- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
The best method for extracting quercetin.
2024-12-02

1. Introduction
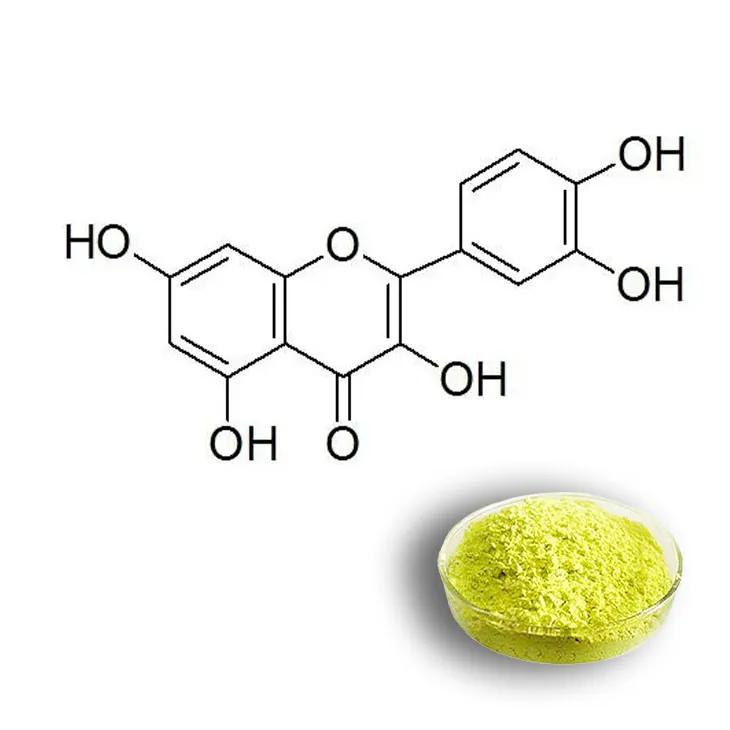
Quercetin is a flavonoid with numerous health - promoting properties, including antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anti - cancer activities. Due to its potential applications in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries, there is a growing interest in efficient extraction methods. This article will explore different extraction methods for Quercetin, namely solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and enzymatic extraction, and analyze their advantages and limitations.

2. Solvent extraction
2.1 Principle
Solvent extraction is based on the principle of solubility. Quercetin has different solubilities in various solvents. Commonly used solvents include ethanol, methanol, ethyl acetate, etc. The plant material containing quercetin is soaked in the solvent, and the quercetin is dissolved into the solvent. Then, through separation and purification steps such as filtration and evaporation, the quercetin can be obtained.
2.2 Advantages
- It is a relatively simple and straightforward method. Laboratories and industries are familiar with the basic operations of solvent extraction.
- It has a wide range of solvent choices, which can be adjusted according to the nature of the raw materials and the requirements of extraction efficiency.
- Low - cost solvents such as ethanol are widely available, making the overall cost of extraction relatively affordable.
2.3 Limitations
- The use of organic solvents may pose environmental and safety risks. For example, some solvents are flammable and volatile, which requires strict safety precautions during the extraction process.
- The extraction selectivity is not very high. In addition to quercetin, other components in the plant may also be extracted, which may require additional purification steps.
- The extraction efficiency may be affected by factors such as the polarity of the solvent and the particle size of the raw materials. Optimization of these factors often requires a large amount of experimental exploration.

3. Supercritical fluid extraction
3.1 Principle
Supercritical fluid extraction utilizes the properties of supercritical fluids. A supercritical fluid is a substance that is above its critical temperature and critical pressure. Carbon dioxide is the most commonly used supercritical fluid in quercetin extraction. Supercritical carbon dioxide has properties similar to both gases and liquids. It can penetrate into the matrix of plant materials like a gas and dissolve substances like a liquid. Quercetin can be selectively extracted from the plant material by adjusting the pressure, temperature, and other parameters of the supercritical fluid.
3.2 Advantages
- It is an environmentally friendly method. Since carbon dioxide is used as the supercritical fluid, it is non - toxic, non - flammable, and does not leave harmful residues, which is in line with the requirements of green chemistry.
- High extraction selectivity. By adjusting the extraction conditions, it can specifically extract quercetin and minimize the extraction of other unwanted components.
- The extraction process is relatively fast, and the extraction efficiency is high. Supercritical fluids have good mass transfer properties, which can quickly dissolve and separate quercetin from plant materials.
3.3 Limitations
- The equipment for supercritical fluid extraction is relatively expensive. High - pressure vessels, pumps, and other components are required, which increases the initial investment cost of the extraction process.
- The operation requires strict control of parameters such as pressure and temperature. A slight deviation may affect the extraction efficiency and selectivity.
- The scale - up of the extraction process from the laboratory to the industrial level may face some challenges, such as ensuring uniform pressure and temperature distribution in large - scale equipment.
4. Enzymatic extraction
4.1 Principle
Enzymatic extraction involves the use of enzymes to break down the cell walls of plant materials. Enzymes such as cellulase, pectinase, etc. can hydrolyze the polysaccharides and pectin in the cell walls, making the intracellular components, including quercetin, more easily released. After the enzymatic treatment, the quercetin can be extracted using a suitable solvent or other extraction methods.
4.2 Advantages
- It is a mild extraction method. Enzymatic treatment does not require harsh reaction conditions such as high temperature and high pressure, which can avoid the degradation of quercetin.
- High extraction yield. By effectively breaking down the cell walls, more quercetin can be released from the plant cells, thereby increasing the extraction efficiency.
- It can be combined with other extraction methods. For example, after enzymatic treatment, solvent extraction can be carried out to further improve the extraction effect.
4.3 Limitations
- The cost of enzymes is relatively high, which increases the overall cost of extraction. Different enzymes are suitable for different plant materials, and the selection of enzymes requires a certain amount of experimental research.
- The enzymatic reaction is affected by factors such as enzyme concentration, reaction time, and pH value. Optimization of these factors is necessary to ensure the best extraction effect, which requires a lot of experimental work.
- The enzymatic extraction process may be relatively complex compared to solvent extraction. It requires strict control of reaction conditions and the addition of appropriate buffers and other substances.

