- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
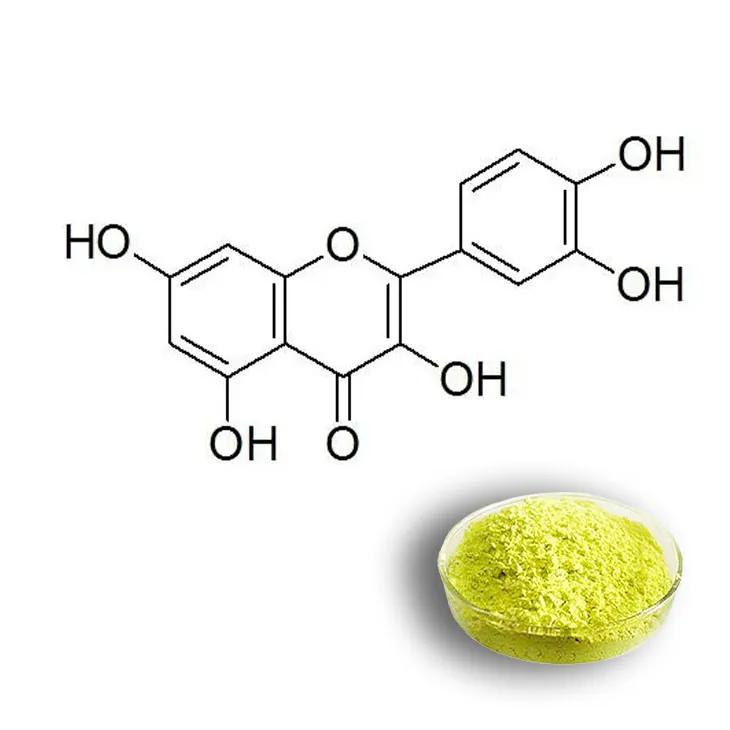
The process of extracting pure quercetin from quercetin.
2024-11-26

1. Introduction
Quercetin is a flavonoid compound that has received significant attention in recent years due to its numerous potential applications in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries. It exhibits antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and anticancer properties, among others. However, to fully realize its potential, it is necessary to obtain pure Quercetin from natural sources. This process is complex and involves several steps, starting from the selection of appropriate raw materials to the final purification of the compound.
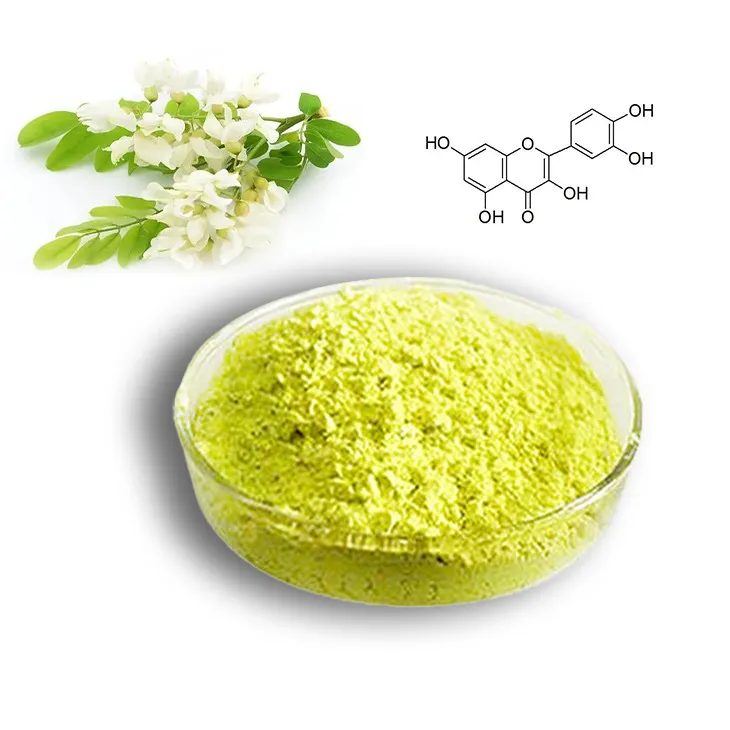

2. Selection of Plant Materials
The first step in the extraction of pure Quercetin is the careful selection of plant materials. Quercetin is found in a variety of plants, such as onions, apples, berries, and certain medicinal plants. The choice of plant material depends on several factors:
2.1. Quercetin Content
Some plants have a higher quercetin content than others. For example, certain species of buckwheat are known to have relatively high levels of quercetin. It is essential to select plants that can provide a sufficient amount of the compound for extraction.
