- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Four Main Methods for Extracting Quercetin from Plants.
2024-12-20

Introduction
Quercetin, a remarkable flavonoid, has been the focus of extensive research due to its numerous health - promoting properties. It is found in various plants, and extracting it efficiently has become an important area of study. There are four main methods that are commonly used for this extraction process, each with its own characteristics and advantages. This article will explore these methods in detail.

Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction is one of the most traditional and widely used methods for extracting Quercetin from plants. This method is based on the principle that Quercetin can be dissolved in certain solvents.
Choice of Solvents
Among the solvents, ethanol is a common choice. Ethanol has several advantages. It has a relatively good solubility for quercetin, and it is also a relatively safe and environmentally friendly solvent compared to some other organic solvents. In addition to ethanol, other solvents such as methanol and ethyl acetate can also be considered depending on the specific plant material and extraction requirements.
Extraction Process
The extraction process typically involves the following steps:
- First, the plant material is collected and dried. Drying helps to remove moisture, which can interfere with the extraction process.
- The dried plant material is then ground into a fine powder. This increases the surface area of the plant material, allowing for better contact with the solvent.
- The powdered plant material is placed in a suitable container, and the selected solvent is added. The ratio of plant material to solvent is an important factor and needs to be optimized according to different situations.
- The mixture is then stirred or shaken for a certain period of time, usually several hours to ensure sufficient dissolution of quercetin.
- After that, the mixture is filtered to separate the liquid extract containing quercetin from the solid residue.
- Finally, the solvent in the extract can be removed through evaporation or other methods to obtain the quercetin - rich product.
Advantages and Limitations
The main advantage of solvent extraction is its simplicity and wide applicability. It can be used for a variety of plant materials. However, it also has some limitations. For example, the extraction process may be relatively time - consuming, and the use of solvents may pose some environmental and safety concerns if not properly managed.

Microwave - Assisted Extraction
Microwave - assisted extraction is a relatively modern method that has shown great potential in quercetin extraction.
Principle of Microwave - Assisted Extraction
This method utilizes microwave energy to enhance the mass transfer process. When the plant material is exposed to microwaves, the polar molecules in the plant cells start to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat, which in turn can disrupt the cell structure and increase the permeability of the cell walls. As a result, it becomes easier for quercetin to be released from the plant material and dissolved in the solvent.
Extraction Procedure
The general procedure for microwave - assisted extraction is as follows:
- Prepare the plant material in a similar way as in solvent extraction, that is, drying and grinding it into a powder.
- Place the powdered plant material and the solvent in a microwave - compatible container.
- Set the appropriate microwave power and irradiation time. The power and time need to be optimized based on the type of plant material, the solvent used, and the expected extraction yield. Typically, relatively low power and short irradiation times are initially tested and then adjusted as needed.
- After microwave irradiation, the mixture is cooled and then filtered to obtain the quercetin - containing extract.
Benefits and Drawbacks
One of the major benefits of microwave - assisted extraction is its efficiency. It can significantly reduce the extraction time compared to traditional solvent extraction. Moreover, it can often achieve a relatively high extraction yield. However, this method also has some drawbacks. For instance, the equipment required for microwave - assisted extraction can be relatively expensive, and there may be some potential issues related to the uniform distribution of microwave energy within the sample.
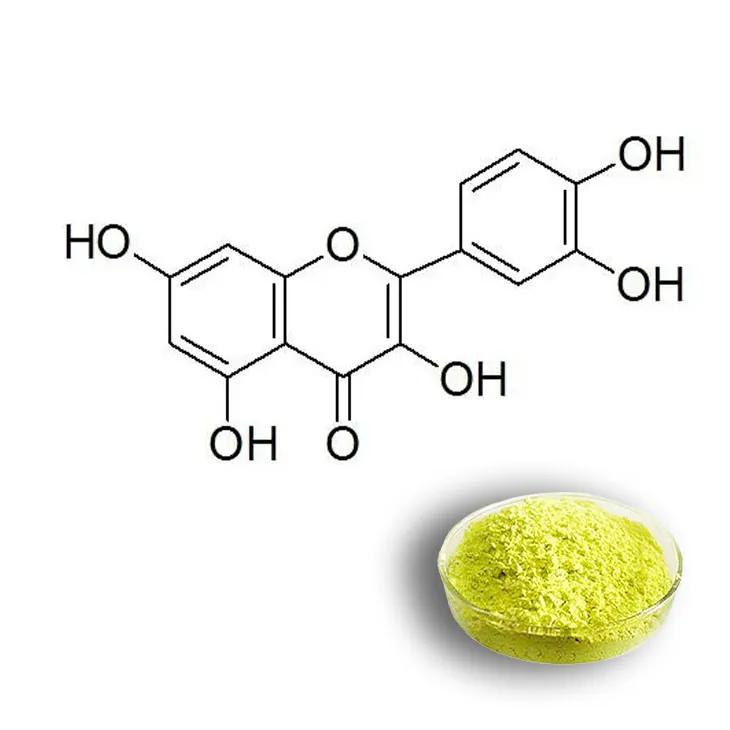
Supercritical Fluid Extraction
Supercritical fluid extraction has emerged as an important method for quercetin extraction, especially considering its environmental - friendly nature.
Supercritical Fluids and Their Properties
In this method, supercritical carbon dioxide is commonly used as the extraction medium. Supercritical fluids have unique properties. They possess the diffusivity of a gas and the density of a liquid. This allows them to penetrate into the plant material effectively and dissolve quercetin. Supercritical carbon dioxide is non - toxic, non - flammable, and has a relatively low critical temperature and pressure, which makes it easy to handle in the extraction process.
Extraction Steps
The extraction process using supercritical fluid extraction typically involves:
- First, the plant material is prepared as in the previous methods, dried and ground.
- The supercritical carbon dioxide is pressurized and heated to reach its supercritical state. The pressure and temperature conditions need to be precisely controlled according to the specific requirements of the extraction.
- The supercritical carbon dioxide is then passed through the plant material, and quercetin is dissolved in it.
- After that, by adjusting the pressure and temperature, the solubility of quercetin in supercritical carbon dioxide is changed, causing the quercetin to be separated from the supercritical fluid. This can be achieved by depressurization or other techniques.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantage of supercritical fluid extraction is its environmental - friendliness. Since carbon dioxide is used, there is no residual solvent problem, which is beneficial for applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. It also has high selectivity for quercetin extraction. However, the equipment for supercritical fluid extraction is very expensive, and the operation process requires strict control of pressure and temperature, which may limit its widespread application.