5. Comparison and selection
The choice of the best extraction method for quercetin depends on various factors. If cost is the primary consideration and a relatively simple method is acceptable, solvent extraction may be a suitable choice. However, for applications where high purity and selectivity are required, and environmental impact is a concern, supercritical fluid extraction may be more preferable. Enzymatic extraction is a good option when a high extraction yield and mild extraction conditions are desired, especially for heat - sensitive quercetin.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, each of the extraction methods for quercetin, namely solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and enzymatic extraction, has its own advantages and limitations. The selection of the best method should be based on specific requirements such as cost, extraction efficiency, selectivity, and environmental impact. Future research may focus on further optimizing these extraction methods or developing new hybrid methods to improve the extraction of quercetin.
FAQ:
What are the main extraction methods for quercetin?
The main extraction methods for quercetin include solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and enzymatic extraction.
What are the advantages of solvent extraction for quercetin?
Solvent extraction is a relatively simple and commonly used method. It can use different solvents according to the solubility characteristics of quercetin. For example, ethanol - water mixtures are often used. It has a relatively wide range of applications and can be adjusted according to different raw materials and extraction conditions. However, it may also have some disadvantages such as the need for solvent removal and potential solvent residue issues.
What are the limitations of supercritical fluid extraction in quercetin extraction?
Supercritical fluid extraction requires special equipment which is relatively expensive. The operation process is also more complex compared to some other methods. Although it has advantages such as high selectivity and environmental - friendliness, the high cost of equipment and operation restricts its widespread application in some cases.
How does enzymatic extraction work for quercetin?
Enzymatic extraction uses specific enzymes to break down the cell walls or complex structures in the raw materials containing quercetin. This helps to release quercetin more effectively. For example, cellulase can be used to break down cellulose in plant cell walls, making quercetin more accessible for extraction. However, the choice of enzymes needs to be carefully considered according to the nature of the raw materials.
How to choose the best extraction method for quercetin?
The choice depends on several factors. If cost - effectiveness and simplicity are the main concerns, solvent extraction may be a choice. For high - purity and environmental - friendly extraction, supercritical fluid extraction might be considered, although it has a higher cost. If the raw material has a complex structure and enzymatic treatment can improve extraction efficiency significantly, enzymatic extraction could be a good option. Also, factors such as the scale of production, available equipment, and required purity of quercetin play important roles in the selection.
Related literature
- Recent Advances in Quercetin Extraction Techniques"
- "Comparative Study of Different Methods for Quercetin Extraction"
- "Optimization of Quercetin Extraction: A Review"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
-
The best lemon juice powder in nature.
2024-12-02
-
Organic Vitamin K2 Powder Suppliers
2024-12-02
-
Bulk purchase of L - tyrosine.
2024-12-02
-
Vitamin K2 Manufacturers
2024-12-02
-
100% Pure Natural Rutin.
2024-12-02
-
Chinese Citrus Bioflavonoid Suppliers.
2024-12-02
-
Citrus Aurantium Extract
2024-12-02
-
Curcumin Extract
2024-12-02
-
Apricot Powder
2024-12-02
-
Selenium yeast
2024-12-02
-
Aguaje Extract
2024-12-02
-
Angelica sinensis extract
2024-12-02
-
Dandelion Root Extract
2024-12-02
-
Curcuma Longa Extract/Turmeric extract
2024-12-02
-
Quercetin
2024-12-02
-
Okra Extract
2024-12-02




