2.2. Availability and Cost
Plants that are readily available and cost - effective are more preferable. Common fruits and vegetables like apples and onions are widely available and can be a good source of quercetin, especially when large - scale extraction is not required. However, for industrial - scale extraction, more abundant and less expensive plant sources may be sought.
2.3. Purity of the Extract
The presence of other compounds in the plant material can affect the purity of the quercetin extract. Some plants may contain fewer interfering substances, making it easier to obtain pure quercetin during the extraction and purification processes.

3. Extraction Methods
Once the appropriate plant materials are selected, the next step is the extraction of quercetin from the plant matrix. There are several extraction methods available, each with its own advantages and limitations.
3.1. Maceration
Maceration is one of the simplest extraction methods. In this process:
- The plant material is finely chopped or ground to increase the surface area.
- It is then soaked in a suitable solvent, such as ethanol or methanol, for a period of time. The solvent penetrates the plant cells and dissolves the quercetin along with other soluble compounds.
- The mixture is stirred occasionally to ensure better extraction. After the extraction period, the liquid extract is separated from the solid residue.
3.2. Soxhlet Extraction
Soxhlet extraction is a more efficient method, especially for extracting quercetin from plant materials with a relatively low quercetin content. Here's how it works:
- The plant material is placed in a Soxhlet extractor, which is a specialized glass apparatus.
- A suitable solvent, like ethyl acetate or acetone, is continuously circulated through the plant material. The solvent vaporizes in the Soxhlet apparatus, rises, condenses, and then drips back onto the plant material, continuously extracting the quercetin.
- After a sufficient number of cycles, the extract is collected, and the solvent is evaporated to obtain a concentrated quercetin extract.
4. Filtration
After the extraction process, whether it is maceration or Soxhlet extraction, filtration is a crucial step. The purpose of filtration is to remove solid residues from the extract. These solid residues may include plant debris, cell walls, and other insoluble materials.
There are different types of filtration methods that can be used:
4.1. Gravity Filtration
This is the simplest form of filtration. A filter paper is placed in a funnel, and the extract is poured through it. The solid particles are retained on the filter paper, while the liquid quercetin - containing extract passes through under the force of gravity. However, this method may be slow, especially for large volumes of extract.
4.2. Vacuum Filtration
Vacuum filtration is a faster method. In this process:
- A Büchner funnel with a filter paper is used. The funnel is connected to a vacuum source.
- The extract is poured into the funnel, and the vacuum sucks the liquid through the filter paper, leaving the solid residues behind. This method is more efficient for removing fine particles and can be used for larger volumes of extract.

5. Purification of Quercetin Extract
After filtration, the obtained quercetin extract still contains impurities. To obtain pure quercetin, purification methods are required. These methods are designed to separate quercetin from other compounds present in the extract.
5.1. Preparative Thin - Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Preparative TLC is a useful technique for purifying small to medium amounts of quercetin extract. Here's how it is carried out:
- A thin layer of adsorbent material, such as silica gel, is coated on a glass plate.
- The quercetin extract is spotted near the bottom of the plate.
- The plate is then placed in a developing chamber containing a suitable mobile phase, such as a mixture of chloroform and methanol. The mobile phase moves up the plate by capillary action, carrying the components of the extract with it.
- Since different compounds have different affinities for the adsorbent and the mobile phase, they separate on the plate. Quercetin can be identified based on its characteristic Rf value (the ratio of the distance traveled by the compound to the distance traveled by the solvent front).
- The pure quercetin band can be scraped off the plate, and the compound can be eluted from the silica gel using a suitable solvent.
5.2. High - Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
HPLC is a more advanced and widely used method for purifying quercetin on a larger scale. The process involves:
- A sample of the quercetin extract is injected into a HPLC system, which consists of a pump, a column filled with a stationary phase (such as a reversed - phase C18 column), and a detector.
- The mobile phase, which is a carefully selected solvent or solvent mixture (e.g., acetonitrile - water), is pumped through the column at a constant flow rate.
- As the sample passes through the column, the different components of the extract, including quercetin, interact differently with the stationary and mobile phases. Based on these interactions, the compounds are separated and eluted from the column at different times.
