologies are necessary to meet the market needs.

FAQ:
What are the common solvents used for quercetin extraction?
Common solvents for quercetin extraction include ethanol, methanol, and acetone. Ethanol is often preferred in many cases as it is relatively safe, cost - effective, and can effectively extract quercetin from plant materials. Methanol also has good extraction capabilities but is more toxic. Acetone can be used as well, especially for certain types of plant sources where it may show better solubility for quercetin.
How does extraction time affect quercetin extraction?
The extraction time plays a crucial role. Longer extraction times generally lead to higher yields of quercetin up to a certain point. However, if the extraction time is too long, it may also lead to the extraction of other unwanted compounds or degradation of quercetin itself. There is an optimal extraction time range depending on the solvent, temperature, and the nature of the raw materials. For example, in some ethanol - based extractions, extraction times between 2 - 6 hours might be suitable.
What is the significance of temperature in quercetin extraction?
Temperature affects the solubility of quercetin in the solvent and the rate of extraction. Higher temperatures usually increase the solubility and the extraction rate. But extremely high temperatures can cause the degradation of quercetin. Moderate temperatures are often ideal. For instance, in some extraction processes using ethanol, a temperature range of 50 - 70 °C might be appropriate to balance high extraction efficiency and the stability of quercetin.
How are impurities removed during the purification of quercetin?
During the purification of quercetin, several methods can be used to remove impurities. One common method is column chromatography, which can separate quercetin from other compounds based on their different affinities to the stationary and mobile phases. Another method is crystallization, where quercetin is selectively crystallized out while impurities remain in the solution. Filtration techniques can also be employed to remove solid impurities at different stages of the purification process.
What are the main plant sources for quercetin production?
There are several main plant sources for quercetin production. Onions are a well - known source, containing a relatively high amount of quercetin. Apples, especially their skins, also have quercetin. Buckwheat is another important source, which is rich in quercetin - related compounds. In addition, certain types of berries such as cranberries and blueberries also contain quercetin.
Related literature
- Optimization of Quercetin Extraction from Plant Materials: A Review"
- "Quercetin: Production, Properties and Potential Applications in the Food Industry"
- "Advanced Extraction Techniques for Quercetin from Natural Sources"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
-
Chinese Cassia Seed Extract Suppliers.
2024-11-30
-
Suppliers of Organic Diosmin Powder.
2024-11-30
-
Hesperidin with the best reviews.
2024-11-30
-
Organic Epimedium Extract Powder Supplier.
2024-11-30
-
The best olive leaf extract in nature.
2024-11-30
-
Cordyceps extract suppliers.
2024-11-30
-
Chinese aguaje extract powder manufacturers.
2024-11-30
-
Hericium erinaceus extract powder
2024-11-30
-
Shikonin
2024-11-30
-
Garcinia Cambogia Extract
2024-11-30
-
White Willow Bark Extract
2024-11-30
-
Nettle leaf extract
2024-11-30
-
Ivy Extract
2024-11-30
-
Uridine-5'-monophosphate Disodium salt
2024-11-30
-
Sophora Flavescens Root Extract
2024-11-30
-
Oyster Mushroom Extract Powder
2024-11-30
-
White Peony Extract
2024-11-30





















