- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Standard - process astaxanthin.
2024-11-27

1. Introduction to Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid pigment. It is renowned for its vivid red - orange color and a host of remarkable properties. This unique compound has attracted significant attention in various fields due to its potential benefits for human health, as well as its applications in different industries.
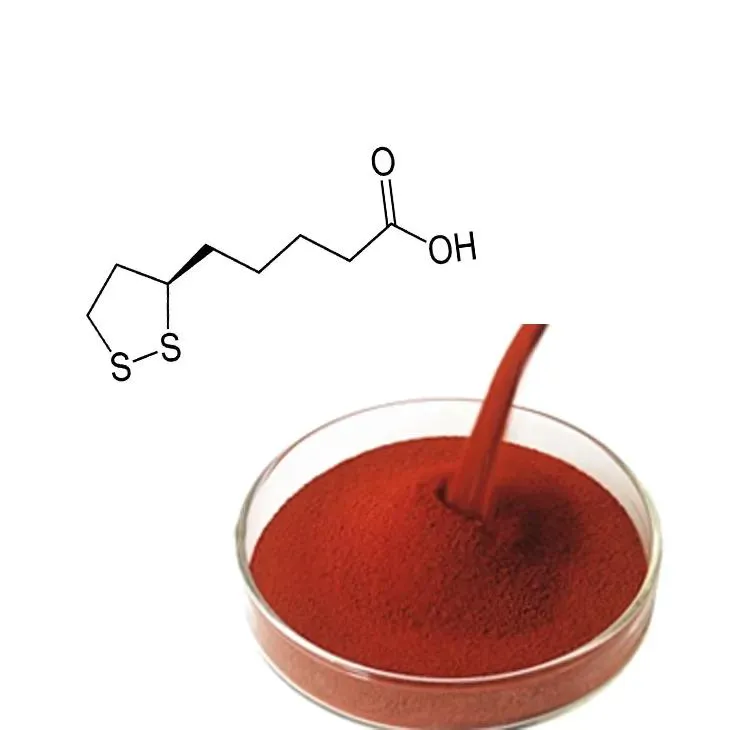
2. Production of Standard - process Astaxanthin
2.1 Cultivation of Raw Material Sources
The production of standard - process astaxanthin begins with the cultivation of its raw material sources. This is a highly regulated process with strict environmental controls.
- Microalgae Cultivation: Microalgae, such as Haematococcus pluvialis, are one of the primary sources of astaxanthin. These microalgae are cultivated in specialized facilities. The growth environment needs to be carefully monitored and controlled. For example, factors like light intensity, temperature, and nutrient availability play crucial roles. High - quality light sources are often provided to ensure optimal photosynthesis, which is essential for the production of astaxanthin within the microalgae cells. Temperature is maintained within a specific range to support the growth and astaxanthin synthesis of the microalgae. Nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and various trace elements, are supplied in precise amounts.
- Water Quality: The quality of water used in microalgae cultivation is of utmost importance. It must be free from contaminants such as heavy metals and harmful microorganisms. Regular water quality testing is carried out to ensure that the microalgae are growing in a clean and suitable environment. This helps to produce high - quality microalgae rich in astaxanthin.
2.2 High - tech Extraction Process
Once the microalgae are fully grown and have accumulated a sufficient amount of astaxanthin, the extraction process begins. This is a complex and high - tech procedure.
- Cell Disruption: The first step in the extraction process is to break open the microalgae cells to release the astaxanthin. Various methods can be used for cell disruption, such as mechanical methods (e.g., high - pressure homogenization) or enzymatic methods. High - pressure homogenization involves subjecting the microalgae suspension to high - pressure forces, which cause the cells to rupture. Enzymatic methods use specific enzymes to break down the cell walls of the microalgae, allowing for the release of astaxanthin in a more gentle and targeted way.
- Solvent Extraction: After cell disruption, solvent extraction is often employed to isolate astaxanthin from the microalgae matrix. Organic solvents, such as hexane or ethyl acetate, are commonly used. However, it is crucial to ensure that the solvents are of high purity and do not introduce any contaminants into the final product. The extraction process is carefully optimized to achieve a high yield of astaxanthin while maintaining its purity.
- Purification and Concentration: The extracted astaxanthin solution then undergoes purification and concentration steps. This may involve techniques such as chromatography to separate astaxanthin from other impurities. Chromatography can be used to separate different components based on their chemical properties, allowing for the isolation of pure astaxanthin. The purified astaxanthin is then concentrated to increase its potency, resulting in a final product with high purity and activity.