- The detector, such as a UV - Vis detector, detects the eluted compounds. By monitoring the signal at the appropriate wavelength (for quercetin, typically around 370 nm), pure quercetin can be collected as it elutes from the column.
6. Characterization of Pure Quercetin
Once pure quercetin is obtained, it is important to characterize it to confirm its identity and purity. There are several methods for characterizing quercetin:
6.1. Spectroscopic Methods
- UV - Vis Spectroscopy: Quercetin has characteristic absorption peaks in the UV - Vis region, particularly around 370 nm. By measuring the absorption spectrum of the purified compound, it can be compared with the known spectrum of quercetin to confirm its identity.
- IR Spectroscopy: Infrared spectroscopy can be used to identify the functional groups present in quercetin. The IR spectrum of pure quercetin shows peaks corresponding to hydroxyl groups, carbonyl groups, and aromatic rings, which are characteristic of the compound.
6.2. Chromatographic Methods
- HPLC: As mentioned earlier, HPLC can be used not only for purification but also for characterization. By comparing the retention time of the purified compound with that of a standard quercetin sample, its identity can be verified. Additionally, the purity of the compound can be determined by analyzing the peak area and the absence of other peaks corresponding to impurities.
- GC - MS (Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry): Although quercetin is a polar compound and not directly amenable to gas chromatography, derivatization techniques can be used to make it volatile. GC - MS can then be used to obtain the mass spectrum of quercetin, which provides information about its molecular weight and fragmentation pattern, further confirming its identity.
7. Conclusion
The extraction of pure quercetin from quercetin - containing sources is a multi - step process that involves careful selection of plant materials, extraction, filtration, purification, and characterization. Each step is crucial for obtaining high - quality, pure quercetin that can be used in various industries. With the increasing demand for natural compounds with beneficial properties like quercetin, continuous research and improvement in extraction and purification techniques are necessary to meet the market requirements and fully explore the potential applications of this valuable flavonoid.
FAQ:
What are the suitable plant materials for extracting quercetin?
Common plant materials for quercetin extraction include onions, apples, buckwheat, and some types of berries. These plants are rich in quercetin - containing compounds.
What are the advantages of Soxhlet extraction in the quercetin extraction process?
Soxhlet extraction is advantageous as it allows for continuous extraction with a relatively small amount of solvent. It can effectively extract quercetin from plant materials over an extended period, leading to a higher yield compared to some other simple extraction methods.
Why is filtration important after the extraction of quercetin?
Filtration is crucial after extraction because it helps to remove solid residues such as plant debris, undissolved particles, and other impurities. These residues can interfere with subsequent purification steps and the quality of the final quercetin product.
How does preparative thin - layer chromatography purify quercetin?
Preparative thin - layer chromatography purifies quercetin by separating it from other components based on differences in their affinities for the stationary and mobile phases. The quercetin compound migrates at a different rate compared to contaminants on the thin - layer plate, allowing for its isolation.
What are the applications of pure quercetin in the pharmaceutical industry?
In the pharmaceutical industry, pure quercetin has antioxidant, anti - inflammatory, and potential anti - cancer properties. It can be used in the development of drugs for treating various diseases related to oxidative stress and inflammation.
Related literature
- Quercetin: A Promising Molecule for Health Benefits"
- "Extraction and Purification of Quercetin: Current Trends and Future Perspectives"
- "The Role of Quercetin in the Food and Pharmaceutical Sciences"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
-
Organic non - transgenic lemon extract.
2024-11-26
-
Manufacturers of Organic Bromelain Powder.
2024-11-26
-
Certified organic mulberry extract.
2024-11-26
-
China L - Cysteine Factories.
2024-11-26
-
Pineapple protease manufacturers from China.
2024-11-26
-
Withania Somnifera Extract
2024-11-26
-
Senna Leaf Extract
2024-11-26
-
Astaxanthin
2024-11-26
-
Red Wine Extract
2024-11-26
-
Bamboo Leaf extract
2024-11-26
-
Berberis aristata Extract
2024-11-26
-
Carrageenan Extract Powder
2024-11-26
-
Hawthorn powder
2024-11-26
-
Lemon Balm Extract
2024-11-26
-
Dandelion Leaf Extract
2024-11-26





