Enzymatic Extraction
Enzymatic extraction is a promising method that has attracted increasing attention in recent years for quercetin extraction.
Role of Enzymes
In enzymatic extraction, specific enzymes are used. These enzymes can break down the cell walls of the plant material. For example, cellulases and pectinases can hydrolyze the cellulose and pectin components in the cell walls respectively. By breaking down the cell walls, the access to quercetin within the plant cells is increased, and the release of quercetin into the extraction medium is facilitated.
Extraction Process
The enzymatic extraction process generally includes the following steps:
- Prepare the plant material by drying and grinding as before.
- Add the appropriate enzyme or enzyme mixture to the plant material in a buffer solution. The selection of enzymes and the concentration of the enzyme solution need to be optimized according to the plant species and the characteristics of the cell walls.
- Incubate the mixture at a suitable temperature and pH for a certain period of time. During this time, the enzymes will act on the cell walls to break them down.
- After incubation, add the solvent to extract quercetin from the enzymatically treated plant material. The subsequent steps of filtration and solvent removal are similar to those in other extraction methods.
Advantages and Challenges
Enzymatic extraction has several advantages. It can improve the extraction yield and selectivity for quercetin. It is also a relatively mild method that can preserve the bioactivity of quercetin better. However, the cost of enzymes can be relatively high, and the enzymatic reaction conditions need to be carefully controlled, which may add complexity to the extraction process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the four main methods for extracting quercetin from plants, namely solvent extraction, microwave - assisted extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and enzymatic extraction, each have their own unique features. Solvent extraction is simple and widely applicable, microwave - assisted extraction is efficient, supercritical fluid extraction is environmentally friendly, and enzymatic extraction has good selectivity and can improve the extraction yield. The choice of method depends on various factors such as the type of plant material, the scale of extraction, cost - effectiveness, and environmental requirements. Future research may focus on further optimizing these methods or developing hybrid methods to achieve more efficient and sustainable extraction of quercetin from plants.
FAQ:
What are the solvents commonly used in solvent extraction for quercetin?
Ethanol is one of the commonly used solvents in solvent extraction for quercetin. However, other solvents may also be applicable depending on the nature of the plant material and the extraction requirements.
How does microwave - assisted extraction enhance the extraction of quercetin?
Microwave - assisted extraction enhances the extraction of quercetin by using microwave energy. This energy promotes mass transfer within the plant material, which helps in more effectively dissolving and extracting quercetin. It can break down some of the barriers within the plant cells and tissues, allowing the quercetin to be more easily transferred from the plant material into the extraction medium.
What are the advantages of supercritical fluid extraction using supercritical carbon dioxide for quercetin extraction?
The main advantage of using supercritical carbon dioxide in supercritical fluid extraction for quercetin is that it is environmentally friendly. Supercritical carbon dioxide has properties that make it a good medium for extraction. It can selectively extract quercetin while leaving behind unwanted components. Also, it can be easily removed from the final extract, leaving a relatively pure quercetin product.
How does enzymatic extraction improve the yield and selectivity of quercetin?
Enzymatic extraction improves the yield and selectivity of quercetin by using specific enzymes to break down the cell walls of the plant material. By breaking down these cell walls, the quercetin, which is often trapped inside the cells, can be more easily released. The enzymes can be chosen to specifically target the components surrounding quercetin, thus improving the selectivity of the extraction process and leading to a higher yield of quercetin.
Which method is the most cost - effective for quercetin extraction?
The cost - effectiveness of each method for quercetin extraction depends on various factors such as the scale of extraction, the cost of equipment, solvents, and enzymes, and the availability of plant materials. Solvent extraction may be relatively cost - effective in some cases as ethanol is a commonly available and relatively inexpensive solvent. However, in large - scale industrial applications, supercritical fluid extraction with its high selectivity and potential for easy purification may prove to be more cost - effective in the long run. Enzymatic extraction may be more costly due to the cost of enzymes, but it can offer high selectivity and yield, which could offset the cost in certain situations. Microwave - assisted extraction also requires specific equipment, which may add to the cost, but its efficiency could make it cost - effective depending on the overall setup and requirements.
Related literature
- “Quercetin Extraction and Purification from Plant Sources: A Review”
- “Advanced Techniques for Quercetin Isolation from Plants”
- “Optimization of Quercetin Extraction Methods: A Comparative Study”
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
- ▶ blog5
-
Pure 85% Tomentil Extract.
2024-12-20
-
Red Date Extract
2024-12-20
-
Pueraria Lobata Extract
2024-12-20
-
Pine bark Extract Powder
2024-12-20
-
Phellodendron Extract
2024-12-20
-
Avocado Extract Powder
2024-12-20
-
Beta Carotene
2024-12-20
-
Mulberry leaf Extract
2024-12-20
-
Kidney Bean Extract
2024-12-20
-
Clove Powder
2024-12-20
-
Natural grape seed extract
2024-12-20





