3. Characteristics of Standard - process Astaxanthin
3.1 High Purity
The standard - process astaxanthin is characterized by its high purity. Through the meticulous production process described above, impurities are effectively removed. This high purity is crucial for its various applications. In the field of health products, for example, a high - purity astaxanthin ensures that consumers are getting a product with maximum effectiveness and minimum risk of adverse reactions. In cosmetics, high - purity astaxanthin can provide more stable and reliable anti - aging effects without being affected by other substances.
3.2 High Activity
Another important characteristic of standard - process astaxanthin is its high activity. The high - tech extraction and purification methods help to preserve the natural activity of astaxanthin. This high activity is closely related to its antioxidant and anti - inflammatory capabilities. Astaxanthin's antioxidant activity is much stronger than many other common antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E. It can scavenge free radicals more effectively, protecting cells from oxidative damage. Its anti - inflammatory properties also make it a valuable substance in the treatment and prevention of various inflammatory diseases.
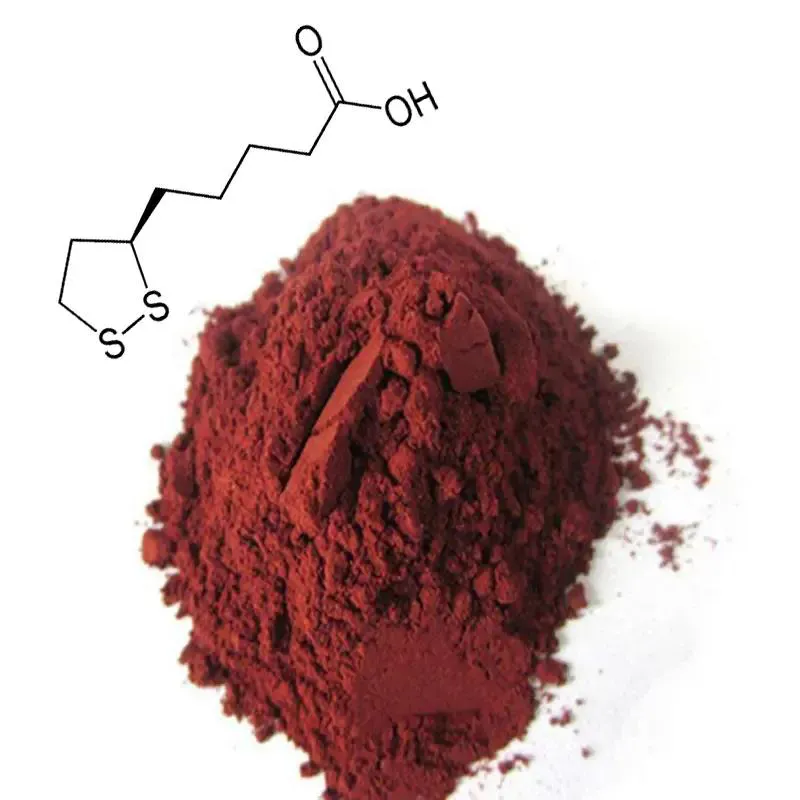
4. Applications of Standard - process Astaxanthin
4.1 In Cosmetics for Skin Anti - aging
Standard - process astaxanthin has found extensive applications in the cosmetics industry, particularly in skin anti - aging products.
- Antioxidant Protection for Skin: The skin is constantly exposed to environmental stressors such as ultraviolet radiation, pollution, and free radicals. Astaxanthin's powerful antioxidant properties can neutralize these harmful factors, preventing oxidative damage to skin cells. This helps to reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots, keeping the skin looking youthful and radiant.
- Enhancing Skin Elasticity: Astaxanthin also has the ability to stimulate collagen production in the skin. Collagen is a key protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. By promoting collagen synthesis, astaxanthin can improve skin firmness and elasticity, reducing sagging and maintaining a smooth complexion.
4.2 In Health Products for Enhancing Immunity
When it comes to health products, standard - process astaxanthin plays an important role in enhancing immunity.
- Immune Cell Modulation: Astaxanthin can modulate the function of immune cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes. It can enhance the phagocytic activity of macrophages, which are responsible for engulfing and destroying foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. At the same time, it can also regulate the activity of lymphocytes, promoting a balanced immune response.
- Reducing Inflammation in the Body: Chronic inflammation can weaken the immune system. Astaxanthin's anti - inflammatory properties can help to reduce inflammation throughout the body, creating a more favorable internal environment for the immune system to function effectively. This, in turn, helps to prevent diseases and infections.
4.3 In Aquaculture for Improving the Quality of Aquatic Products
In the aquaculture industry, standard - process astaxanthin is widely used to improve the quality of aquatic products.
- Color Enhancement in Fish: Many fish species, such as salmon and trout, have a natural pink or red color due to the presence of astaxanthin in their diet. In aquaculture, adding astaxanthin to fish feed can enhance the color of the fish, making them more visually appealing to consumers. This is an important factor in the marketability of fish products.
- Improving Fish Health and Growth: Astaxanthin also has beneficial effects on fish health and growth. It can enhance the antioxidant capacity of fish, protecting their cells from oxidative stress. This can lead to better growth performance, including increased weight gain and improved survival rates. Additionally, astaxanthin can improve the quality of fish flesh, making it more nutritious and flavorful.
5. Conclusion
Standard - process astaxanthin is indeed a remarkable substance. Its production process, from the cultivation of raw material sources with strict environmental controls to the high - tech extraction process, ensures its high purity and high activity. These characteristics, in turn, endow it with excellent antioxidant and anti - inflammatory capabilities, making it widely applicable in various industries. Whether in cosmetics for skin anti - aging, health products for enhancing immunity, or aquaculture for improving the quality of aquatic products, astaxanthin has shown great potential and value. As research continues, it is expected that more applications and benefits of standard - process astaxanthin will be discovered in the future.
FAQ:
What are the main raw material sources for producing astaxanthin?
The main raw material sources for producing astaxanthin include microalgae such as Haematococcus pluvialis. Some crustaceans also contain astaxanthin, but microalgae are a more common and sustainable source for large - scale production.
How is the high - tech extraction process of astaxanthin carried out?
There are several methods for the high - tech extraction of astaxanthin. One common method is supercritical fluid extraction, which uses supercritical carbon dioxide as the solvent. This method can effectively extract astaxanthin with high purity while minimizing the damage to its activity. Another method is solvent extraction, but it requires careful selection of solvents to ensure the quality of the final product.
What makes standard - process astaxanthin have high antioxidant capabilities?
The chemical structure of astaxanthin is such that it can easily donate electrons to neutralize free radicals. Its conjugated double - bond system allows it to be a very effective antioxidant. During the standard process, the high purity and activity of astaxanthin are maintained, which further enhances its antioxidant capabilities.
How does astaxanthin contribute to skin anti - aging in cosmetics?
Astaxanthin can protect skin cells from oxidative stress caused by free radicals. It helps in reducing the appearance of wrinkles, improving skin elasticity, and enhancing skin hydration. By neutralizing free radicals, it can prevent damage to collagen and elastin in the skin, which are important for maintaining a youthful appearance.
In aquaculture, how does astaxanthin improve the quality of aquatic products?
In aquaculture, astaxanthin is added to the feed of aquatic animals. It accumulates in the tissues of these animals, such as fish and shrimp. This gives them a more attractive color, which is important for marketability. Additionally, astaxanthin can also improve the health and immunity of these aquatic animals, resulting in better growth and survival rates, and ultimately improving the overall quality of the aquatic products.
Related literature
- Title: Advances in Astaxanthin Production and Its Applications"
- Title: "The Role of Astaxanthin in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation"
- Title: "Astaxanthin in Cosmetics: A Review of its Efficacy and Safety"
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ citrus bioflavonoids
- ▶ plant extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Beetroot powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Reishi mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin Extract
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Problems
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol Extract
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ blog3
- ▶ blog4
-
Nature's best vitamin D3.
2024-11-27
-
The best velvet antlers in 2024.
2024-11-27
-
Lycopene
2024-11-27
-
Purple Sweet Potato Extract
2024-11-27
-
Lemon Extract
2024-11-27
-
Ginger Extract
2024-11-27
-
Centella Asiatica Extract
2024-11-27
-
Lemon Juice Powder
2024-11-27
-
Sugarcane Extract
2024-11-27
-
White Peony Extract
2024-11-27
-
Maitake Mushroom Extract
2024-11-27
-
Sophora Japonica Flower Extract
2024-11-27





















